图论中的算法
图论的概念:图论是数学的一个分支,它是以图为研究对象,图论中的图是由若干个给定的点及连接两点的线所构成的图形,这种图形通常用来描述某些实体之间的某种特定的关系,用点代表实体,用连接两点之间的线表示两个实体之间具有某种关系。
图的分类:
- 无权无向图
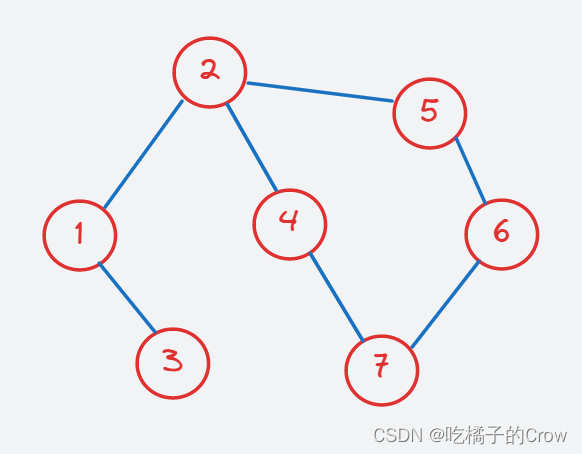
无向就是可以互相通向,没有进行方向的限制,就好比双向指向:

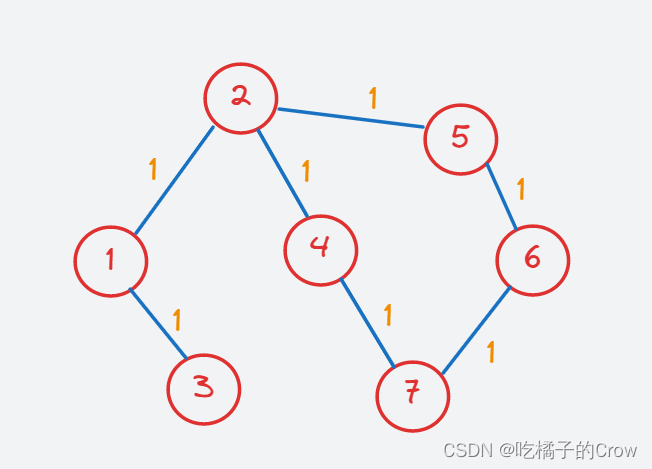
- 无权有向图

无权就是好比每条路线占的权重一致,没有区别,故我们可以把无权图假设为每个权重都是1的有权图:
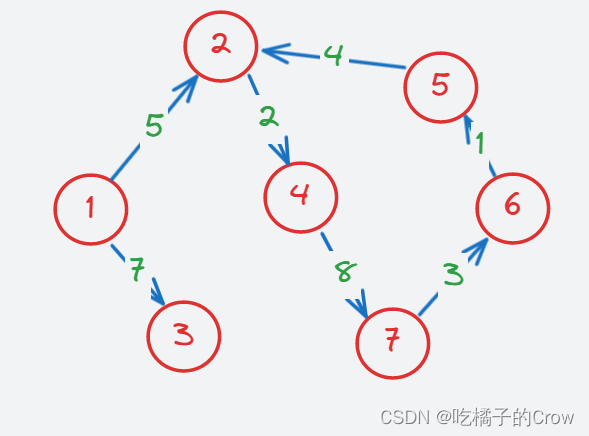
- 有权无向图

- 有权有向图
BFS和DFS
我们首先来了解什么是BFS?什么又是DFS?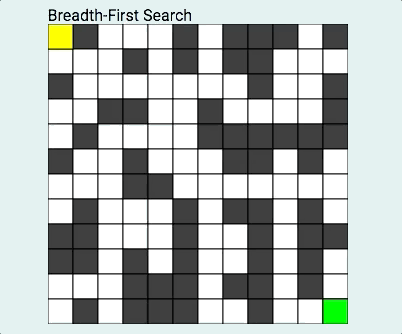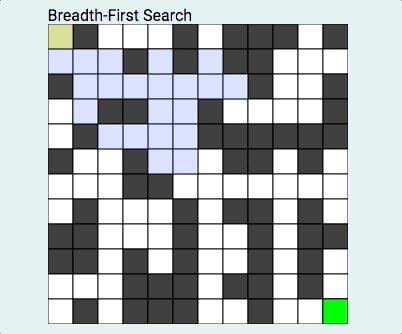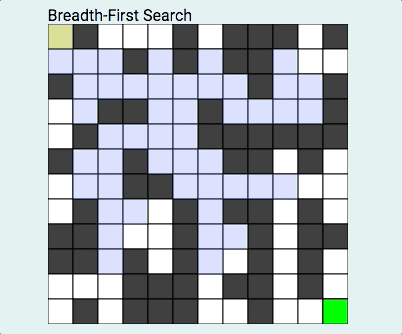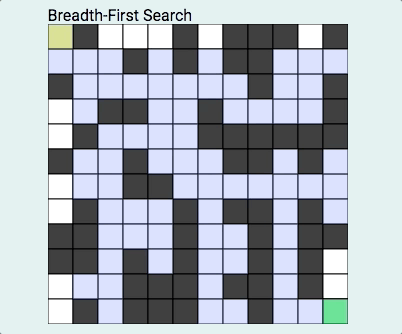
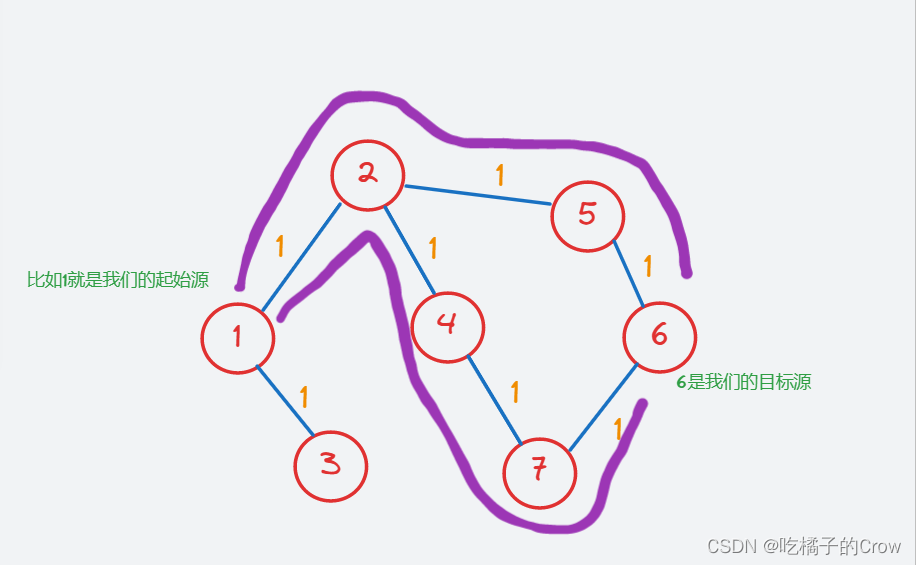
DFS俗称深度优先算法,有一种不撞南墙不回头的感觉,认准一条路,一致往下走,直到走不通位置,然后再重新返回再重复刚才的操作,直到找到目标节点为止。DFS关键点是递归以及回溯,一般用栈进行操作。在图中我们经常这样:
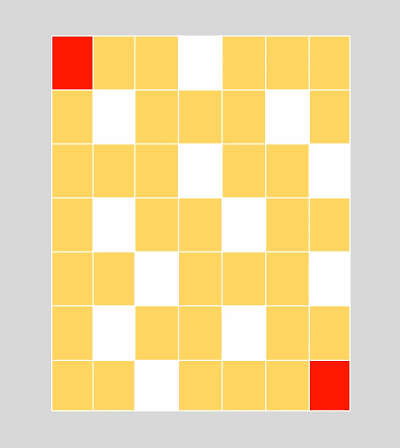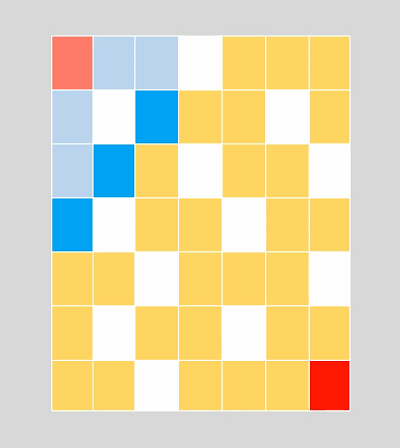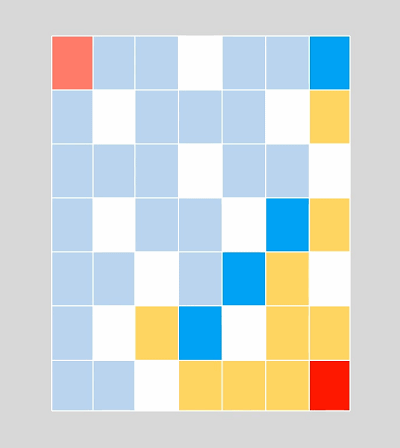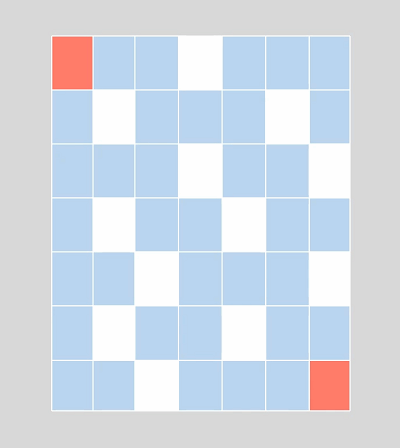
BFS俗称广度优先算法,相对于深度优先算法,如果把深度优先算法当成是一个莽夫的话,广度优先算法像是一个文人墨客,广度优先算法在面临一个路口时,把所有的路口记录下来,然后选择其中一个进入,然后再回退再进入另一个路口,直到找到目标节点为止。BFS关键点是状态的选取和标记,一般用队列去解决问题,在图中我们经常这样:

图的存储结构
- 邻接矩阵
概念:所谓邻接矩阵存储结构就是每个顶点用一个一维数组存储边的信息,这样所有点合起来就是用矩阵表示图中各顶点之间的邻接关系。所谓矩阵其实就是二维数组。对于有n个顶点的图 G=(V,E) 来说,我们可以用一个 n× n 的矩阵A来表示G中各顶点的相邻关系
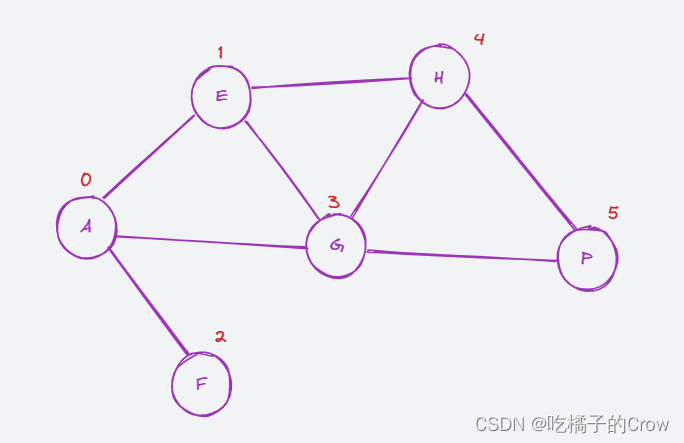
对应的邻接矩阵为:
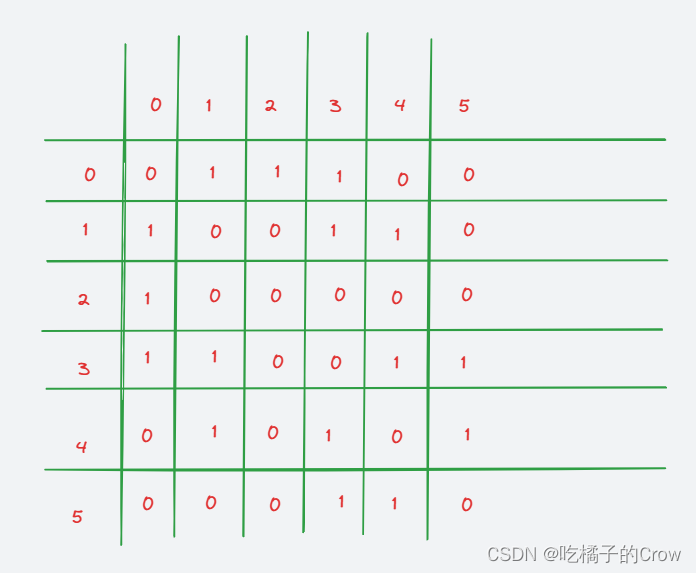
与对应点直接相连为1,不直接相连为0
构建邻接矩阵:
package graphtheory;import java.util.Arrays;/*** 图的表示--使用邻接矩阵*/public class Graph01 {private char[] V;//顶点上的值private Vertex[] vertexs;//顶点数组private int N;//邻接矩阵private int[][] adj;//图的构造函数public Graph01(char[] arr) {//{'A','E','F','G','H','P'}//拿到数组的长度int length = arr.length;this.N = length;V = new char[length];//arr元素赋值 到Vthis.V = Arrays.copyOf(arr, length);//构建图中的结点vertexs = new Vertex[length];for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {vertexs[i] = new Vertex(i,this.V[i]);//}this.adj = new int[length][length];}//打印邻接矩阵public void show() {System.out.print(" ");for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {System.out.format("%4c", this.V[i]);}System.out.println();for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {System.out.format("%4c",this.V[i]);for (int j = 0; j < this.N; j++) {System.out.format("%4s", this.adj[i][j] > 0?