ES查询的实时性问题详解
前言
我们都知道ES是一款近实时的搜索引擎产品。那么为什么是近实时而不是实时呢?为什么新添加的数据开始查询不到,后来又可以检索到?有哪些办法能够提高ES的实时性呢?
今天让我们一起来探究ES查询的实时性问题。
一、实战演示
1、新建索引
在settings中通过refresh_interval参数指定索引每60s刷新一次。
PUT my-index-000001{"mappings": {"properties": {"city": {"type": "keyword"}}},"settings": { "refresh_interval": "60s"}}
2、添加数据
PUT my-index-000001/_doc/1{"city": "北京"}PUT my-index-000001/_doc/2{"city": "天津"}PUT my-index-000001/_doc/3{"city": "武汉"}POST my-index-000001/_doc/4?refresh=true{ "city": "成都" }
3、GET API
通过索引id查询记录
GET my-index-000001/_doc/1
执行结果:
{"_index" : "my-index-000001","_type" : "_doc","_id" : "1","_version" : 1,"_seq_no" : 0,"_primary_term" : 1,"found" : true,"_source" : {"city" : "北京"}}
说明
新增的数据立刻被检索到,说明GET API是实时的。
GET API主要包含以下请求:
GET <index>/_doc/<_id>HEAD <index>/_doc/<_id>GET <index>/_source/<_id>HEAD <index>/_source/<_id>
默认情况下,Get API 是实时的,不受索引刷新率的影响(当数据对搜索可见时)。 如果请求存储的字段(请参阅 stored_fields 参数)并且文档已更新但尚未刷新,则 get API 将必须解析和分析源以提取存储的字段。 为了禁用实时 GET,可以将 realtime 参数设置为 false。
GET my-index-000001/_doc/1?realtime=false
4、query查询
GET my-index-000001/_search{"query": {"bool": {"filter": [{ "term": {"city": "北京"}}]}}}## 新增数据并刷新POST my-index-000001/_doc/4?refresh=true{ "city": "成都" }GET my-index-000001/_search{"query": {"bool": {"filter": [{ "term": {"city": "成都"}}]}}}
执行结果:
在新增北京记录操作的60s内执行查询操作,没有查询到新增的记录,因为还没有执行refresh动作。
而新增成都记录时,由于添加了refresh=true参数,会在执行添加操作后立刻执行refresh动作,所以可以根据条件即时查询到成都的记录。
二、ES写入过程分析
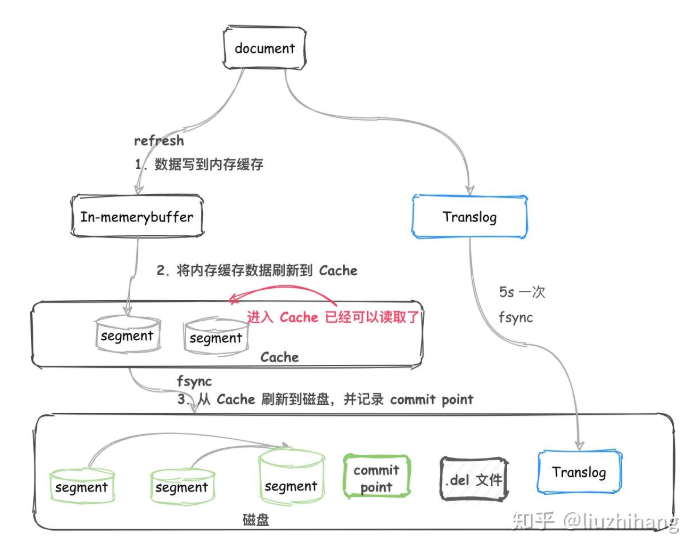
ES写入过程说明:
- 不断将 Document 写入到 In-memory buffer (内存缓冲区)。
- 当满足一定条件后内存缓冲区中的 Documents刷新到 高速缓存(cache)。
- 生成新的 segment ,这个 segment 还在 cache 中。 (在cache中生成的segment就可以被检索到了)
- 这时候还没有 commit,但是已经可以被读取了。
- translog 事务日志主要用来失败恢复,防止服务器宕机出现内存中没有刷写到磁盘的数据丢失。
数据从 buffer 到 cache 的过程是定期每秒刷新一次。所以新写入的 Document 最慢 1 秒就可以在 cache 中被搜索到。
而 Document 从 buffer 到 cache 的过程叫做 refresh ,默认是 1 秒刷新一次。这也就是为什么说 Elasticsearch 是准实时的。
Elasticsearch通过引入translog,多副本,以及定期执行flush,merge等操作保证了数据可靠性和较高的存储性能。
