入门Spring Boot(一)
从今天起,我们使用SpringBoot进行Web开发。
前言:为什么要学习Spring Boot?
java一直被人诟病的一点就是臃肿、麻烦。当我们还在辛苦的搭建项目时,可能Python程序员已经把功能写好了,究其原因主要是两点:
- 复杂的配置 项目各种配置其实是开发时的损耗, 因为在思考 Spring 特性配置和解决业务问题之间需要进行思维切换,所以写配置挤占了写应用程序逻辑的时间。
- 混乱的依赖管理 项目的依赖管理也是件吃力不讨好的事情。决定项目里要用哪些库就已经够让人头痛的了,你还要知道这些库的哪个版本和其他库不会有冲突,这也是件棘手的问题。并且,依赖管理也是一种损耗,添加依赖不是写应用程序代码。一旦选错了依赖的版本,随之而来的不兼容问题毫无疑问会是生产力杀手。
而Spring Boot让这一切成为过去!
1、简介
Spring Boot 主要特征是:
- 创建独立的spring应用程序
- 直接内嵌tomcat、jetty和undertow(不需要打包成war包部署)
- 提供了固定化的“starter”配置,以简化构建配置
- 尽可能的自动配置spring和第三方库
- 提供产品级的功能,如:安全指标、运行状况监测和外部化配置等
- 绝对不会生成代码,并且不需要XML配置
使用SpringBoot;
1)、创建SpringBoot应用,选中我们需要的模块;
2)、SpringBoot已经默认将这些场景配置好了,只需要在配置文件中指定少量配置就可以运行起来
3)、自己编写业务代码;
自动配置原理?
这个场景SpringBoot帮我们配置了什么?能不能修改?能修改哪些配置?能不能扩展?xxx
xxxxAutoConfiguration:帮我们给容器中自动配置组件;
xxxxProperties:配置类来封装配置文件的内容;
2、SpringBoot对静态资源的映射规则;
默认的静态资源路径为:
- classpath:/META-INF/resources/
- classpath:/resources/
- classpath:/static/
- classpath:/public/
只要静态资源放在这些目录中任何一个,SpringMVC都会帮我们处理
3、模板引擎
JSP、Velocity、Freemarker、Thymeleaf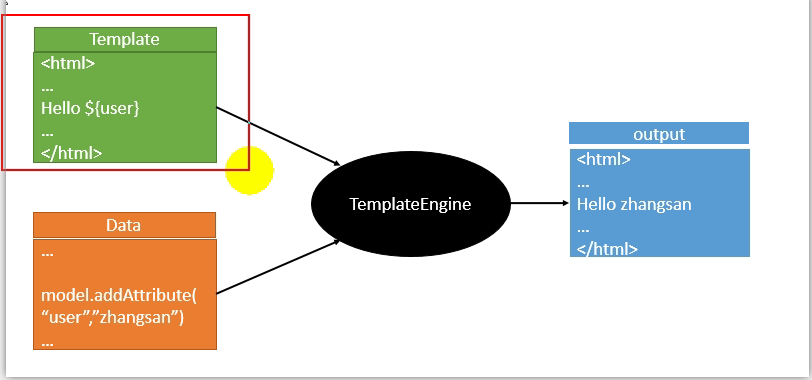
模板引擎的作用就是,我们写一个页面模板,比如有些值是动态的,我们组装一些数据,把这些数据找到,然后把模板和数据交给模板引擎,模板引擎根据数据帮我们把表达式解析,填充到指定的位置,然后把数据写成我们想要的内容展示出来,不管是jsp,还是freemarker,都是这个思想,只不过不同的模板引擎语法不一样。
SpringBoot推荐的Thymeleaf;
语法更简单,功能更强大;
简单说, Thymeleaf 是一个跟 Velocity、FreeMarker 类似的模板引擎,它可以完全替代 JSP相较于其他的模板引擎,它有如下四个极吸引人的特点:
- 动静结合:Thymeleaf 在有网络和无网络的环境下皆可运行,即它可以让美工在浏览器查看页面的静态效果,也可以让程序员在服务器查看带数据的动态页面效果。这是由于它支持
html 原型,然后在 html 标签里增加额外的属性来达到模板+数据的展示方式。浏览器解释 html 时会忽略未定义的标签属性,所以thymeleaf 的模板可以静态地运行;当有数据返回到页面时,Thymeleaf 标签会动态地替换掉静态内容,使页面动态显示。- 开箱即用:它提供标准和spring标准两种方言,可以直接套用模板实现JSTL、 OGNL表达式效果,避免每天套模板、改jstl、改标签的困扰。同时开发人员也可以扩展和创建自定义的方言。
- 多方言支持:Thymeleaf 提供spring标准方言和一个与 SpringMVC 完美集成的可选模块,可以快速的实现表单绑定、属性编辑器、国际化等功能。
- 与SpringBoot完美整合,SpringBoot提供了Thymeleaf的默认配置,并且为Thymeleaf设置了视图解析器,我们可以像以前操作jsp一样来操作Thymeleaf。代码几乎没有任何区别,就是在模板语法上有区别。
接下来,我们就通过入门案例来体会Thymeleaf的魅力:
1、引入thymeleaf;
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>2.1.6</dependency>切换thymeleaf版本<properties><thymeleaf.version>3.0.9.RELEASE</thymeleaf.version><!-- 布局功能的支持程序 thymeleaf3主程序 layout2以上版本 --><!-- thymeleaf2 layout1--><thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>2.2.2</thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version></properties>
2、Thymeleaf使用
