Netty4源码再次分析
先上个demo,好顺着往里跟代码
public class Netty4Hello {/** * 服务端监听的端口地址 */private static final int portNumber = 7878;public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();try {ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup);b.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);b.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();// 以("\n")为结尾分割的 解码器pipeline.addLast("framer", new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(8192, Delimiters.lineDelimiter()));// 字符串解码 和 编码pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());// 自己的逻辑Handlerpipeline.addLast("handler", new HelloServerHandler());}});// 服务器绑定端口监听ChannelFuture f = b.bind(portNumber).sync();// 监听服务器关闭监听f.channel().closeFuture().sync();// 可以简写为/* b.bind(portNumber).sync().channel().closeFuture().sync(); */} finally {bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();}}}
NioSocketChannel 的初始化
在 Netty 中, Channel 是一个 Socket 的抽象, 它为用户提供了关于 Socket 状态(是否是连接还是断开) 以及对 Socket 的读写等操作. 每当 Netty 建立了一个连接后, 都会有一个对应的 Channel 实例.
io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#channel>io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#channelFactory(io.netty.channel.ChannelFactory<? extends C>)>构造io.netty.channel.ReflectiveChannelFactory
Channel 实例化
Channel 是通过工厂方法 ChannelFactory.newChannel() 来实例化的, 那么 ChannelFactory.newChannel() 方法在哪里调用呢?
跟踪调用
io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap#connect(java.net.SocketAddress, java.net.SocketAddress)>io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap#doResolveAndConnect>io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#initAndRegister>io.netty.bootstrap.ChannelFactory#newChannel
在 newChannel 中, 通过类对象的 newInstance 来获取一个新 Channel 实例, 因而会调用NioSocketChannel 的默认构造器.
NioServerSocketChannel
io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel#NioServerSocketChannel()>io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel#newSocket>java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider#openServerSocketChannel
