SPRING CLOUD微服务实战笔记--微服务构建:Spring Boot
文章目录
- 快速入门
- 配置详解
- SpringBoot默认配置文件位置
- YAML配置格式
- 自定义参数
- 参数引用
- 生成随机数
- 命令行参数
- 多环境配置
- 加载顺序
- 监控与管理
- 初识actuator
- 原生端点
- 应用配置类
- 度量指标类
- 操作控制类
快速入门
1.实现RESTful API
@RestControllerpublic class HelloController{@RequestMapping("/hello")public String hello(){return "hello world!";}}
2.启动Spring Boot应用
- 方式一:直接通过main函数来启动
- 方式二:
mvn spring-boot : run 方式三:mvn install打包成jar包,再通过
java -jar xxx.jar注:SpringBootApplication的位置不要改变,将启动类换了位置可能就启动不了了
3.编写单元测试@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@WebAppConfiguration
public class HelloApplicationTests {private MockMvc mvc;@Beforepublic void setUp() throws Exception{mvc = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(new HelloController()).build();}@Testpublic void hello() throws Exception{mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/hello").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)).andExpect(status().isOk()).andExpect(content().string(equalTo("Hello World!")));}
}
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class):书中为@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class),引入Spring对JUnit4的支持@SpringBootTest:书中为@SpringApplicationConfiguration,指定SpringBoot的启动类@WebAppConfiguration:开启Web应用的配置,用于模拟ServletContextMockMvc对象:用于模拟调用Controller的接口发起请求,在@Test定义的hello测试用例中,perform执行一次请求调用,accept用于执行接收的数据类型,andExpect用于判断接口返回的期望值@Before:JUnit定义在测试用例@Test内容执行前预加载的内容,这里用来初始化对HelloController的模拟
配置详解
SpringBoot默认配置文件位置
src/main/resources/application.properties
YAML配置格式
environments:dev:url: http://dev.bar.comname: developer setup
自定义参数
book.name=SpringCloudApplication@Componentpublic class Book{@Value("${book.name}")private String name;}
参数引用
属性文件中的各个参数也可相互调用
book.name=SpringCloudbook.author=hahabook.desc=${book.author} is writing <${book.name}>
生成随机数
${random}的配置方式主要有以下几种#随机字符串blog.value=${random.value}#随机intblog.number=${random.int}#随机longblog.bignumber=${random.log}#10以内的随机数blog.test1=${random.int(10)}#10~20以内的随机数blog.test2=${random.int[10,20]}
命令行参数
通过java -jar xxx.jar --server.port=8888可以将配置文件中server.port修改为8888
多环境配置
spring.profiles.active属性设置{profile}值
例如:spring.profiles.active=test就会加载application-test.properties
加载顺序
1)在命令行传入的参数
2)SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON中的属性,SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON是以JSON格式
配置在系统环境变量中的内容
3)java:comp/env中的JNDI属性
4)Java的系统属性,可以通过System.getProperties()获得的内容
5)操作系统的环境变量
6)通过random.*配置的随机属性
7)jar包之外,不同环境对应的application-{profile}配置文件
8)jar包之内,不同环境对应的application-{profile}配置文件
9)jar包之外的application.properties或YAML
10)jar包之内的application.properties或YAML
11)@Configuration修改的类,通过@PropertySource注解定义的属性
12)应用默认属性,使用SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties定义的内容
以上数字越小优先级越高
监控与管理
初识actuator
引入依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId></dependency>
刷新pom,此处若不刷新会报错
重启应用,控制台输出
访问http://localhost:8080/health可以实时获取应用的各项监控指标
原生端点
1.应用配置类:获取应用程序中加载的应用配置,环境变量,自动化配置报告等与SpringBoot应用密切相关的配置类信息
2.度量指标类:获取应用程序运行过程中用于监控的度量指标,比如内存信息,线程池信息,HTTP请求统计等
3.操作控制类:提供了对应用的关闭等操作类功能
应用配置类
若要端点能够生效,需要在application.properties中加入management.security.enabled=false
否则会出现如下报错:status=401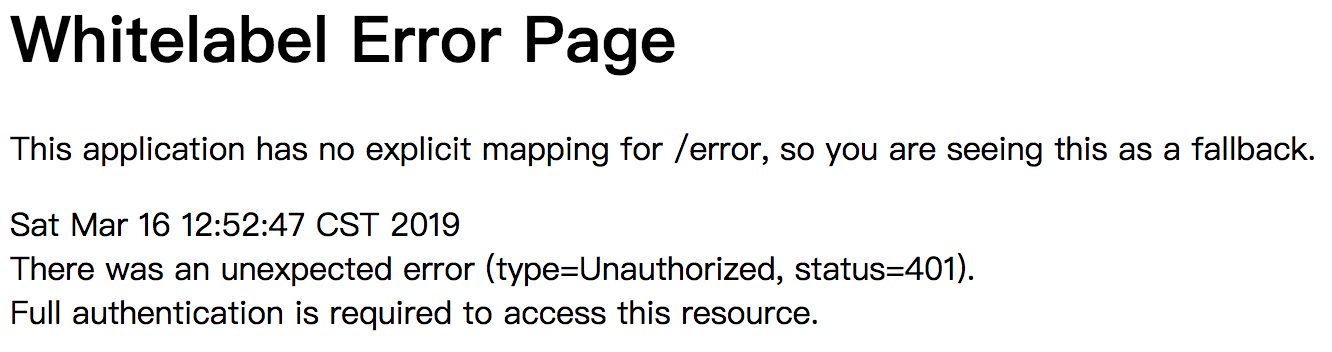
/autoconfig:该端点用来获取应用的自动化配置报告positiveMatches中返回的是条件匹配成功的自动化配置negativeMatches中返回的是条件匹配不成功的自动化配置,可以查看具体没有生效的原因/beans:该端点用来获取应用上下文中创建的所有bean/configprops:该端点用于获取应用中配置的属性信息报告/env:用来获取所有可用的环境属性报告,如环境变量,JVM属性,应用的配置属性,命令行中的参数,可以通过@ConfigurationProperties注解来引入到应用程序中使用/mappings:该端点用来返回所有SpringMvc的控制器映射关系报告/info:该端点用来返回一些应用自定义的信息
比如在application.properties中通过info前缀设置属性:info.app.name=spring-boot-hello
度量指标类
/metrics:该端点用来返回当前应用的各类重要度量指标,比如内存信息,线程信息,垃圾回收信息等/health:该端点用于获取应用的各类健康指标信息.
| 检测器 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| DiskSpaceHealthIndicator | 低磁盘空间检测 |
| DataSourceHealthIndicator | 检测DataSource的连接是否可用 |
| MongoHealthIndicator | 检测Mongo数据库是否可用 |
| RedisHealthIndicator | 检测Redis服务器是否可用 |
对于没有自动化配置的检测器,需要自己来实现
@Componentpublic class RocketMQHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator{@Overridepublic Health health() {int errorCode = check();if(errorCode != 0){return Health.down().withDetail("Error Code",errorCode).build();}return Health.up().build();}private int check(){//对监控对象的检测操作return 1;}}
/dump:该端点用于暴露程序运行时的线程信息/trace:该端点用于返回基本的HTTP跟踪信息
操作控制类
/shutdown可以通过如下配置来开启,需要加入保护机制如定制化的actuator的端点路径或者整合Spring Security进行安全校验等endpoints.shutdown.enabled=true



































还没有评论,来说两句吧...