重入锁、读写锁实现
前置知识AQS //blog.csdn.net/qq_37598011/article/details/88871352
//blog.csdn.net/qq_37598011/article/details/88871352
重入锁
实现重入
重进入是指任意线程在获取到锁之后能够再次获取该锁而不会被锁所阻塞,该特性需要解决以下两个问题。
- 线程再次获取锁:锁需要去识别获取锁的线程是否为当前占据锁的线程,如果是,则再次成功获取。
锁的最终释放:线程重复n次获取了锁,随后在第n次释放该锁后,其他线程能够获取到该锁。锁的最终释放要求锁对于获取进行计数自增,计数表示当前锁被重复获取的次数,而锁被释放时,计数自减,当计数等于0时表示锁已经成功释放。
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5179523762034025860L;/*** Performs {@link Lock#lock}. The main reason for subclassing* is to allow fast path for nonfair version.*/abstract void lock();/*** Performs non-fair tryLock. tryAcquire is implemented in* subclasses, but both need nonfair try for trylock method.*/final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();//获取当前线程int c = getState();if (c == 0) {//第一次获取锁if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true;}}else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {//判断是否是当前线程重入int nextc = c + acquires;if (nextc < 0) // overflowthrow new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");setState(nextc);return true;}return false;}protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {int c = getState() - releases;//计算同步状态if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();boolean free = false;if (c == 0) {//表示可以释放锁free = true;setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);//释放线程}setState(c);return free;}}
nonfairTryAcquire方法通过判断当前线程是否为获取锁的线程来决定操作是否成功,如果是获取锁的线程再次请求,则将同步状态进行增加并返回true,表示获取同步状态成功。
当释放锁的时候则会执行tryRelease方法,可以看到,如果这个锁被获取了n次,那么前n-1次它会返回false,当同步状态为0时会将这个锁释放,并将占有线程置为null,最后返回true,表示释放成功。
公平与非公平获取锁的区别
公平性与否是针对获取锁而言的,如果一个锁是公平的,那么锁的获取顺序就应该符合请求的绝对时间顺序,也就是FIFO。
/*** Sync object for fair locks*/static final class FairSync extends Sync {private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;final void lock() {acquire(1);}/*** Fair version of tryAcquire. Don't grant access unless* recursive call or no waiters or is first.*/protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();int c = getState();if (c == 0) {if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true;}}else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {int nextc = c + acquires;if (nextc < 0)throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");setState(nextc);return true;}return false;}}public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();//判断是否公平锁}public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {// The