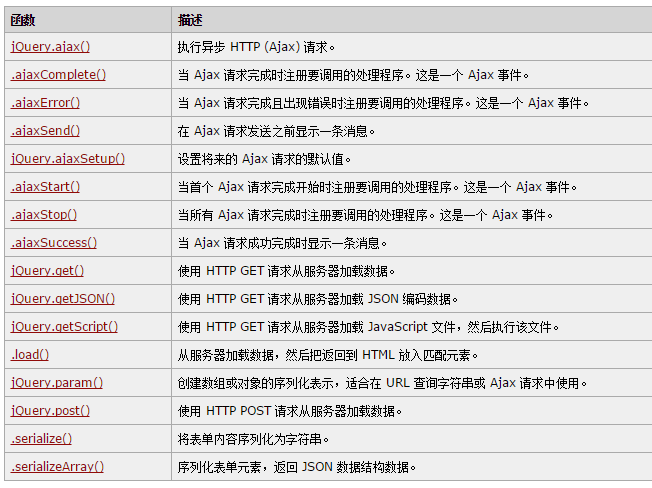
SpringBoot使用RestFul风格路径
Java知识点总结:想看的可以从这里进入
目录
- 2.16、RestFul风格
2.16、RestFul风格
SpringBoot因为本身就继承了SpringMVC,所以使用RestFul和SpringMVC一样。
RestFul风格是一种当前比较流行的互联网软件架构模式,它利用HTTP 协议的特性,规定了一套资源获取的方式,,它可以使软件更简洁,更有层次,易于实现缓存等机制。
在 web开发中,Rest使用HTTP协议连接器来标识对资源的操作,用 HTTP GET标识获取查询资源,HTTP POST标识创建资源,HTTP PUT标识修改资源,HTTP DELETE标识删除资源,这样就构成了 Rest风格数据处理的核心,它的增删改查在在Controller中通过四种注解来区分(也可以用@RequestMapping的属性method):
| 资源操作 | 对应注解 | HTTP 请求方式 |
|---|---|---|
| 获取资源(SELECT) | @GetMapping、 @RequestMapping(value = “”,method = RequestMethod.GET) | GET |
| 新增资源(INSERT) | @PostMapping @RequestMapping(value = “”,method = RequestMethod.POST) | POST |
| 修改资源(UPDATE) | @PutMapping @RequestMapping(value = “”,method = RequestMethod.PUT) | PUT |
| 删除资源(DELETE) | @DeleteMapping @RequestMapping(value = “”,method = RequestMethod.DELETE) | DELETE |
传统的资源操作是通过不同的参数来实现的
@Controllerpublic class RestfulController {@RequestMapping("/summation")public String summation(int num1, int num2, Model model){int result = num1+num2;model.addAttribute("result","和为:"+result);return "";}}
http://localhost:8080/summation?num1=15&num2=3
RestFul可以用相同的路径,通过修改提交方式达到不同请求的结果:
访问路径都为http://localhost:8080/user,但根据不同的访问方式实现了增删改查四种操作
@RestControllerpublic class RestFulController {@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;//get对应查@GetMapping("/user")public String getUser(@PathVariable("id") int id){User user = userService.selectByPrimaryKey(id);return JSON.toJSONString(user);}//post对应新增@PostMapping("/user")public int postUser(@RequestBody User user){return userService.insert(user);}//put对应修改@PutMapping("/user")public int putUser(@RequestBody User user){return userService.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(user);}//delete对应删除@DeleteMapping("/user")public int deleteUser(int id){return userService.deleteByPrimaryKey(id);}}
使用MockMvc对其进行测试
@SpringBootTest@AutoConfigureMockMvcpublic class RestFulControllerTest {
@Autowiredprivate MockMvc mockMvc;//查@Testpublic void getTest() throws Exception {MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = get("/user").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED).param("id","1");mockMvc.perform(builder).andDo(print()).andReturn();}//增@Testpublic void postTest() throws Exception {User user = new User(null,"mockMvc","123456",true);String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(user);MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = post("/user").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).content(jsonString);MvcResult mvcResult = mockMvc.perform(builder).andDo(print()).andReturn();System.out.println("输出 " + mvcResult.getResponse().getContentAsString());}//改@Testpublic void putTest() throws Exception {User user = new User(3,"restful","123456",true);String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(user);MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = put("/user").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).content(jsonString);MvcResult mvcResult = mockMvc.perform(builder).andDo(print()).andReturn();System.out.println("输出 " + mvcResult.getResponse().getContentAsString());}//删除@Testpublic void deleteTest() throws Exception {MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = delete("/user").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).param("id","9");MvcResult mvcResult = mockMvc.perform(builder).andDo(print()).andReturn();System.out.println("输出 " + mvcResult.getResponse().getContentAsString());}}![image-20220925183855756][]
需要注意几个注解:
- @RequestParam(value = “绑定值的名称”,required = 是否必须绑定):用在参数前,用来处理简单类型的绑定,原理是通过Request.getParameter() 获取参数值
- @RequestBody:用在参数前,主要用来处理JSON格式的数据映射
- @PathVariable:如果RestFul风格的路径中有 {id}这种的,可以用来与参数进行映射































还没有评论,来说两句吧...