NioEventLoopGroup构造
类结构图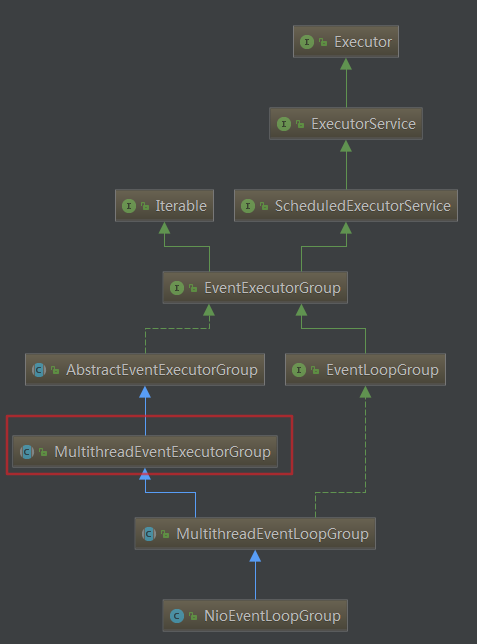
NioEventLoop 有几个重载的构造器, 不过内容都没有什么大的区别, 最终都是调用的父类MultithreadEventLoopGroup构造器:
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup#NioEventLoopGroup(int)>io.netty.channel.MultithreadEventLoopGroup#MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int, java.util.concurrent.Executor, java.lang.Object...)>io.netty.util.concurrent.MultithreadEventExecutorGroup#MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int, java.util.concurrent.Executor, io.netty.util.concurrent.EventExecutorChooserFactory, java.lang.Object...)>executor netty实现的线程池管理 io.netty.util.concurrent.ThreadPerTaskExecutor>选择策略io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory>拒绝策略io.netty.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionHandlers// 大小为 nThreads NioEventLoop>children = new EventExecutor[nThreads];>children[i] = newChild(executor, args)>io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup#newChild
NioEventLoop解析
类图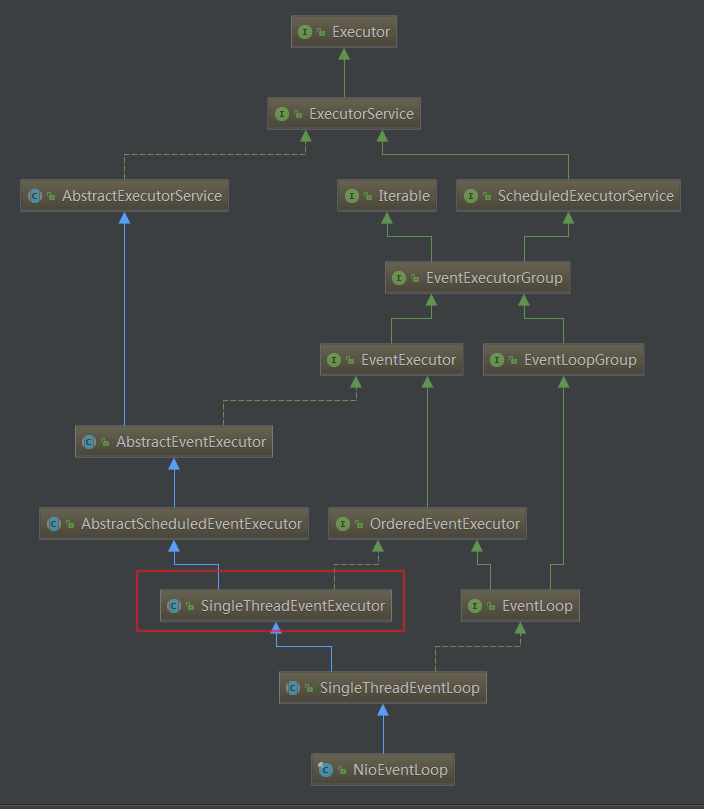
NioEventLoop 继承于 SingleThreadEventLoop, 而 SingleThreadEventLoop 又继承于 SingleThreadEventExecutor. SingleThreadEventExecutor 是 Netty 中对本地线程的抽象, 它内部有一个 Thread thread 属性, 存储了一个本地 Java 线程. 因此我们可以认为, 一个 NioEventLoop 其实和一个特定的线程绑定, 并且在其生命周期内, 绑定的线程都不会再改变.
- 在 AbstractScheduledEventExecutor 中, Netty 实现了 NioEventLoop 的 schedule 功能, 即我们可以通过调用一个 NioEventLoop 实例的 schedule 方法来运行一些定时任务.
- 在 SingleThreadEventLoop 中, 又实现了任务队列的功能, 通过它, 我们可以调用一个 NioEventLoop 实例的 execute 方法来向任务队列中添加一个 task, 并由 NioEventLoop 进行调度执行.
在此方法的一开始调用的 fetchFromScheduledTaskQueue() 其实就是将 scheduledTaskQueue 中已经可以执行的(即定时时间已到的 schedule 任务) 拿出来并添加到 taskQueue 中, 作为可执行的 task 等待被调度执行.
NioEventLoop 肩负着两种任务,
- 第一个是作为 IO 线程, 执行与 Channel 相关的 IO 操作, 包括 调用 select 等待就绪的 IO
事件、读写数据与数据的处理等; - 第二个任务是作为任务队列, 执行 taskQueue 中的任务, 例如用户调用 eventLoop.schedule