correctness of this depends on head being initialized// before tail and on head.next being accurate if the current// thread is first in queue.Node t = tail; // Read fields in reverse initialization orderNode h = head;Node s;return h != t &&((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());}**该方法与nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires)比较,唯一不同的位置为判断条件多了 hasQueuedPredecessors()方法,它会判断同步队列中当前节点是否有前驱节点,如果该方法返回true,则表示有线程比当前线程更早地请求获取锁,因此需要等待前驱线程获取并释放锁之后才能继续获取锁。**
测试:
import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.List;import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;import org.junit.Test;/** @author zzf* @date 2019年4月1日 上午10:30:02*/public class FairAndUnfairTest {private static Lock fairLock = new ReentrantLock2(true);private static Lock unfairLock = new ReentrantLock2(false);@Testpublic void fair() throws InterruptedException {testLock(fairLock);}@Testpublic void unfair() throws InterruptedException {testLock(unfairLock);}private void testLock(Lock lock) throws InterruptedException {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {Thread thread = new Thread(new Job(lock)){public String toString() {return getName();}};thread.setName("" + i);thread.start();}Thread.sleep(11000);}private static class Job extends Thread {private Lock lock;public Job(Lock lock) {this.lock = lock;}public void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {lock.lock();try {Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println("获取锁的当前线程[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "], 同步队列中的线程" + ((ReentrantLock2)lock).getQueuedThreads() + "");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.unlock();}}}}// 连续2次打印当前的Thread和等待队列中的Thread(略)private static class ReentrantLock2 extends ReentrantLock {public ReentrantLock2(boolean fair) {super(fair);}public Collection<Thread> getQueuedThreads() {List<Thread> arrayList = new ArrayList<Thread>(super.getQueuedThreads());Collections.reverse(arrayList);return arrayList;}}}
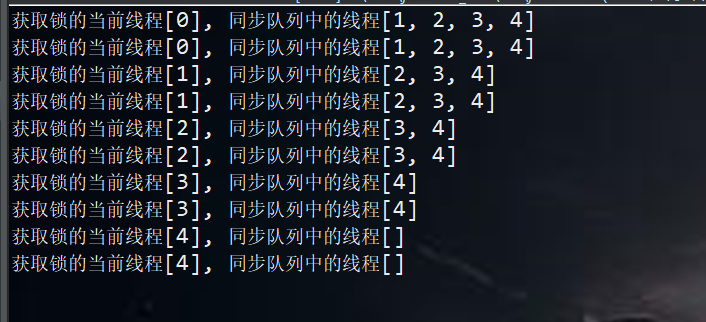
非公平:
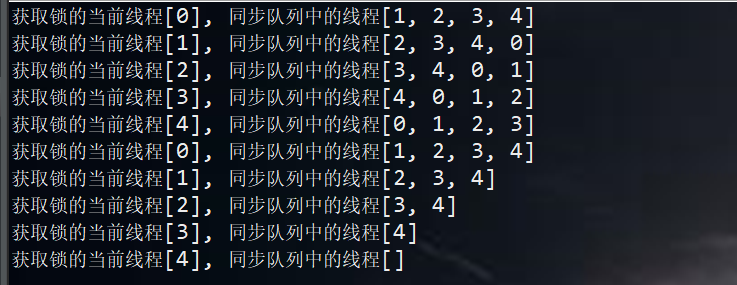
公平:
为什么说非公平比公平锁性能好,并且从上述输出中可以看的它会重复获取锁原因就在以下这块代码中:if (c == 0) {if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true;}}//公平锁if (c == 0) {if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true;}}//非公平锁