(this.adj[i][j]):"-");}System.out.println();}}/*** 创建顶点类*/private class Vertex {char v;//值int index;//索引public Vertex(int index, char c) {this.index = index;this.v = v;}}public static void main(String[] args) {char arr[] = {'A', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'P'};//构建graph01Graph01 graph01 = new Graph01(arr);//进行连接int[][] adjMatrix = graph01.adj;adjMatrix[0][1]=1;adjMatrix[0][2]=1;adjMatrix[0][3]=1;adjMatrix[1][0]=1;adjMatrix[1][3]=1;adjMatrix[1][4]=1;adjMatrix[2][0]=1;adjMatrix[3][0]=1;adjMatrix[3][1]=1;adjMatrix[3][4]=1;adjMatrix[3][5]=1;adjMatrix[4][1]=1;adjMatrix[4][3]=1;adjMatrix[4][5]=1;adjMatrix[5][3]=1;adjMatrix[5][4]=1;graph01.show();}}

- 邻接表
邻接表的概念:邻接表的思想是,对于图中的每一个顶点,用一个数组来记录这个点和哪些点相连。由于相邻的点会动态的添加,所以对于每个点,我们需要用List来记录。

对应的邻接表为:

package graphtheory;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.List;/*** 图的表示--使用邻接矩阵*/public class Graph02 {private char[] V;//顶点上的值private Vertex[] vertexs;//顶点数组private int N;//邻接矩阵private List<Integer>[] adj;//图的构造函数public Graph02(char[] arr) {//{'A','E','F','G','H','P'}//拿到数组的长度int length = arr.length;this.N = length;V = new char[length];//arr元素赋值 到Vthis.V = Arrays.copyOf(arr, length);//构建图中的结点vertexs = new Vertex[length];for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {vertexs[i] = new Vertex(i, this.V[i]);}this.adj = new List[length];for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {this.adj[i]=new ArrayList<>();}}//打印邻接矩阵public void show() {System.out.println(" ");for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {System.out.format("%-4c", this.V[i]);//拿到邻接表相邻结点的集合List<Integer> linkedList = this.adj[i];for (int j = 0; j < linkedList.size(); j++) {System.out.print(this.V[linkedList.get(j)] + "---->");}System.out.println();System.out.format("%-4d",vertexs[i].index);for (int j = 0; j < linkedList.size(); j++) {System.out.print(vertexs[linkedList.get(j)].index + "---->");}System.out.println();}}/*** 