document同时写入In-memory buffer (内存缓冲区)和translog的过程类似mysql中的double write,主要目的也是失败恢复,防止数据丢失。translog是顺序追加写入。
使文档立即可见:
PUT /test/_doc/1?refresh{ "test": "test"}// 或者PUT /test/_doc/2?refresh=true{ "test": "test"}
三、Get API的实时性
简单来说,就是通过get请求直接根据id获取索引记录,是实时操作。
#默认情况下,get API是实时的GET my-index-000001/_doc/0#通过realtime=false设置请求为非实时GET my-index-000001/_doc/0?realtime=false
(注: 如果是realtime=true, 则先从translog中读取source, 没有读取到才从索引中读取)
四、java API中实时性
在ES 的java API中,如何控制数据写入操作后,即时刷新,使得新增的数据立即可见呢?
答案是通过刷新策略WriteRequest.RefreshPolicy。
下面的代码演示,采用highLevelClient.bulk实现批量插入数据中,通过bulkRequest.setRefreshPolicy指定刷新策略为即使刷新。
public boolean bulk(String indice, List<String> jsonStrList) {boolean result = true;try {BulkRequest bulkRequest = new BulkRequest();//设置刷新策略bulkRequest.setRefreshPolicy(WriteRequest.RefreshPolicy.IMMEDIATE);for (String jsonStr : jsonStrList) {IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest(indice,"_doc");indexRequest.source(jsonStr, XContentType.JSON);bulkRequest.add(indexRequest);}BulkResponse bulkResponse = highLevelClient.bulk(bulkRequest);if (bulkResponse.hasFailures()) {result = false;}} catch (Exception e) {result = false;}return result;}
查看源码发现:
public static enum RefreshPolicy implements Writeable {NONE("false"),IMMEDIATE("true"),WAIT_UNTIL("wait_for");……}
可知有以下三种刷新策略:
RefreshPolicy#IMMEDIATE:
请求向ElasticSearch提交了数据,立即进行数据刷新,然后再结束请求。
优点:实时性高、操作延时短。
缺点:资源消耗高。RefreshPolicy#WAIT_UNTIL:
请求向ElasticSearch提交了数据,等待数据完成刷新,然后再结束请求。
优点:实时性高、操作延时长。
缺点:资源消耗低。RefreshPolicy#NONE:
默认策略。
请求向ElasticSearch提交了数据,不关系数据是否已经完成刷新,直接结束请求。
优点:操作延时短、资源消耗低。
缺点:实时性低。
总结
文本主要对ES数据写入后查询的实时性问题进行了分析。
1、通过分析ES的写入流程,说明了ES查询数据为什么会产生延迟,即为什么说ES是准实时的
2、说明了Get API默认是实时的原因,主要是Get API默认情况下优先读取的是translog中的数据。
3、可以通过设置refresh_interval参数,缩短索引refresh的间隔时间,增大实时性。
4、可以通过写入操作后添加refresh参数,让写入的数据被即时检索到。
5、介绍了ES java API中通过设置写入操作的刷新策略RefreshPolicy,改变写入数据的实时性。


































还没有评论,来说两句吧...