当一个线程请求锁时,只要获取了同步状态即成功获取锁。在这个前提下,刚释放锁的线程再次获取同步状态的几率会非常大,使得其他线程只能在同步队列中等待。而公平锁则会严格按照队列的顺序来获取锁。
总结:公平性锁保证了锁的获取按照FIFO原则,而代价是进行大量的线程切换。非公平性锁虽然可能造成线程“饥饿”,但极少的线程切换,保证了其更大的吞吐量。
读写锁
读写锁在同一时刻可以允许多个读线程访问,但是在写线程访问时,所有的读线程和其他写线程均被阻塞。读写锁维护了一对锁,一个读锁和一个写锁,通过分离读锁和写锁,使得并发性相比一般的排他锁有了很大提升。
读写状态的设计
读写锁同样依赖自定义同步器来实现同步功能,而读写状态就是其同步器的同步状态。 在ReentrantLock中同步状态表示锁被一个线程重复获取的次数,而读写锁的自定义同步器需要在同步状态(一个整型变量)上维护多个读线程和一个写线程的状态,使得该状态的设计成为读写锁实现的关键。
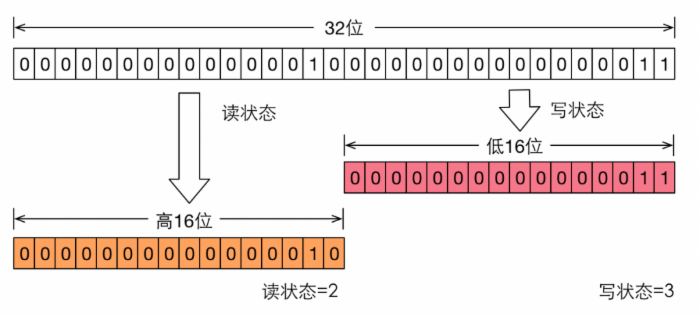
如果在一个整型变量上维护多种状态,就一定需要“按位切割使用”这个变量,读写锁将 变量切分成了两个部分,高16位表示读,低16位表示写。
前置知识,8421码了解下……
当前同步状态表示一个线程已经获取了写锁,且重进入了两次,同时也连续获取了两次读锁。**读写锁通过位运算来确定读写的状态。**假设当前同步状态值为S,写状态等于S&0x0000FFFF(将高16位全部抹去),读状态等于S>>>16(无符号补0右移16位)。当写状态增加1时,等于S+1,当读状态增加1时,等于S+(1<<16),也就是 S+0x00010000。**根据状态的划分能得出一个推论:S不等于0时,当写状态(S&0x0000FFFF)等于0时,则读 状态(S>>>16)大于0,即读锁已被获取。**
写锁的获取与释放
写锁是一个支持重进入的排它锁。如果当前线程已经获取了写锁,则增加写状态。如果当前线程在获取写锁时,读锁已经被获取(读状态不为0)或者该线程不是已经获取写锁的线程, 则当前线程进入等待状态。
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {Thread current = Thread.currentThread();int c = getState();int w = exclusiveCount(c);//计算写锁数if (c != 0) {// w==0表示写锁为0这意味有读锁,或者该线程不是已经获取了写锁的线程if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread())return false;if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT)throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");// Reentrant acquiresetState(c + acquires);return true;}if (writerShouldBlock() ||!compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires))return false;setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true;}static int exclusiveCount(int c) { return c & EXCLUSIVE_MASK; }protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {if (!isHeldExclusively())throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();int nextc = getState() - releases;boolean free = exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0;//判断是否释放完毕写锁if (free)setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);setState(nextc);return free;}
该方法除了重入条件(当前线程为获取了写锁的线程)之外,增加了一个读锁是否存在的判断。如果存在读锁,则写锁不能被获取,原因在于:读写锁要确保写锁的操作对读锁可见,如果允许读锁在已被获取的情况下对写锁的获取,那么正在运行的其他读线程就无法感知到当前写线程的操作。因此,只有等待其他读线程都释放了读锁,写锁才能被当前线程获取,而写锁一旦被获取,则其他读写线程的后续访问均被阻塞。
写锁的释放与ReentrantLock的释放过程基本类似,每次释放均减少写状态,当写状态为0时表示写锁已被释放,从而等待的读写线程能够继续访问读写锁,同时前次写线程的修改对后续读写线程可见。
读锁的获取与释放
读锁是一个支持重进入的共享锁,它能够被多个线程同时获取,在没有其他写线程访问 (或者写状态为0)时,读锁总会被成功地获取,而所做的也只是(线程安全的)增加读状态。如果当前线程已经获取了读锁,则增加读状态。如果当前线程在获取读锁时,写锁已被其他线程获取,则进入等待状态。