创建顶点类*/private class Vertex {char v;//值int index;//索引int weight;//权值public Vertex(int index, char c) {this.index = index;this.v = v;this.weight = weight;}public Vertex(int index) {}}public static void main(String[] args) {char arr[] = {'A', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'P'};//构建graph01Graph02 graph02 = new Graph02(arr);//邻接表List<Integer>[] adj = graph02.adj;adj[0].add(1);adj[0].add(2);adj[0].add(3);adj[1].add(0);adj[1].add(3);adj[1].add(4);adj[2].add(0);adj[3].add(0);adj[3].add(1);adj[3].add(4);adj[3].add(5);adj[4].add(1);adj[4].add(3);adj[4].add(5);adj[5].add(3);adj[5].add(4);graph02.show();}}

使用邻接表求出A—P的所有路径:
package graphtheory;import java.util.*;// 图的表示-- 使用邻接表public class Graph03 {private char[] V;// 顶点数组private Vertex[] vertexs;private int N;// 邻接表private List<Integer>[] adj;public Graph03(char[] arr) { // {'A','E','F','G','H','P'}int length = arr.length;this.N = length;this.V = Arrays.copyOf(arr, length);// 构建图中的结点vertexs = new Vertex[length];for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {vertexs[i] = new Vertex(0, this.V[i]);}this.adj = new List[length];for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {this.adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();}}// 打印邻接矩阵public void show() {for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {System.out.format("%-4c", this.V[i]);List<Integer> linkedList = this.adj[i];for (int j = 0; j < linkedList.size(); j++) {System.out.print(this.V[linkedList.get(j)] + "---->");}System.out.println();System.out.format("%-4c", this.V[i]);for (int j = 0; j < linkedList.size(); j++) {System.out.print(linkedList.get(j) + "---->");}System.out.println();}}public void bfs(int startIndex){boolean visited[] = new boolean[this.N];List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();// 使用队列Queue<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer,Integer>> queue = new LinkedList<>();// 将开始顶点入队queue.add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(startIndex,0));// 