java 中的LongAdder
问题
(1)java8中为什么要新增LongAdder?
(2)LongAdder的实现方式?
(3)LongAdder与AtomicLong的对比?
简介
LongAdder是java8中新增的原子类,在多线程环境中,它比AtomicLong性能要高出不少,特别是写多的场景。
原理
LongAdder的原理是,在最初无竞争时,只更新base的值,当有多线程竞争时通过分段的思想,让不同的线程更新不同的段,最后把这些段相加就得到了完整的LongAdder存储的值。
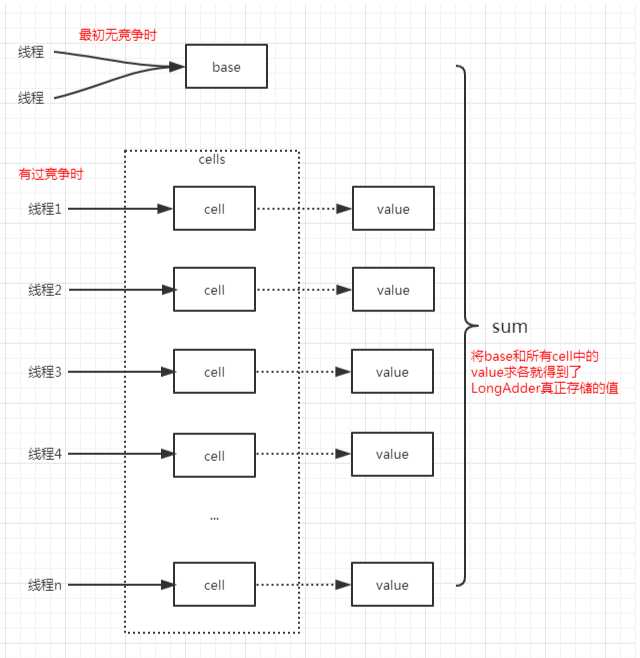
源码分析
LongAdder继承自Striped64抽象类,Striped64中定义了Cell内部类和各重要属性。
主要内部类
// Striped64中的内部类,使用@sun.misc.Contended注解,说明里面的值消除伪共享@sun.misc.Contended static final class Cell {// 存储元素的值,使用volatile修饰保证可见性volatile long value;Cell(long x) { value = x; }// CAS更新value的值final boolean cas(long cmp, long val) {return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapLong(this, valueOffset, cmp, val);}// Unsafe实例private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;// value字段的偏移量private static final long valueOffset;static {try {UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();Class<?> ak = Cell.class;valueOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(ak.getDeclaredField("value"));} catch (Exception e) {throw new Error(e);}}}
Cell类使用@sun.misc.Contended注解,说明是要避免伪共享的。
使用Unsafe的CAS更新value的值,其中value的值使用volatile修饰,保证可见性。
主要属性
// 这三个属性都在Striped64中// cells数组,存储各个段的值transient volatile Cell[] cells;// 最初无竞争时使用的,也算一个特殊的段transient volatile long base;// 标记当前是否有线程在创建或扩容cells,或者在创建Cell// 通过CAS更新该值,相当于是一个锁transient volatile int cellsBusy;
LongAdder VS AtomicLong 性能对比
public class LongAdderVSAtomicLongTest {public static void main(String[] args){testAtomicLongVSLongAdder(1, 10000000);testAtomicLongVSLongAdder(10, 10000000);testAtomicLongVSLongAdder(20, 10000000);testAtomicLongVSLongAdder(40, 10000000);testAtomicLongVSLongAdder(80, 10000000);}static void testAtomicLongVSLongAdder(final int threadCount, final int times){try {System.out.println("threadCount:" + threadCount + ", times:" + times);long start = System.currentTimeMillis();testLongAdder(threadCount, times);System.out.println("LongAdder elapse:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");long start2 = System.currentTimeMillis();testAtomicLong(threadCount, times);System.out.println("AtomicLong elapse:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start2) + "ms");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}static void testAtomicLong(final int threadCount, final int times) throws InterruptedException {AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong();List<Thread> list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i=0;i<threadCount;i++){list.add(new Thread(() -> {for (int j = 0; j<times; j++){atomicLong.incrementAndGet();}}));}for (Thread thread : list){thread.start();}for (Thread thread : list){thread.join();}}static void testLongAdder(final int threadCount, final int times) throws InterruptedException {LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();List<Thread> list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i=0;i<threadCount;i++){list.add(new Thread(() -> {for (int j = 0; j<times; j++){longAdder.add(1);}}));}for (Thread thread : list){thread.start();}for (Thread thread : list){thread.join();}}}
可以看到当只有一个线程的时候,AtomicLong反而性能更高,随着线程越来越多,AtomicLong的性能急剧下降,而LongAdder的性能影响很小。
总结
(1)LongAdder通过base和cells数组来存储值;
(2)不同的线程会hash到不同的cell上去更新,减少了竞争;
(3)LongAdder的性能非常高,最终会达到一种无竞争的状态;
































还没有评论,来说两句吧...