提交的定时任务也是这个线程执行的.
构造方法
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop#NioEventLoop>io.netty.channel.SingleThreadEventLoop#SingleThreadEventLoop(io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup, java.util.concurrent.Executor, boolean, int, io.netty.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionHandler)>io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor#SingleThreadEventExecutor(io.netty.util.concurrent.EventExecutorGroup, java.util.concurrent.Executor, boolean, int, io.netty.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionHandler)
EventLoop 与 Channel 的关联
Netty 中, 每个 Channel 都有且仅有一个 EventLoop 与之关联,
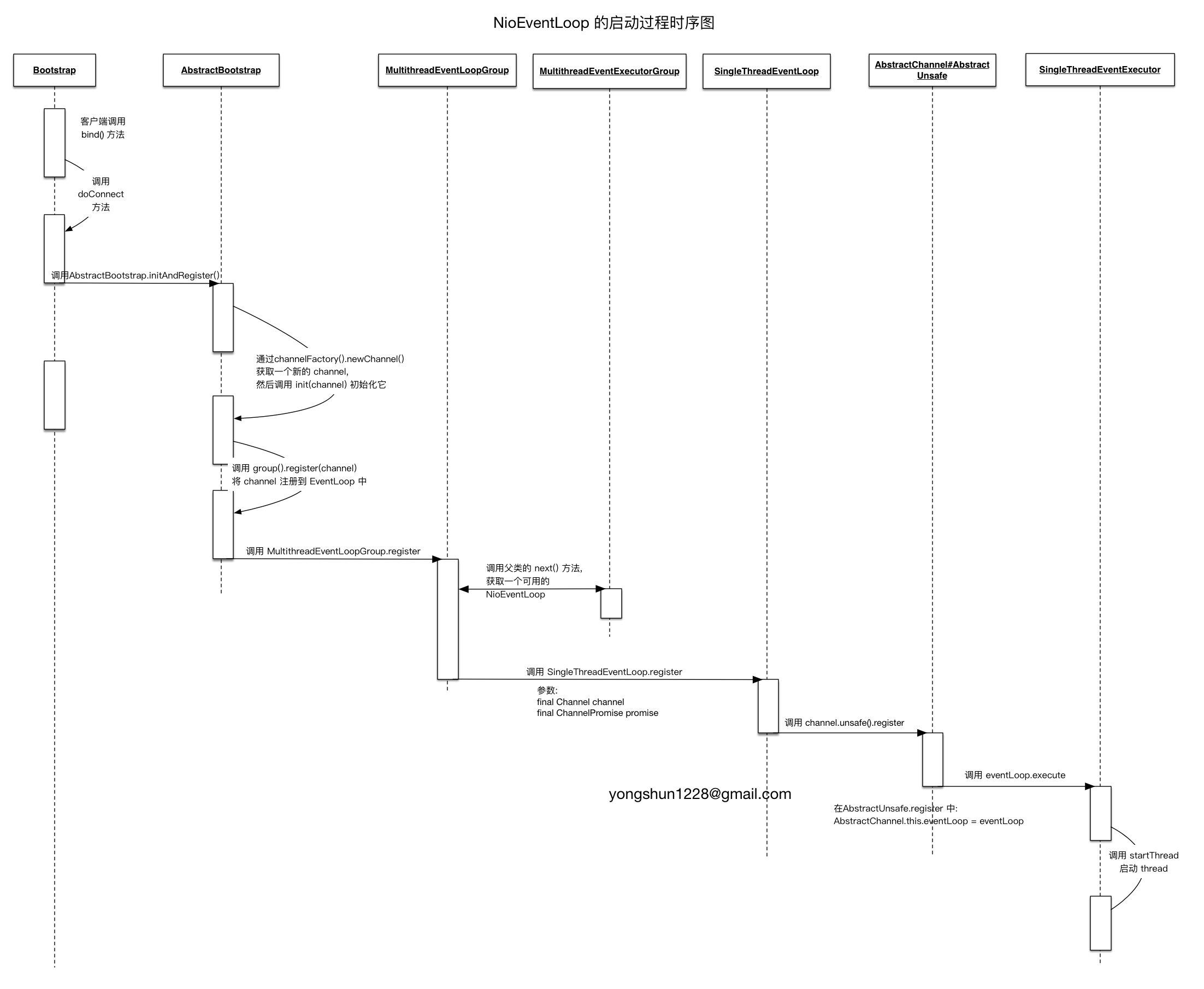
从上图中我们可以看到, 当调用了 AbstractChannel#AbstractUnsafe.register 后, 就完成了 Channel 和 EventLoop 的关联. register 实现如下:
@Overridepublic final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {// 删除条件检查....AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop;if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {register0(promise);} else {try {eventLoop.execute(new OneTimeTask() {@Overridepublic void run() {register0(promise);}});} catch (Throwable t) {...}}}
在 AbstractChannel#AbstractUnsafe.register 中, 会将一个 EventLoop 赋值给 AbstractChannel 内部的 eventLoop 字段, 到这里就完成了 EventLoop 与 Channel 的关联过程.
什么时候启动
EventLoop 与 Channel 的关联完成后,就会调用eventLoop.execute
// 向任务队列中添加一个 taskio.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor#execute>io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor#startThread>io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor#doStartThread>java.util.concurrent.Executor#execute 实现类io.netty.util.concurrent.ThreadPerTaskExecutor
NioEventLoop run方法
上面了解到,当 EventLoop.execute 第一次被调用时, 就会触发 startThread() 的调用, 进而导致了 EventLoop 所对应的 Java 线程的启动.
run 方法可以说是十分简单, 主要就是调用了 SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run() 方法. 而 SingleThreadEventExecutor.run() 是一个抽象方法, 它的实现在 NioEventLoop 中.