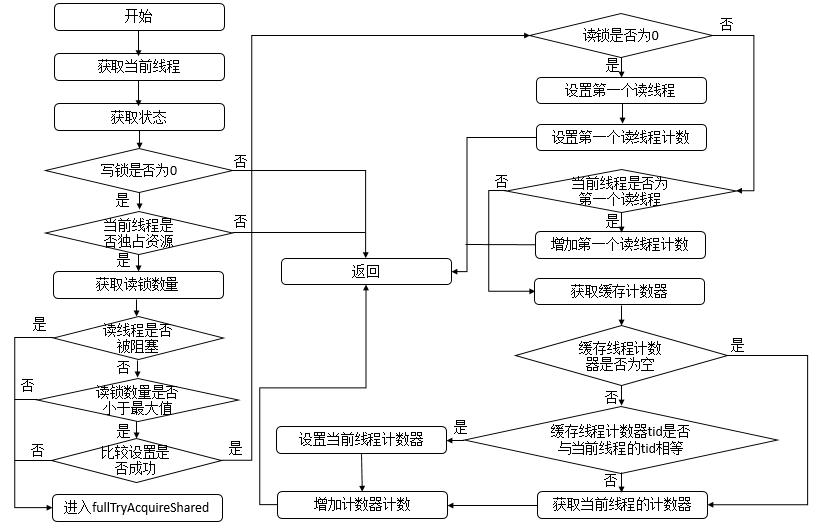
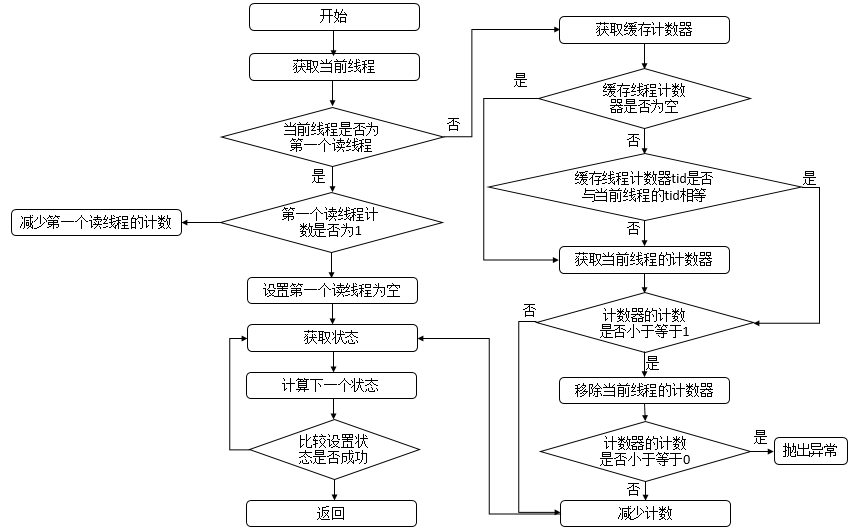
protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {Thread current = Thread.currentThread();int c = getState();//如果写锁线程数 != 0 ,且独占锁不是当前线程则返回失败if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)return -1;//获取读锁数量int r = sharedCount(c);//先判断读线程是否应该被阻塞,并且小于最大值,并且比较设值成功if (!readerShouldBlock() &&r < MAX_COUNT &&compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {if (r == 0) {//第一次firstReader = current;//设置第一个读线程firstReaderHoldCount = 1;//线程占用资源数为1} else if (firstReader == current) {//当前线程重入firstReaderHoldCount++;//线程占用资源数自增} else {//读锁不为0并且不是当前线程HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;//获取计数器//计数器为空或者tid不是当前运行的线程idif (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))//获取当前线程对应的计数器cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();else if (rh.count == 0)//计数为0readHolds.set(rh);//加入到readHolds中rh.count++;//计数加一}return 1;}return fullTryAcquireShared(current);}//readerShouldBlock最后会调用这个方法final boolean apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive() {Node h, s;return (h = head) != null &&(s = h.next) != null &&!s.isShared() &&s.thread != null;}static int sharedCount(int c) { return c >>> SHARED_SHIFT; }**首先判断写锁是否为0并且判断当前线程是否占有独占锁,如果都不符合则直接返回。否则判断读线程是否需要被阻塞并且读锁数量是否小于最大值并且compareAndSetState设值成功,若当前没有读锁,则设置第一个读线程firstReader和firstReaderHoldCount=1,若当前线程线程为第一个读线程,则firstReaderHoldCount+1。否则设置当前线程对应的HoldCounter对象的值。**
如果当前只有一个线程的话它会直接往firstReaderHoldCount这个成员变量里存重入数,当有第二个线程的时候,就要动用ThreadLocal变量readHolds了,每个线程拥有自己的副本,用来保存自己的重入数。
final int fullTryAcquireShared(Thread current) {HoldCounter rh = null;for (;;) { // 自旋int c = getState();if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0) { // 写线程数量不为0if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current) // 不为当前线程return -1;} else if (readerShouldBlock()) { // 写线程数量为0并且读线程被阻塞// Make sure we're not acquiring read lock reentrantlyif (firstReader == current) { // 当前线程为第一个读线程// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;} else { // 当前线程不为第一个读线程if (rh == null) { // 计数器不为空rh = cachedHoldCounter;// 计数器为空或者计数器的tid不为当前正在运行的线程的tidif (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current)) {rh = readHolds.get();if (rh.count == 0)readHolds.remove();}}if (rh.count == 0)return -1;}}if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT) // 读锁数量为最大值,抛出异常throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) { // 比较并且设置成功if (sharedCount(c) == 0) { // 读线程数量为0// 设置第一个读线程firstReader = current;firstReaderHoldCount = 1;} else if (firstReader == current) {firstReaderHoldCount++;} else {if (rh == null)rh = cachedHoldCounter;if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))rh = readHolds.get();else if (rh.count == 0)readHolds.set(rh);rh.count++;cachedHoldCounter = rh; // cache for release}return 1;}}}
在tryAcquireShared函数中,如果下列三个条件不满足(读线程是否应该被阻塞、小于最大值、比较设置成功)则会进入fullTryAcquireShared函数中,它用来保证相关操作可以成功。其逻辑与tryAcquireShared逻辑类似。
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int unused) {Thread current = Thread.currentThread();if (firstReader == current) { // 当前线程为第一个读线程// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;if (firstReaderHoldCount == 1) // 读线程占用的资源数为1firstReader = null; //清理线程else // 占用资源-1firstReaderHoldCount--;} else { // 当前线程不是第一个读线程// 获取缓存的计数器HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current)) // 计数器为空或者计数器的tid不为当前正在运行的线程的tid// 获取当前线程对应的计数器rh = readHolds.get();// 获取计数int count = rh.count;if (count <= 1) { // 计数小于等于1// 移除readHolds.remove();if (count <= 0) // 计数小于等于0,抛出异常throw unmatchedUnlockException();}// 减少计数--rh.count;}for (;;) { // 自旋// 获取状态int c = getState();//计算新的状态int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT;if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc)) // 比较并进行设置// Releasing the read lock has no effect on readers,// but it may allow waiting writers to proceed if// both read and write locks are now free.return nextc == 0;}}**首先判断当前线程是否为第一个读线程firstReader,如果是则判断第一个读线程占有的资源数firstReaderHoldCount是否为1,如果是则设置第一个读线程firstReader设置为空,否则,将第一个读线程占有的资源数firstReaderHoldCount减1。如果当前线程不是第一个读线程,那么首先会获取缓存计数器,若计数器为空或者tid不等于当前线程的tid值,则获取当前线程的计数器,如果计数器的计数count小于等于1,则移除当前线程对应的计数器,如果计数器的计数count小于等于0,则抛出异常,之后再减少计数。最后进入自旋,通过这个自旋可以确保成功设置状态state,并返回是否已全部退出读锁。**
锁降级
锁降级指的是写锁降级成为读锁。锁降级是指把持住(当前拥有的)写锁,再获取到读锁,随后释放(先前拥有的)写锁的过程。 RentrantReadWriteLock不支持锁升级(把持读锁、获取写锁,最后释放读锁的过程)。目的也是保证数据可见性,如果读锁已被多个线程获取,其中任意线程成功获取了写锁并更新了数据,则其更新对其他获取到读锁的线程是不可见的。
参考《Java并发编程的艺术》
推荐博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxi/p/9140541.html
CSDN连接:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_37598011/11068576



































还没有评论,来说两句吧...