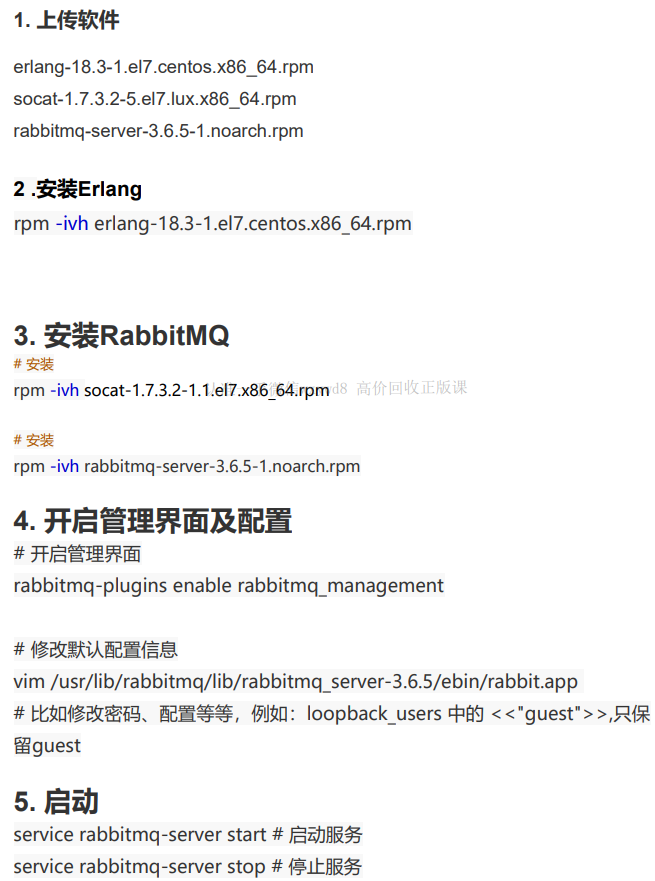
浅谈:ArrayList数组1
ArrayList的几大特点
- ArrayList是一个有序数组
- ArrayList线程不安全
- ArrayList可以存放空值
当前基于jdk 1.8源码分析
继承以及实现关系
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
1.继承抽象的AbstractList类
2.实现
- 实现List基类,具有数组特性
- 实现RandomAccess类,以此支持快速查询
- 实现Cloneable类,支持克隆 Object.writeObject 注意:虽然cloneable是个标记接口无任何实现,若未实例上调用Object.clone() 方法,则会抛出CloneNotSupportedException(克隆不被支持)的异常。
- 实现序列化java.io.Serializable
前提源码分析
创建ArrayList数组默认长度
- private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
空元素
- private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
默认空元素,未添加任何元素时时判断数组信息
- private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
实参(待处理的参数)
- transient Object[] elementData;
当前数组已经添加元素个数
- private int size;
当前数组已经被改变的次数,注意是当前数组结构发生变化 例如新增,删除都会增加,查询或者修改不会变化
- protected transient int modCount = 0;
新增操作源码分析
/*** Appends the specified element to the end of this list.** @param e element to be appended to this list* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})*/public boolean add(E e) {ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); //462 Increments modCount!! 462elementData[size++] = e; //463return true;}private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));//231}private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { //223if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { //224return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); //225} //226return minCapacity; //227}private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { //234modCount++; //235// overflow-conscious codeif (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) //238grow(minCapacity); //239}private void grow(int minCapacity) { //256// overflow-conscious code //258int oldCapacity = elementData.length; //259int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); //260if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) //261newCapacity = minCapacity; //262if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) //263newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); //264// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: //265elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); //266}public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) { //3180return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass()); //3181} //3182public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) { //3208@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") //3209T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class) //3210? (T[]) new Object[newLength]: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0, //3213Math.min(original.length, newLength)); //3214return copy;}
新增操作步骤解析
图一包括两部分操作
- 创建一个存储空间,准备用来存储新元素
- 将新元素赋值到当前新的存储位置
- 图二
图三
创建一个可用的存储空间大小
- 具体来说,若首次创建224行满足,取225行的最大值即Math.max(10,1),即将开辟一块长度为10的内存空间; 只有首次添加元素时才会走225行
- 其他情况取新增元素所需的最小容量值
图四
- 235行此时,已经确定好所需要的空间,当前list即将变化的次数做记录
- 238行,判断当前数组容器是否能容纳新增的数据若,不能容纳需要进行扩容处理
- 239具体扩容操作
图五
- 259行当前未新增前的数组使用长度
- 260行,根据arraylist扩容算法,得到的新的可用长度
- 261,262行若新的可用长度还无法满足需要,直接取所需要的长度
- 263,264若所需要的长度大于MAX_ARRAY_SIZE提示报错
- 266步骤将旧数组copy到新的大数组里
图六
- 3210可参考https://blog.csdn.net/feeltouch/article/details/79190805
- 3213进行数组迁移
删除操作源码分析
首先先普及一个方法,以及使用方式
