【Pytorch学习笔记】2.Pytoch基础
文章目录
- 4.基本数据类型
- 4.1 All is about Tensor
- 4.2 How to denote string
- 4.3 Data type
- 4.4 Type check
- 4.5 Dimension / rank
- 4.6 Mixed
- 5.创建Tensor
- 5.1 Import from numpy
- 5.2 Import from List
- 5.3 uninitialized
- 5.4 set default type
- 5.5 rand / rand_like, randint, randn
- 5.6 full
- 5.7 arrange / range
- 5.8 linspace / logspace
- 5.9 Ones / zeros / eye
- 5.10 randperm
- 6.索引与切片
- 6.1 …
- 6.2 select by mask
- 6.3 select by flatten index
- 7.维度变换
- 7.1 View / reshape
- 7.2 Sequeeze / unsqueeze
- 7.3 Expand / repeat
- 7.4 Transpose / t / permute
- Broadcasting
- 9.拼接与拆分
- 9.1 Cat
- 9.2 Stack
- 9.3 split: by len
- 9.4 Chunk: by num
- 10.基本运算
- 11.数据统计
- 12.高级OP
- 12.1 Where
- 12.2 Gather
根据龙良曲Pytorch学习视频整理,视频链接:
【计算机-AI】PyTorch学这个就够了!
(好课推荐)深度学习与PyTorch入门实战——主讲人龙良曲
4.基本数据类型
4.1 All is about Tensor
| python | PyTorch |
|---|---|
| Int | IntTensor of size() |
| float | FloatTensor of size() |
| Int array | IntTensor of size[d1,d2,…] |
| Float array | FloatTensor of size[d1,d2…] |
| string | – |
4.2 How to denote string
- One-hot:[0, 1, 0, 0,…]
- Embedding:Word2vec,glove
4.3 Data type
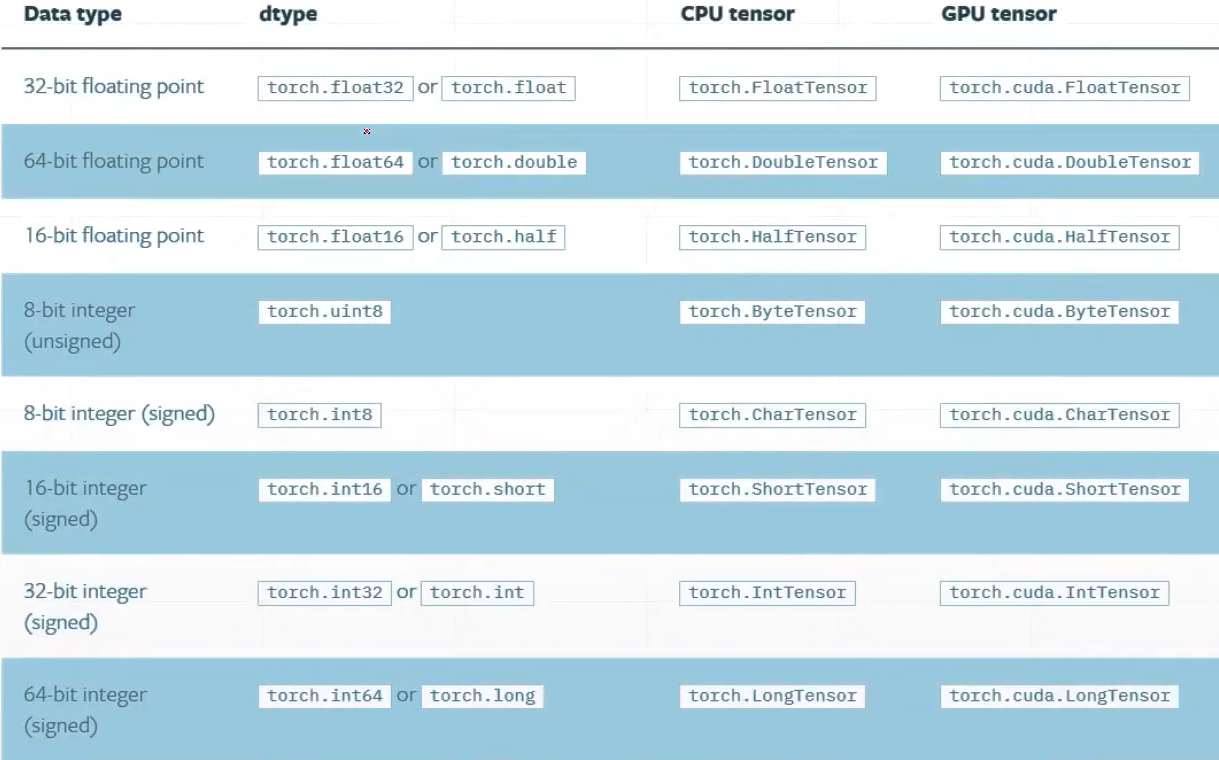
4.4 Type check
a = torch.randn(2, 3)print(a) # tensor([[ 0.3765, 0.6532, -0.8246],# [ 1.3567, -0.3963, 0.1719]])print(a.type()) # torch.FloatTensorprint(type(a)) # <class 'torch.Tensor'>print(isinstance(a, torch.FloatTensor)) # True# 数据位置对数据类型的影响print(isinstance(a, torch.cuda.FloatTensor)) # Falsea = a.cuda()print(isinstance(a, torch.cuda.FloatTensor)) # True
4.5 Dimension / rank
- Dimension 0 :Loss
- Dimension 1 :Bias和Linear Input
- Dimension 2 :Linear Input batch
- Dimension 3 :RNN Input Batch
- Dimension 4 :CNN[b, c, h, w]
4.6 Mixed
a = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5)print(a.size()) # torch.Size([2, 3, 4, 5])print(a.shape) # torch.Size([2, 3, 4, 5])print(len(a.shape)) # 4print(a.dim()) # 维度:4print(a.numel()) # 具体的数据大小:120
5.创建Tensor
5.1 Import from numpy
a = np.ones(2)print(a) # [1. 1.]print(torch.from_numpy(a)) # tensor([1., 1.], dtype=torch.float64)
5.2 Import from List
a = torch.tensor([2, 3.2])print(a) # tensor([2.0000, 3.2000])
torch.Tensor()接受数据的类型torch.tensor()接收现成的数据
5.3 uninitialized
初始化的数据可能会非常大或者非常小,不建议使用
- torch.empty()
- torch.FloatTensor(d1, d2, d3)
- torch.IntTensor(d1, d2, d3)
5.4 set default type
print(torch.tensor([1.2, 3]).type()) # torch.FloatTensortorch.set_default_tensor_type(torch.DoubleTensor)print(torch.tensor([1.2, 3]).type()) # torch.DoubleTensor
5.5 rand / rand_like, randint, randn
推荐使用这个随机初始化
a = torch.rand(2, 1)print(a) # tensor([[0.1746],# [0.6831]])print(torch.rand_like(a)) # tensor([[0.5452],# [0.4782]])print(torch.randint(1, 5, [2, 1])) # tensor([[3],# 限定了最小值和最大值,左闭右开 # [4]])
torch.randn() 输出随机数服从正态分布(0, 1)torch.normal(mean=torch.full([10], 0), std=torch.arrange(1, 0, -0.1)) 自定义正态分布均值和标准差
5.6 full
print(torch.full([], 7)) # 标量:tensor(7)print(torch.full([1], 7)) # 张量:tensor([7])
5.7 arrange / range
print(torch.arange(0, 10, 2)) # tensor([0, 2, 4, 6, 8])print(torch.range(0, 10, 2)) # 不建议使用,tensor([ 0., 2., 4., 6., 8., 10.])
5.8 linspace / logspace
print(torch.linspace(0, 10, steps=3)) # 等差均分为steps份:tensor([ 0., 5., 10.])print(torch.logspace(0, -1, steps=5)) # 对数均分为steps份:tensor([1.0000, 0.5623, 0.3162, 0.1778, 0.1000])
5.9 Ones / zeros / eye
print(torch.ones(1, 2)) # 全1矩阵:tensor([[1., 1.]])print(torch.zeros(1, 2)) # 全0矩阵:tensor([[0., 0.]])print(torch.eye(2)) # 单位矩阵:tensor([[1., 0.],# [0., 1.]])