设置startIndex已经被访问visited[startIndex]=true;while(!queue.isEmpty()){AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer,Integer> pair = queue.poll();int key = pair.getKey(); //顶点的索引int val = pair.getValue();// 层if(result.size() == val){ArrayList list = new ArrayList();result.add(list);}List<Integer> levelList = result.get(val);levelList.add(key);// 找和key顶点直接相连的的索引List<Integer> list = this.adj[key];for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){if(!visited[list.get(i)]){queue.add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry(list.get(i),val+1));visited[list.get(i)]=true;}}}for(int i=0;i<result.size();i++){System.out.println("level:"+(i+1));for(int j=0;j<result.get(i).size();j++){System.out.format("%-4d",result.get(i).get(j));}System.out.println();}}public void dfs(int startIndex,int endIndex){//创建一个数组,用来记录是否已经被访问boolean visited[] = new boolean[this.N];// 标记开始结点已经被访问过LinkedList<Character> path = new LinkedList<>();dfs(startIndex,endIndex,visited,path);}// 递归向下去找private void dfs(int startIndex,int endIndex,boolean[] visited, LinkedList<Character> path){// 递归终止的条件if(startIndex == endIndex){path.offerLast(this.V[startIndex]);System.out.println(path);// 从路径的尾部删掉最后的顶点path.pollLast();return;}// 将当前顶点加到路径中去path.offer(this.V[startIndex]);// 标识startIndex已经被访问了visited[startIndex]=true;// 递归操作// 1、先找和startIndex直接连接的顶点有哪些List<Integer> list = this.adj[startIndex];// 2、处理每一个直接连接的顶点for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){if(!visited[list.get(i)]){dfs(list.get(i),endIndex,visited,path);}}visited[startIndex]=false; // 回溯path.pollLast();}private class Vertex {char v;int index;//权值int weight;public Vertex(int index, char v, int weight) {this.index = index;this.v = v;this.weight = weight;}public Vertex(int index, char v) {this(index, v, 1);}}public static void main(String[] args) {char arr[] = {'A', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'P' };Graph03 graph03 = new Graph03(arr);// 邻接表List<Integer>[] adj = graph03.adj;adj[0].add(1);adj[0].add(2);adj[0].add(3);adj[1].add(0);adj[1].add(3);adj[1].add(4);adj[2].add(0);adj[3].add(0);adj[3].add(1);adj[3].add(4);adj[3].add(5);adj[4].add(1);adj[4].add(3);adj[4].add(5);adj[5].add(3);adj[5].add(4);graph03.bfs(5);}}