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,Object dest, int destPos,int length);int index = 1;int numMoved = 8;int[] oldElementData = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};log.info("迁移前数据:{}",oldElementData);System.arraycopy(oldElementData, index + 1, oldElementData, index, numMoved);log.info("迁移后数据:{}",oldElementData);ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {arrayList.add(i);}System.out.println(arrayList);arrayList.remove(1);
arraycopy就是将某一个数组src,从指定的位置srcPos,按照指定的长度length”迁移”到目标数组destPos中
- 目标数组也可以是当前源数组,最终的迁移结果 会把原数组上索引destPos—descPost+length元素替换掉
对于arrayList的删除,一次执行一条删除操作,即偏移量是1,且arrayList是一个连续的数组,且删除操作数组长度不会增加,即只需在原数组基础进行操作
public E remove(int index) { //495
rangeCheck(index); //496modCount++; //498E oldValue = elementData(index); //499int numMoved = size - index - 1; //501if (numMoved > 0) //502System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, //503numMoved); //504elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work //505return oldValue; //507}
int index = 1;int numMoved = 8;int[] oldElementData = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};log.info("迁移前数据:{}",oldElementData);System.arraycopy(oldElementData, index + 1, oldElementData, index, numMoved);log.info("迁移后数据:{}",oldElementData);
删除操作步骤解析
步骤一
- 源码486行,rangeCheck(index); 校验删除的元素位置有没有越界,越界抛异常
步骤二
- 源码498行,数组结构删除一个元素,数组结构发生变化自增++
步骤三
- 源码499行,即取出当前要删除的元素,最为返回值使用
步骤四
- 要移动的数组长度,如果删除的是最后一位的话,numModed就不需要移动
图五
- 如果删除的是最后一位的话,不需要移动
- 否则numMoved>0,执行迁移操作
图六
- 删除的数据,后面所有的数据都会向前平移一位,导致最后一位数据会重复出现两边
int index = 1;
int numMoved = 8;int[] oldElementData = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};log.info("迁移前数据:{}",oldElementData);System.arraycopy(oldElementData, index + 1, oldElementData, index, numMoved);log.info("迁移后数据:{}",oldElementData);

步骤七
- 最后把最后一位多余的数据,赋null值等待,GC回收
修改操作源码分析
public E set(int index, E element) { //447rangeCheck(index); //448E oldValue = elementData(index); //450elementData[index] = element; //451return oldValue;}
说明:修改操作有点类似于 工作过程中,修改操作场景 index类似于主键id,element类似于修改元素
删除操作步骤解析
步骤一
- 源码448行,rangeCheck(index); 校验修改的元素位置有没有越界,越界抛异常(同删除操作)
步骤二
- 源码450行,即取出当前要删除的元素,最为返回值使用(同删除操作)
步骤三
- elementData[index] = element;将待修改的新元素 放到指定的位置
查询操作源码分析
/*** Returns the element at the specified position in this list.** @param index index of the element to return* @return the element at the specified position in this list* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}*/public E get(int index) { //432rangeCheck(index); //433return elementData(index); //435}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")E elementData(int index) { //421return (E) elementData[index]; //422}
步骤一
- 源码433行,rangeCheck(index); 校验查询的元素位置有没有越界,越界抛异常(同删除,修改操作)
步骤二
- 返回索引index对应的元素
其他说明
ArrayList与Vector的区别
扩容不同
- ArrayList扩容问题,具体扩容多少与初始容积有关,可以指定初始容积,默认初始容积为10 无扩容因子
- vector有扩容因子,默认初始容积为10 可以指定每次扩容的大小
ArrayList的扩容说明int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);arrayList的扩容说明int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
线程安全性
- vector增加、删除操作使用synchronized修饰,方法级别是线程安全的
public synchronized E remove(int index)public synchronized boolean add(E e)public synchronized E set(int index, E element)public synchronized E get(int index)


































还没有评论,来说两句吧...