NIO之通道Channel【FileChannel介绍】
通道(channel)介绍
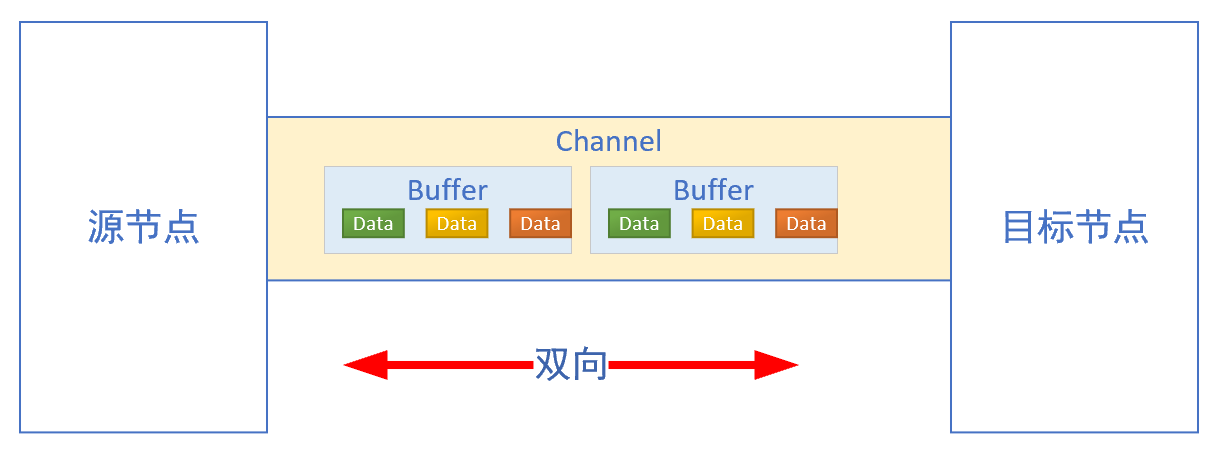
Channel是一个对象,作用是用于源节点和目标节点的连接,在java NIO中负责缓冲区数据的传递。Channel本身不存储数据,因此需要配合缓冲区进行传输。
主要的实现类有
主要的实现类有如下四个: FileChannel, SocketChannel, ServerSocketChannel, DatagramChannel,都实现了java.nio.channels.Channel接口
获取通道
- Java针对支持通道的类提供了getChannel()方法
| 本地IO | 网络IO |
|---|---|
| FileInputStream/FileOutputStream | Socket |
| RandomAccessFile | ServerSocket |
| 无 | DatagramSocket |
- 在JDK1.7中的NIO.2针对各个通道提供了静态方法open()
在JDK1.7中的NIO.2的Files工具类的newByteChannel()
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1本地IO获取通道FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("c:/tools/a.txt");FileChannel fileChannel = in.getChannel();// 2.通过open方法获取FileChannel.open(Paths.get("c:/tools/a.txt"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
}
案例-文件复制
1.使用FileChannel配合缓冲区实现文件复制的功能
/** * FileChannel实现文件复制功能 * @param args * @throws Exception */public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("c:/tools/a.txt");FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("c:/tools/a-copy1.txt");FileChannel inChannel = in.getChannel();FileChannel outChannel = out.getChannel();// 分配指定大小的缓冲区ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);// 将通道中的数据存入缓冲区中while(inChannel.read(bb)!=-1){bb.flip();// 切换到读取模式outChannel.write(bb); // 将缓冲区的数据写入到输出通道中bb.clear(); // 清空缓冲区}outChannel.close();inChannel.close();}
2.内存映射文件的方式实现文件复制
/** * 使用直接缓冲区来完成文件的复制【内存映射文件】 * @param args * @throws Exception */public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("c:/tools/a.txt"),StandardOpenOption.READ );FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("c:/tools/aa.txt"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.CREATE,StandardOpenOption.READ);// 获取内存映射文件MappedByteBuffer inMap = inChannel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, inChannel.size());MappedByteBuffer outMap = outChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, inChannel.size());byte[] b = new byte[inMap.limit()];// 从磁盘文件中获取数据写入到b字节数组中inMap.get(b);// 将b字节数组中的数据写入到磁盘文件中outMap.put(b);inChannel.close();outChannel.close();}
3.Channel-to-channel方式实现复制
/** * 使用直接缓冲区来完成文件的复制【内存映射文件】 * @param args * @throws Exception */public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("c:/tools/a.txt"),StandardOpenOption.READ );FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("c:/tools/aa1.txt"),StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.CREATE,StandardOpenOption.READ);//Channel-to-channel 传输是可以极其快速的,特别是在底层操作系统提供本地支持的时候。某些//操作系统可以不必通过用户空间传递数据而进行直接的数据传输。对于大量的数据传输,这会是一个巨大的帮助inChannel.transferTo(0, inChannel.size(), outChannel);inChannel.close();outChannel.close();}
scatter和gather
分散(scatter)
从Channel中读取是指在读操作时将读取的数据写入多个buffer中,将从Channel中读取的数据“分散(scatter)”到多个Buffer中

/** * 分散:scatter * @param args * @throws IOException */public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileChannel channel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("c:/tools/a.txt"), StandardOpenOption.READ);// TODO Auto-generated method stubByteBuffer header = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);ByteBuffer body = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);ByteBuffer[] bufferArray = { header, body };channel.read(bufferArray);bufferArray[0].flip();bufferArray[1].flip();System.out.println(new String(bufferArray[0].array(),0,bufferArray[0].limit()));System.out.println("---------");System.out.println(new String(bufferArray[1].array(),0,bufferArray[1].limit()));}
注意buffer首先被插入到数组,然后再将数组作为channel.read() 的输入参数。read()方法按照buffer在数组中的顺序将从channel中读取的数据写入到buffer,当一个buffer被写满后,channel紧接着向另一个buffer中写。
Scattering Reads在移动下一个buffer前,必须填满当前的buffer,这也意味着它不适用于动态消息(译者注:消息大小不固定)。换句话说,如果存在消息头和消息体,消息头必须完成填充(例如 128byte),Scattering Reads才能正常工作。
聚集(gather)
写入Channel是指在写操作时将多个buffer的数据写入同一个Channel, 将多个Buffer中的数据“聚集(gather)”后发送到Channel

/** * 聚集gether * @param args * @throws IOException */public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileChannel channel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("c:/tools/ag.txt"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE);ByteBuffer header = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);ByteBuffer body = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);// 写入内容header.put("bobo".getBytes());// 转换为读模式header.flip();// 写入内容body.put("hello".getBytes());// 转换为读模式body.flip();//write data into buffersByteBuffer[] bufferArray = { header, body };// 将这两个缓冲区的数据依次写入到文件中channel.write(bufferArray);}
buffers数组是write()方法的入参,write()方法会按照buffer在数组中的顺序,将数据写入到channel,注意只有position和limit之间的数据才会被写入。因此,如果一个buffer的容量为128byte,但是仅仅包含58byte的数据,那么这58byte的数据将被写入到channel中。因此与Scattering Reads相反,Gathering Writes能较好的处理动态消息。


































还没有评论,来说两句吧...