迪杰斯特拉算法
概念:即先求出长度最短的一条最短路径,再参照它求出长度次短的一条最短路径,依次类推,直到从源点v 到其它各顶点的最短路径全部求出为止。

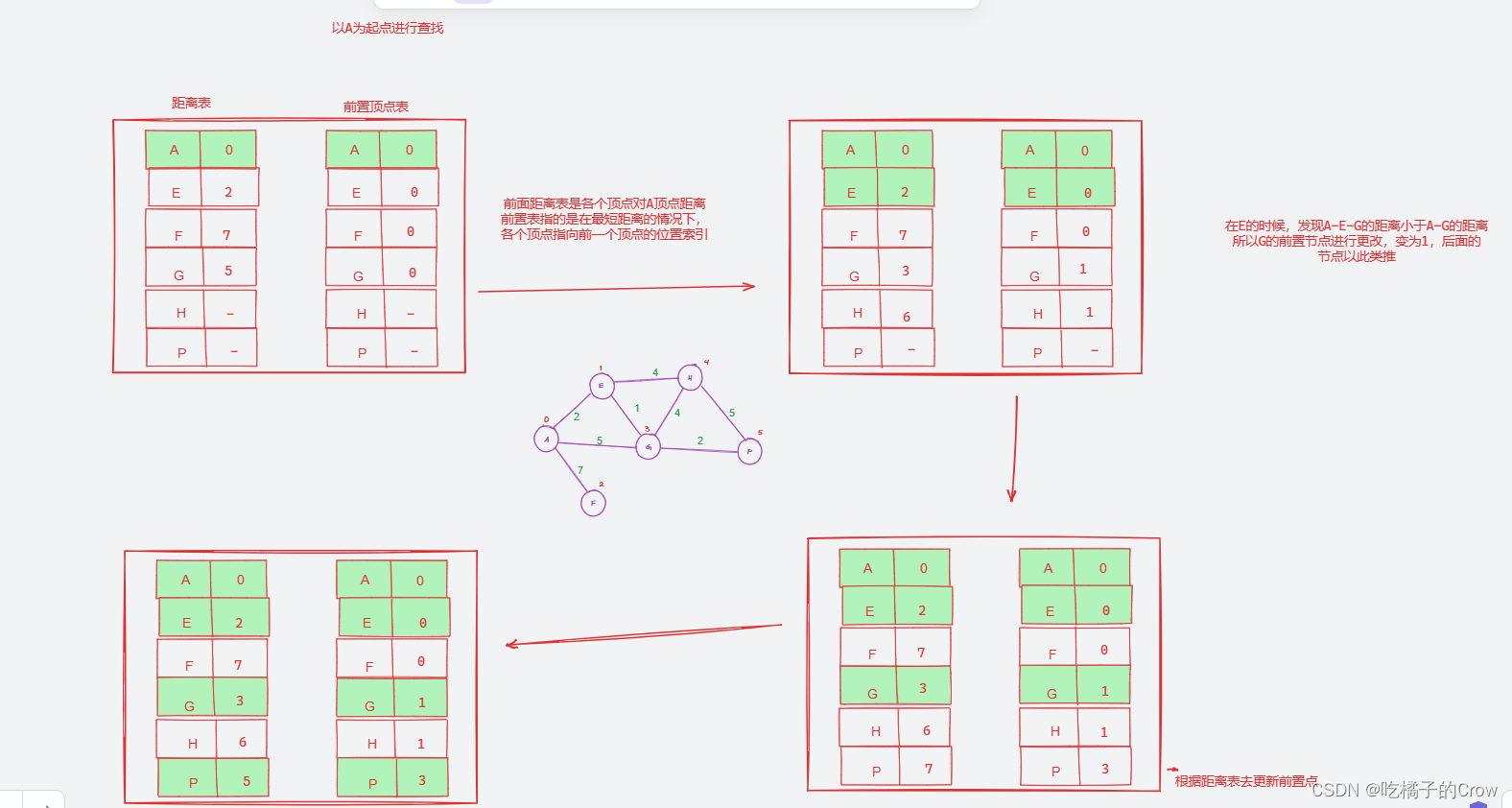
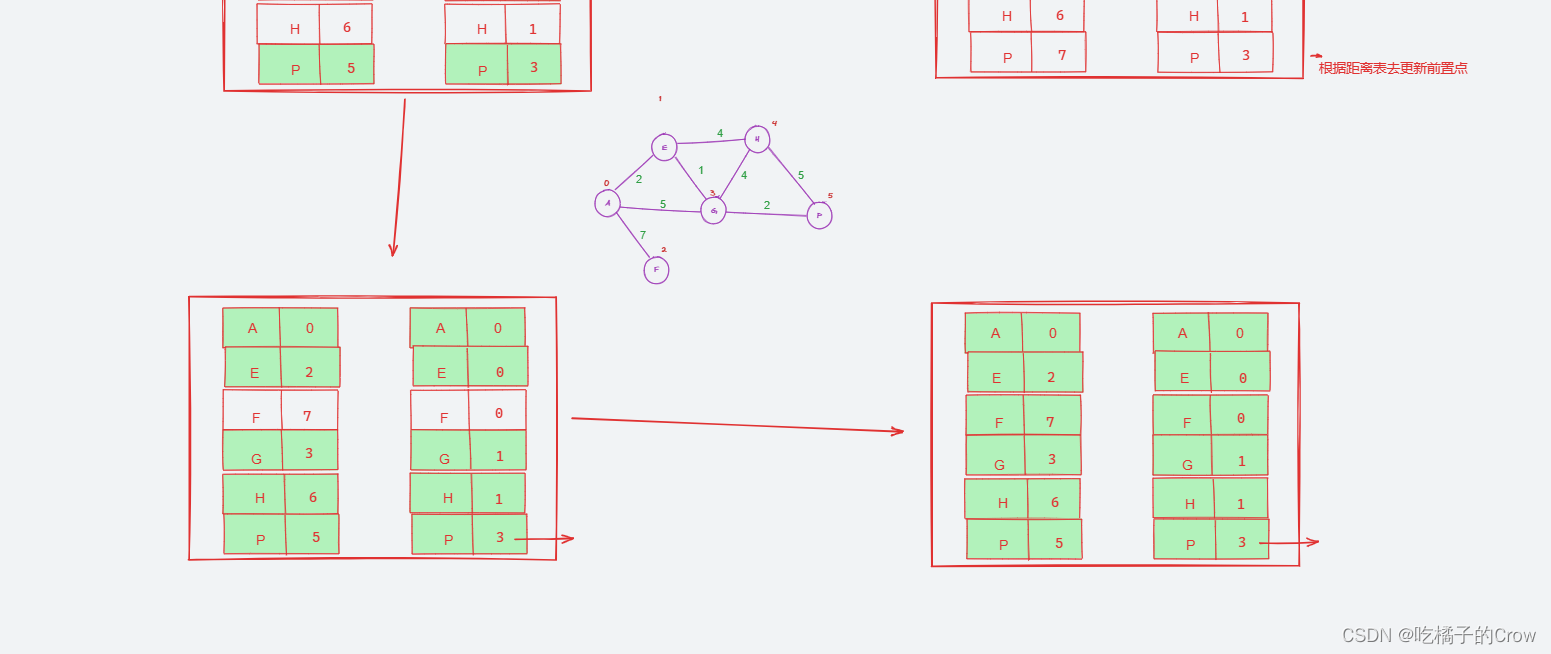
假设我们求A点到各点的最短距离
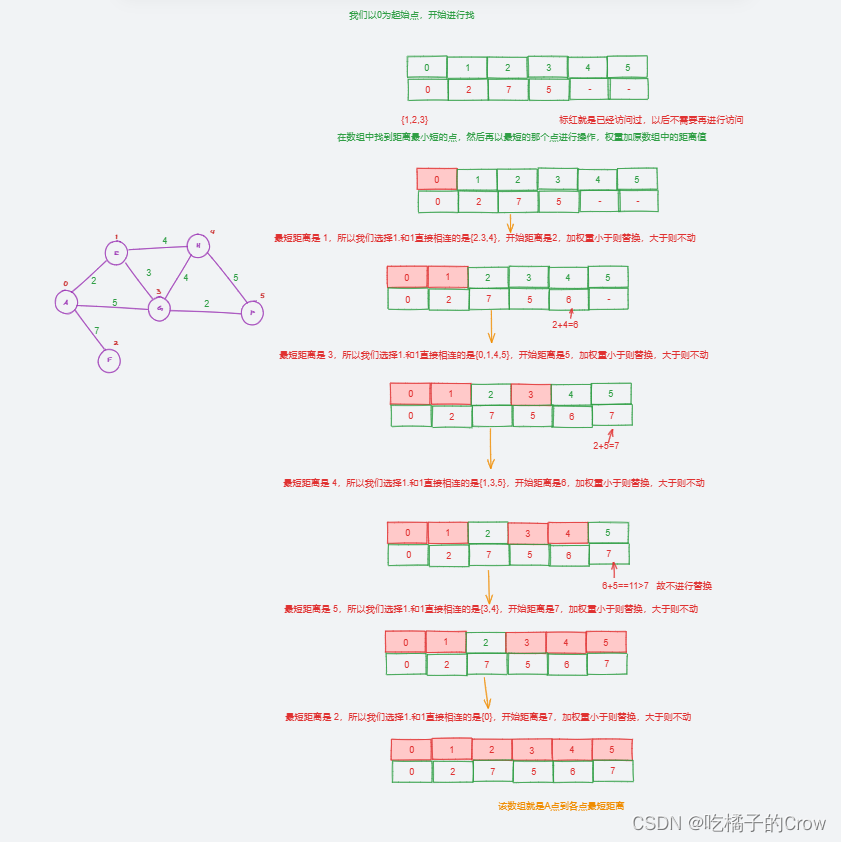 迪杰斯特拉算法过程(原理)
迪杰斯特拉算法过程(原理)
package graphtheory;import java.util.*;// 图的单源最最短路径-迪杰斯特拉算法(从一个顶点到图中各个顶点的最短距离)public class Graph04 {private char[] V;// 顶点数组private Vertex[] vertexs;private int N;// 邻接表private List<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>>[] adj; // key:顶点索引,val:权值public Graph04(char[] arr) { // {'A','E','F','G','H','P'}int length = arr.length;this.N = length;this.V = Arrays.copyOf(arr, length);// 构建图中的结点vertexs = new Vertex[length];for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {vertexs[i] = new Vertex(i, this.V[i]);}this.adj = new List[length];for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {this.adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();}}public int[] dijkstra(int sourceIndex) {// 1、创建距离表int[] dist = new int[this.N];Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);// 2、创建一个标识顶点是否被访问的数组boolean[] visited = new boolean[this.N];// 3、初始化距离表// 3-1dist[sourceIndex] = 0; // 自身到自身的距离visited[sourceIndex] = true;// 3-2、找和sourceIndex直接相连的顶点List<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>> list = this.adj[sourceIndex];for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer> vertex = list.get(i);int key = vertex.getKey();//顶点索引int val = vertex.getValue();//权值// 3-3 更新距离表dist[key] = val;}for (int k = 1; k < this.N; k++) {//4、在上述的最短路径dist[]中,从未被访问的顶点中选一条最短的路径长度int minDist = Integer.MAX_VALUE;int minDistIndex = -1;for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {if (!visited[i] && dist[i] != Integer.MAX_VALUE && dist[i] < minDist) {minDist = dist[i];minDistIndex = i;}}// 最最短的路径长度所在的顶点与其它顶点都没有相连if (minDistIndex == -1) {break;}//5、更新距离表()// 5-1 