@Overrideprotected void run() {for (;;) {try {switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:continue;case SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT:// fall-through to SELECT since the busy-wait is not supported with NIOcase SelectStrategy.SELECT:// 关键1:select事件select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false));if (wakenUp.get()) {selector.wakeup();}// fall throughdefault:}cancelledKeys = 0;needsToSelectAgain = false;// 有意思点:ioRatio 默认是 50, 则表示 IO 操作和执行 task 的所占用的线程执行时间比是 1 : 1.final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;if (ioRatio == 100) {try {processSelectedKeys();} finally {// Ensure we always run tasks.runAllTasks();}} else {final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();try {// 迭代 selectedKeys 获取就绪的 IO 事件processSelectedKeys();} finally {// 处理IO的时间,按比例处理任务final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;// 有限时间内执行taskQueue任务runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);}}} catch (Throwable t) {handleLoopException(t);}// Always handle shutdown even if the loop processing threw an exception.try {if (isShuttingDown()) {closeAll();if (confirmShutdown()) {return;}}} catch (Throwable t) {handleLoopException(t);}}}io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop#run>io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop#select>
分析select方法
2个关键步骤,见下代码
private void select(boolean oldWakenUp) throws IOException {Selector selector = this.selector;try {int selectCnt = 0;long currentTimeNanos = System.nanoTime();long selectDeadLineNanos = currentTimeNanos + delayNanos(currentTimeNanos);for (;;) {long timeoutMillis = (selectDeadLineNanos - currentTimeNanos + 500000L) / 1000000L;if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {if (selectCnt == 0) {selector.selectNow();selectCnt = 1;}break;}// If a task was submitted when wakenUp value was true, the task didn't get a chance to call// Selector#wakeup. So we need to check task queue again before executing select operation.// If we don't, the task might be pended until select operation was timed out.// It might be pended until idle timeout if IdleStateHandler existed in pipeline.// 关键步骤1:有任务则执行selectNow(不阻塞),将wakenUp CAS设置为trueif (hasTasks() && wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)) {selector.selectNow();selectCnt = 1;break;}// 关键步骤2:没有任务,则执行select (阻塞超时时间)int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);selectCnt ++;if (selectedKeys != 0 || oldWakenUp || wakenUp.get() || hasTasks() || hasScheduledTasks()) {// - Selected something,// - waken up by user, or// - the task queue has a pending task.// - a scheduled task is ready for processingbreak;}if (Thread.interrupted()) {// Thread was interrupted so reset selected keys and break so we not run into a busy loop.// As this is most likely a bug in the handler of the user or it's client library we will// also log it.//// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2426if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely because " +"Thread.currentThread().interrupt() was called. Use " +"NioEventLoop.shutdownGracefully() to shutdown the NioEventLoop.");}selectCnt = 1;break;}long time = System.nanoTime();if (time - TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(timeoutMillis) >= currentTimeNanos) {// timeoutMillis elapsed without anything selected.selectCnt = 1;} else if (SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD > 0 &&selectCnt >= SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD) {// The selector returned prematurely many times in a row.// Rebuild the selector to work around the problem.logger.warn("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row; rebuilding Selector {}.",selectCnt, selector);rebuildSelector();selector = this.selector;// Select again to populate selectedKeys.selector.selectNow();selectCnt = 1;break;}currentTimeNanos = time;}if (selectCnt > MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row for Selector {}.",selectCnt - 1, selector);}}} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + " raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?",selector, e);}// Harmless exception - log anyway}}
最后总结下调用流程
io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#bind(int)>io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#bind(int)>io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#doBind>io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#initAndRegister>io.netty.bootstrap.ChannelFactory#newChannel 调用NioServerSocketChannel构造器实例化>NioServerSocketChannel构造,并注册SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT事件io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel#NioServerSocketChannel(java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel)> io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#init>io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap#init>io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline初始化>添加Acceptor Handler io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap.ServerBootstrapAcceptor>接收OP_ACCEPT到事件后分发给WorkerGroup处理>(WorkerGroup)childGroup io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup#register(io.netty.channel.Channel)>io.netty.channel.SingleThreadEventLoop#register(io.netty.channel.ChannelPromise)>io.netty.channel.AbstractChannel.AbstractUnsafe#register>NioEventLoop java.util.concurrent.Executor#execute>io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor#execute>io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor#addTask>io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor#startThread






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...