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.thymeleaf")public class ThymeleafProperties {private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING = Charset.forName("UTF-8");private static final MimeType DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE = MimeType.valueOf("text/html");public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";//
只要我们把HTML页面放在classpath:/templates/,thymeleaf就能自动渲染;
使用:
1、导入thymeleaf的名称空间
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
2、使用thymeleaf语法;
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title></head><body><h1>成功!</h1><!--th:text 将div里面的文本内容设置为 --><div th:text="${hello}">这是显示欢迎信息</div></body></html>
3、语法规则
1)th:text;改变当前元素里面的文本内容;
th:任意html属性;来替换原生属性的值

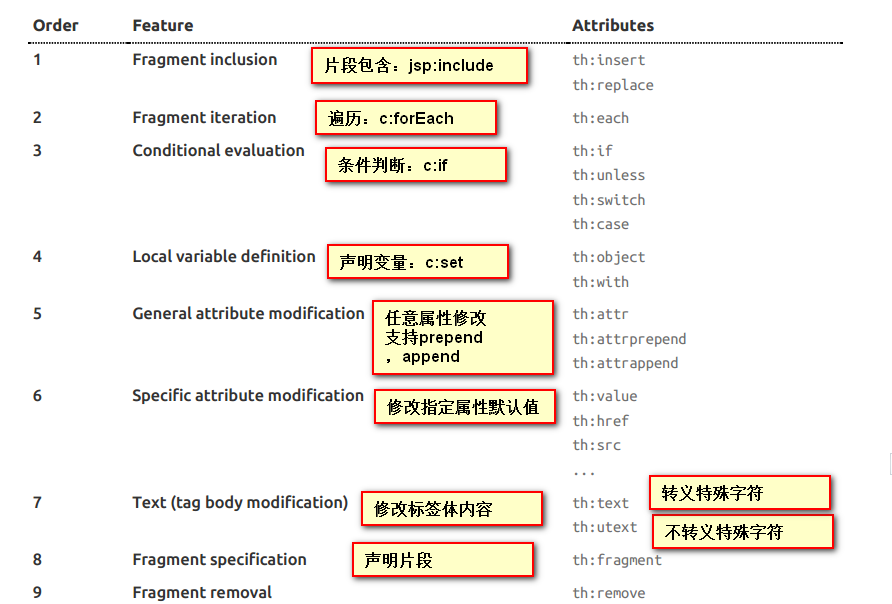
2)表达式
Simple expressions:(表达式语法)Variable Expressions: ${...}:获取变量值;OGNL;1)、获取对象的属性、调用方法2)、使用内置的基本对象:#ctx : the context object.#vars: the context variables.#locale : the context locale.#request : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletRequest object.#response : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletResponse object.#session : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpSession object.#servletContext : (only in Web Contexts) the ServletContext object.${session.foo}3)、内置的一些工具对象:#execInfo : information about the template being processed.#messages : methods for obtaining externalized messages inside variables expressions, in the same way as they would be obtained using #{…} syntax.#uris : methods for escaping parts of URLs/URIs#conversions : methods for executing the configured conversion service (if any).#dates : methods for java.util.Date objects: formatting, component extraction, etc.#calendars : analogous to #dates , but for java.util.Calendar objects.#numbers : methods for formatting numeric objects.#strings : methods for String objects: contains, startsWith, prepending/appending, etc.#objects : methods for objects in general.#bools : methods for boolean evaluation.#arrays : methods for arrays.#lists : methods for lists.#sets : methods for sets.#maps : methods for maps.#aggregates : methods for creating aggregates on arrays or collections.#ids : methods for dealing with id attributes that might be repeated (for example, as a result of an iteration).Selection Variable Expressions: *{...