将最最短的路径长度所在的顶点设置成已访问visited[minDistIndex] = true;// 5-2 找到和最短路径长度所在顶点直接相连的顶点List<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>> list2 = this.adj[minDistIndex];// 5-3 minDist+权值与距离表中的数据进行比较for (int i = 0; i < list2.size(); i++) {AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer> vertex = list2.get(i);int key = vertex.getKey();//顶点索引int val = vertex.getValue();//权值int newVal = minDist + val;if (!visited[key] && newVal < dist[key]) {dist[key] = newVal;}}}return dist;}private class Vertex {char v;int index;public Vertex(int index, char v) {this.index = index;this.v = v;}}public static void main(String[] args) {char arr[] = {'A', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'P'};Graph04 graph04 = new Graph04(arr);// 邻接表List<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>>[] adj = graph04.adj;adj[0].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(1, 5));adj[0].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(2, 4));adj[0].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(5, 2));adj[1].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(0, 5));adj[1].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(5, 1));adj[1].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(4, 3));adj[2].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(0, 4));adj[3].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(4, 3));adj[3].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(5, 4));adj[4].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(1, 3));adj[4].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(5, 2));adj[4].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(3, 3));adj[5].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(0, 2));adj[5].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(1, 1));adj[5].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(4, 2));adj[5].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(3, 4));int[] dist = graph04.dijkstra(0);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dist));}}
怎么样才能求出我们距离最短的路径呢?