5.10 randperm
a = torch.rand(4, 3)print(a)idx = torch.randperm(3) # 随机生成索引print(idx)print(a[[1, 0, 2]])""" tensor([[0.1708, 0.2821, 0.8163], [0.8898, 0.6628, 0.2350], [0.3743, 0.4281, 0.5309], [0.4996, 0.7259, 0.5485]]) tensor([1, 0, 2]) tensor([[0.8898, 0.6628, 0.2350], [0.1708, 0.2821, 0.8163], [0.3743, 0.4281, 0.5309]]) """
6.索引与切片
索引和切片的方式同python list[start steps]
steps]
- Indexing
- select first / last N
- select by steps
- select by specific index
6.1 …
连续全部取值
a = torch.rand(4, 3, 28, 28)print(a[0, 1].shape) # torch.Size([28, 28])print(a[0, 0, 2, 4]) # tensor(0.9485)print(a.index_select(2, torch.arange(8)).shape) # torch.Size([4, 3, 8, 28])print(a[:,:1,...].shape) #torch.Size([4, 1, 28, 28])
6.2 select by mask
x = torch.randn(3, 4)print(x)mask = x.ge(0.5) # 元素大于0.5的print(mask)print(torch.masked_select(x, mask))""" tensor([[-1.8692, 0.9687, -0.4978, 0.7836], [-2.5662, 0.0487, 0.3978, -0.3676], [-1.5896, -0.1129, -1.9687, 0.5585]]) tensor([[False, True, False, True], [False, False, False, False], [False, False, False, True]]) tensor([0.9687, 0.7836, 0.5585]) """
6.3 select by flatten index
reshape为一维后取索引
src = torch.tensor([[4, 3, 5],[6, 7, 8]])print(torch.take(src, torch.tensor([0, 2, 5]))) # tensor([4, 5, 8])
7.维度变换
7.1 View / reshape
view的size前后必须一致,view的size要有实际意义,避免产生数据污染