}:选择表达式:和${}在功能上是一样;补充:配合 th:object="${session.user}:<div th:object="${session.user}"><p>Name: <span th:text="*{firstName}">Sebastian</span>.</p><p>Surname: <span th:text="*{lastName}">Pepper</span>.</p><p>Nationality: <span th:text="*{nationality}">Saturn</span>.</p></div>Message Expressions: #{...}:获取国际化内容Link URL Expressions: @{...}:定义URL;@{/order/process(execId=${execId},execType='FAST')}Fragment Expressions: ~{...}:片段引用表达式<div th:insert="~{commons :: main}">...</div>Literals(字面量)Text literals: 'one text' , 'Another one!' ,…Number literals: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,…Boolean literals: true , falseNull literal: nullLiteral tokens: one , sometext , main ,…Text operations:(文本操作)String concatenation: +Literal substitutions: |The name is ${name}|Arithmetic operations:(数学运算)Binary operators: + , - , * , / , %Minus sign (unary operator): -Boolean operations:(布尔运算)Binary operators: and , orBoolean negation (unary operator): ! , notComparisons and equality:(比较运算)Comparators: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )Equality operators: == , != ( eq , ne )Conditional operators:条件运算(三元运算符)If-then: (if) ? (then)If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)Special tokens:No-Operation: _
附:循环遍历list数组
controller
package com.xuchen.springboot.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.Map;@Controllerpublic class HelloWorld {@ResponseBody@RequestMapping("/hello")public String hello(){return "你好";}@RequestMapping("/sucess")public String sucess(Map<String,Object> map){map.put("hello","<h1>你好<h1>");map.put("users",Arrays.asList("张三","李四","王五"));return "sucess";}}<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title></head><body><div th:text="${hello}"></div><div th:utext="${hello}"></div><hr/><!-- th:each每次遍历都会生成当前这个标签: 3个h4 --><h4 th:text="${user}" th:each="user:${users}"></h4><hr/><h4><!-- 一个h4标签下三个span标签 --><span th:each="user:${users}"> [[${user}]] </span></h4><h1>模板引擎成功</h1></body></html>
模板缓存
Thymeleaf会在第一次对模板解析之后进行缓存,极大的提高了并发处理能力。但是这给我们开发带来了不便,修改页面后并不会立刻看到效果,我们开发阶段可以关掉缓存使用:
开发阶段关闭thymeleaf的模板缓存
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
注意:在Idea中,我们需要在修改页面后按快捷键:Ctrl + Shift + F9对项目进行rebuild才可以。





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...