我们这里需要一个前置顶点表进行记录:
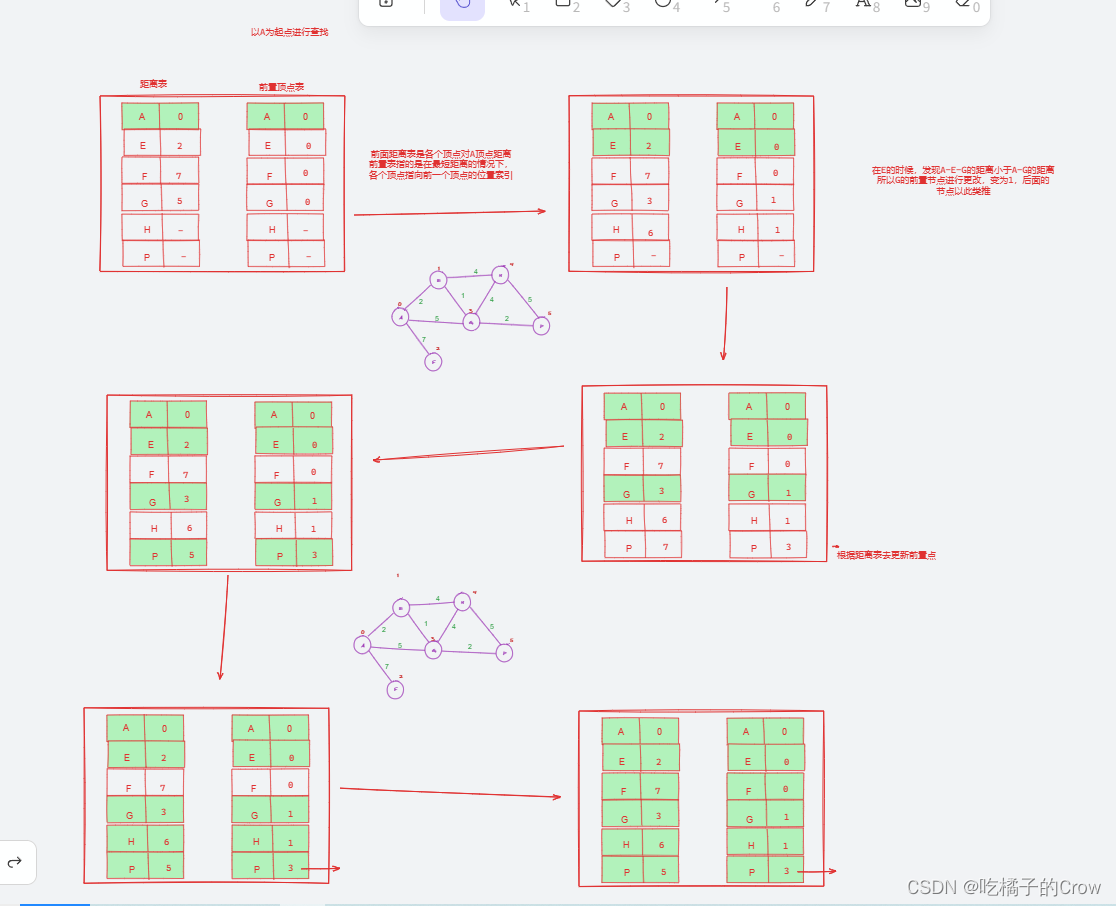
分图:
package graphtheory;import java.util.*;// 图的单源最最短路径-迪杰斯特拉算法(从一个顶点到图中各个顶点的最短距离)public class Graph04 {private char[] V;// 顶点数组private Vertex[] vertexs;private int N;// 邻接表private List<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>>[] adj; // key:顶点索引,val:权值// 1、创建距离表private int[] dist;private int[] pre;public Graph04(char[] arr) { // {'A','E','F','G','H','P'}int length = arr.length;this.N = length;this.V = Arrays.copyOf(arr, length);this.dist = new int[this.N];Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);// 创建最短路径的前驱顶点表(为了表示最短路径)this.pre=new int[this.N];Arrays.fill(this.pre,-1);// 构建图中的结点vertexs = new Vertex[length];for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {vertexs[i] = new Vertex(0, this.V[i]);}this.adj = new List[length];for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {this.adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();}}public void dijkstra(int sourceIndex) {// 2、创建一个标识顶点是否被访问的数组boolean[] visited = new boolean[this.N];// 3、初始化距离表// 3-1dist[sourceIndex] = 0; // 自身到自身的距离visited[sourceIndex] = true;// 3-2、找和sourceIndex直接相连的顶点List<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>> list = this.adj[sourceIndex];for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer> vertex = list.get(i);int key = vertex.getKey();//顶点索引int val = vertex.getValue();//权值// 3-3 更新距离表this.dist[key] = val;// 更新前驱顶点表this.pre[key]=sourceIndex;}for (int k = 1; k < this.N; k++) {//4、在上述的最短路径dist[]中,从未被访问的顶点中选一条最短的路径长度int minDist = Integer.MAX_VALUE;int minDistIndex = -1;for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {if (!visited[i] && dist[i] != Integer.MAX_VALUE && dist[i] < minDist) {minDist = dist[i];minDistIndex = i;}}// 最最短的路径长度所在的顶点与其它顶点都没有相连if (minDistIndex == -1) {break;}//5、更新距离表()// 5-1 将最最短的路径长度所在的顶点设置成已访问visited[minDistIndex] = true;// 5-2 找到和最短路径长度所在顶点直接相连的顶点List<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>> list2 = this.adj[minDistIndex];// 5-3 minDist+权值与距离表中的数据进行比较for (int i = 0; i < list2.size(); i++) {AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer> vertex = list2.get(i);int key = vertex.getKey();//顶点索引int val = vertex.getValue();//权值int newVal = minDist + val;if (!visited[key] && newVal < dist[key]) {this.dist[key] = newVal;// 更新前驱顶点表this.pre[key] = minDistIndex;}}}}public void showDist(){System.out.println(Arrays.toString(this.dist));}public void getMinDist(int sourceIndex ,int targetIndex){Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();stack.push(targetIndex);int preIndex = this.pre[targetIndex];while(preIndex !