a = torch.rand(4, 1, 28, 28)print(a.view(4, 28*28).shape) # torch.Size([4, 784])print(a.unsqueeze(4).shape) # torch.Size([4, 1, 28, 28, 1])
7.2 Sequeeze / unsqueeze
unsqueeze插入一个维度,不会改变数据本身
squeeze若给定的挤压维度为1则被挤压掉,若不为1则保持原来数据维度不变
b = torch.tensor([1, 2])print(b.unsqueeze(-1)) # tensor([[1],# [2]])print(b.unsqueeze(0)) # tensor([[1, 2]])c = torch.rand(1, 31, 1, 1)print(c.shape) # torch.Size([1, 31, 1, 1])print(c.squeeze().shape) # torch.Size([31])print(c.squeeze(0).shape) # torch.Size([31, 1, 1])print(c.squeeze(1).shape) # torch.Size([1, 31, 1, 1])
7.3 Expand / repeat
- Expand(broadcasting)
repeat(memory copied)
a = torch.rand(1,32,1,1)
print(a.shape) # torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 1])
print(a.expand(4,32,14,14).shape) # torch.Size([4, 32, 14, 14])
print(a.repeat(4,32,1,1).shape) # torch.Size([4, 1024, 1, 1])
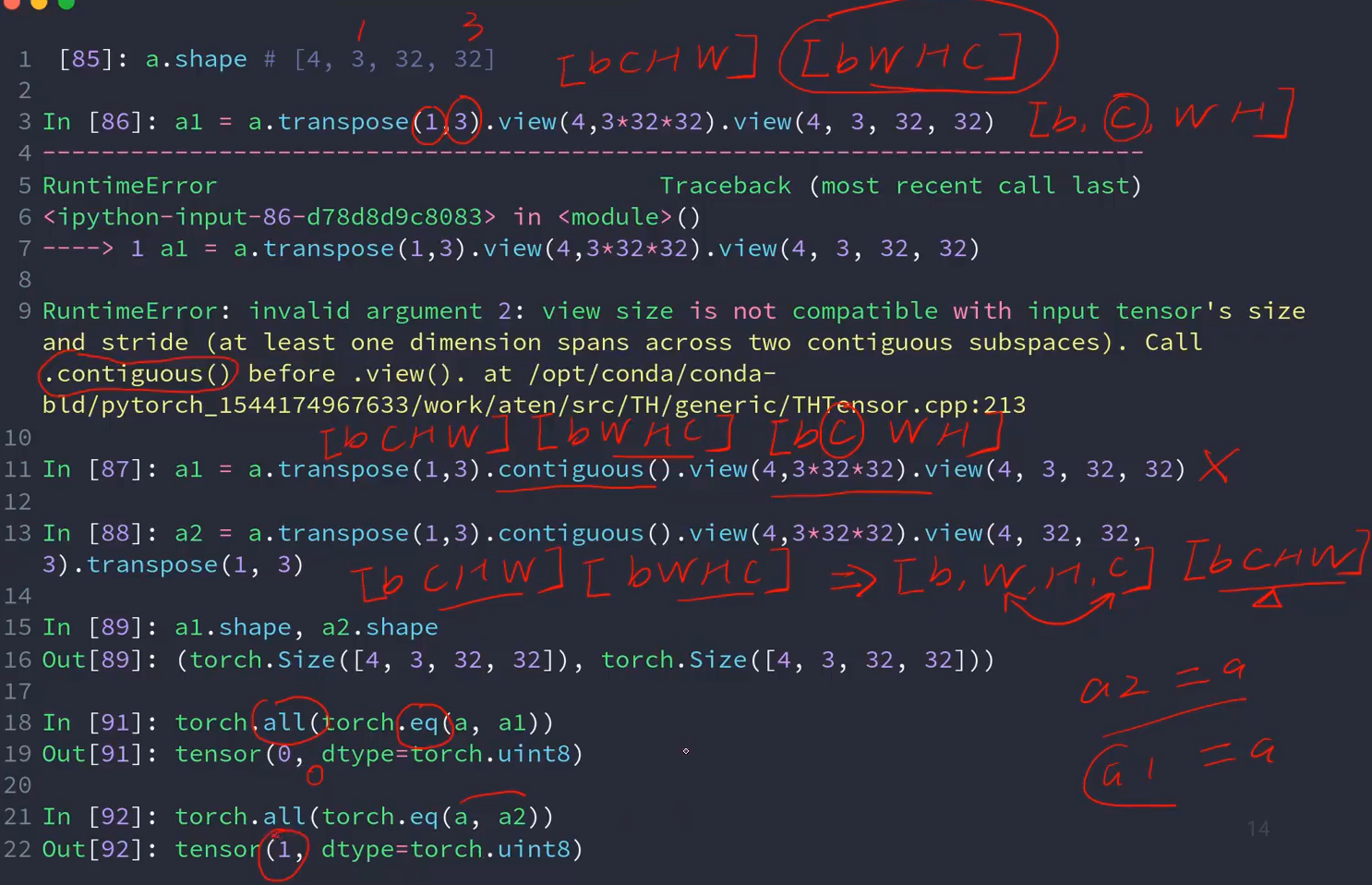
7.4 Transpose / t / permute
t()只能转置二维矩阵,否则报错
a = torch.rand(2,3)print(a.t().shape) # torch.Size([3, 2])b = torch.rand(4,3,28,28)print(b.transpose(1,3).transpose(1,2).shape) # torch.Size([4, 28, 28, 3])print(b.permute(0,2,3,1).shape) # torch.Size([4, 28, 28, 3])
8. Broadcasting
- Expand
- without copying data
key idea
- insert 1 dim ahead
- Expand dims with size 1 to same size
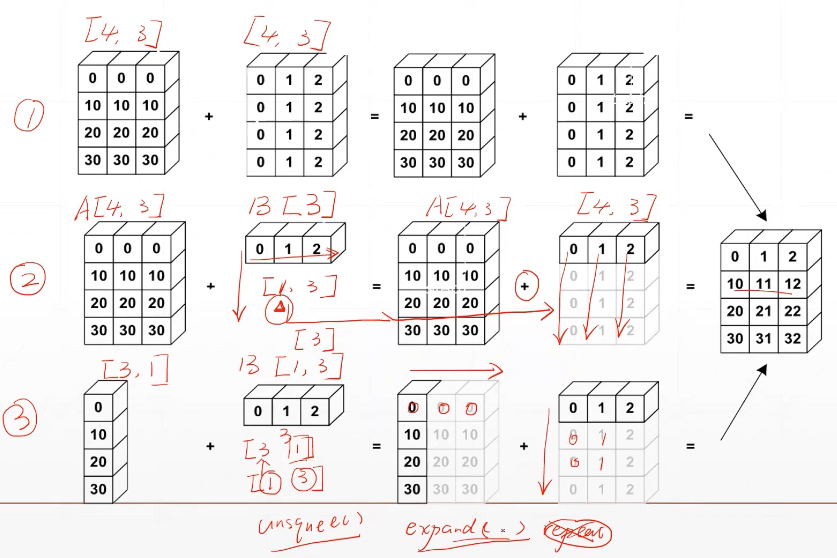
Why broadcasting - for actual demanding
- memory consumption
Is it broadcating-able?
- Match from Last dim
if current dim=1, expand to same
if either has no dim, insert one dim and expand to same
otherwise, NOT broadcasting-able
9.拼接与拆分
9.1 Cat
只能在维度不同的dim上进行cat
a = torch.rand(4, 32, 8)b = torch.rand(5, 32, 8)print(torch.cat([a, b], dim=0).shape) # torch.Size([9, 32, 8])
9.2 Stack
会创建新的维度,两个维度必须一致
a = torch.rand(32, 8)b = torch.rand(32, 8)print(torch.stack([a, b], dim=0).shape) # torch.Size([2, 32, 8])
9.3 split: by len
a = torch.rand(4, 32, 8)aa, bb = a.split(2, dim=0)print(aa.shape, bb.shape) # torch.Size([2, 32, 8]) torch.Size([2, 32, 8])cc, dd = a.split([3, 1], dim=0)print(cc.shape, dd.shape) # torch.Size([3, 32, 8]) torch.Size([1, 32, 8])
9.4 Chunk: by num
a = torch.rand(4, 32, 8)aa, bb = a.chunk(2, dim=0)print(aa.shape, bb.shape) #torch.Size([2, 32, 8]) torch.Size([2, 32, 8])
10.基本运算
- Add / minus / multiply / divide
torch.add()torch.sub()torch.mul()torch.div() - Matmul矩阵乘法
torh.mm()only for 2dtorch.matmul()@ - Pow
tensor.pow(n)=tensor**(n) - Sqrt / rsqrt
sqrt()开平方rsqrt()开平方的倒数 - Exp log
torch.exp()torch.log() - Approximation
tensor.floor()tensor.ceil()tensor.round()tensor.trunc()整数部分tensor.frac()小数部分 clamp
gradient clippingimport torch
import numpy as npgrad = torch.rand(2, 3) * 15
print(grad)
print(grad.min())
print(grad.median())
print(grad.max())
print(grad.clamp(10))
print(grad.clamp(0, 10))
“”” tensor([[11.9217, 3.4733, 1.3133], [ 7.1854, 13.8410, 13.8098]]) tensor(1.3133) tensor(7.1854) tensor(13.8410) tensor([[11.9217, 10.0000, 10.0000], [10.0000, 13.8410, 13.8098]]) tensor([[10.0000, 3.4733, 1.3133], [ 7.1854, 10.0000, 10.0000]]) “””
11.数据统计
norm-p 范数(简单的理解)、范数的用途、什么是范数1
import torch
import numpy as npa = torch.full([8], 1.0)
print(a)
b = a.view(2, 4)
print(b)
c = a.view(2, 2, 2)
print(c)print(a.norm(1), b.norm(1), c.norm(1))
print(a.norm(2), b.norm(2), c.norm(2))print(b.norm(1, dim=1))
print(b.norm(2, dim=1))print(c.norm(1, dim=0))
print(c.norm(2, dim=0))
“”” tensor([1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]) tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.]]) tensor([[[1., 1.], [1., 1.]], [[1., 1.], [1., 1.]]]) tensor(8.) tensor(8.) tensor(8.) tensor(2.8284) tensor(2.8284) tensor(2.8284) tensor([4., 4.]) tensor([2., 2.]) tensor([[2., 2.], [2., 2.]]) tensor([[1.4142, 1.4142], [1.4142, 1.4142]]) “””tensor.mean()均值tensor.prod()累乘tensor.sum()累加tensor.argmin(),tensor.argmax()最大、小值索引dim=n, keepdim=True设置维度,保持维度不变- kthvalue, topk
tensor.topk(n, dim=, largest=False)某一维度上最小的前n个tensor.kthvalue(n, dim=)某一维度上最小的第n个 compare
a = torch.rand(2, 3)
print(a)
print(torch.gt(a, 0.5)) # 大于0.5
print(torch.eq(a, a))
print(torch.equal(a, a))
“”” tensor([[0.5229, 0.7868, 0.0872], [0.3480, 0.4691, 0.2402]]) tensor([[ True, True, False], [False, False, False]]) tensor([[True, True, True], [True, True, True]]) True “””
12.高级OP
12.1 Where
torch.where(condition, x, y)
- Return a tensor of elements selected from either x or y, depending on condition.
- where相较于python的if else优点是可以部署在GPU上,实现高度并行
12.2 Gather
torch.gather(input, dim, index, out=None)
- Gathers values along an axis specified by dim.
retrieve global label
argmax(pred) to get relative labeling
On some condtion, our label is dinstinct from relative labelingimport torch
import numpy as npprob = torch.randn(4, 10)
idx = prob.topk(dim=1, k=3)
print(idx)
“”” torch.return_types.topk( values=tensor([[1.3319, 0.8338, 0.4407], [2.0854, 0.9303, 0.2608], [1.7225, 1.0136, 0.5523], [1.3715, 1.3115, 1.0049]]), indices=tensor([[2, 9, 3], [1, 3, 8], [3, 5, 0], [3, 7, 1]])) “””label = torch.arange(10) + 100
print(label)
“”” tensor([100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109]) “””print(torch.gather(label.expand(4, 10), dim=1, index=idx1.long()))
“”” tensor([[102, 109, 103], [101, 103, 108], [103, 105, 100], [103, 107, 101]]) “””






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...