=-1 && preIndex!=sourceIndex){stack.push(preIndex);preIndex = this.pre[preIndex];}// 将 sourceIndex放入栈if(preIndex !=-1){stack.push(sourceIndex);}// 出栈StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();while(!stack.isEmpty()){res.append(this.V[stack.pop()]+"-->");}System.out.println(res);}private class Vertex {char v;int index;public Vertex(int index, char v) {this.index = index;this.v = v;}}public static void main(String[] args) {char arr[] = {'A', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'P'};Graph04 graph04 = new Graph04(arr);// 邻接表List<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>>[] adj = graph04.adj;adj[0].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(1, 5));adj[0].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(2, 4));adj[0].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(5, 2));adj[1].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(0, 5));adj[1].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(5, 1));adj[1].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(4, 3));adj[2].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(0, 4));adj[3].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(4, 3));adj[3].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(5, 4));adj[4].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(1, 3));adj[4].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(5, 2));adj[4].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(3, 3));adj[5].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(0, 2));adj[5].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(1, 1));adj[5].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(4, 2));adj[5].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(3, 4));int sourceIndex = 5;graph04.dijkstra(sourceIndex);graph04.showDist();int targetIndex = 3;// 求从源到目标顶点的最短路径graph04.getMinDist(sourceIndex,targetIndex);}}
弗洛伊德算法
具体思想:邻接矩阵dist储存路径,同时最终状态代表点点的最短路径。如果没有直接相连的两点那么默认为一个很大的值,而自身到自身的长度为0.

A和B不认识,所以A找不到B,但是这时候A的朋友D来了,说他可以介绍B给A认识,所以A就通过D找到了B
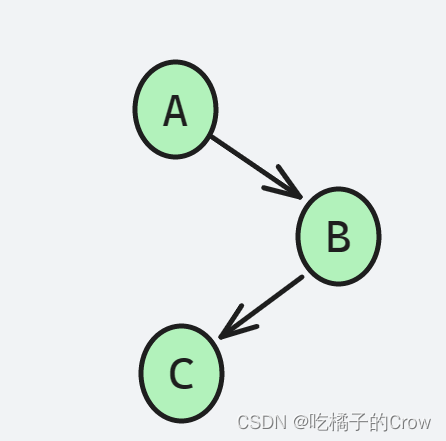
弗洛伊德算法就是用了这样的思想
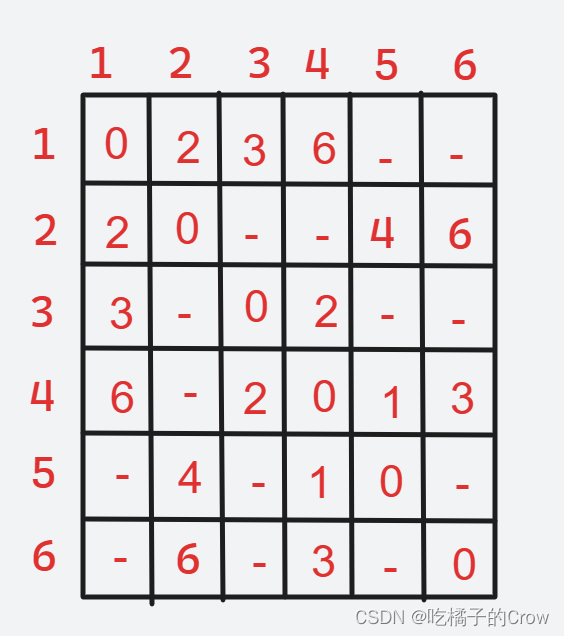
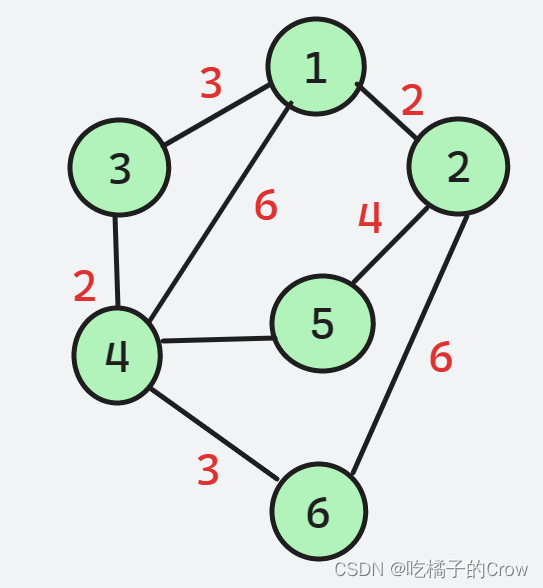
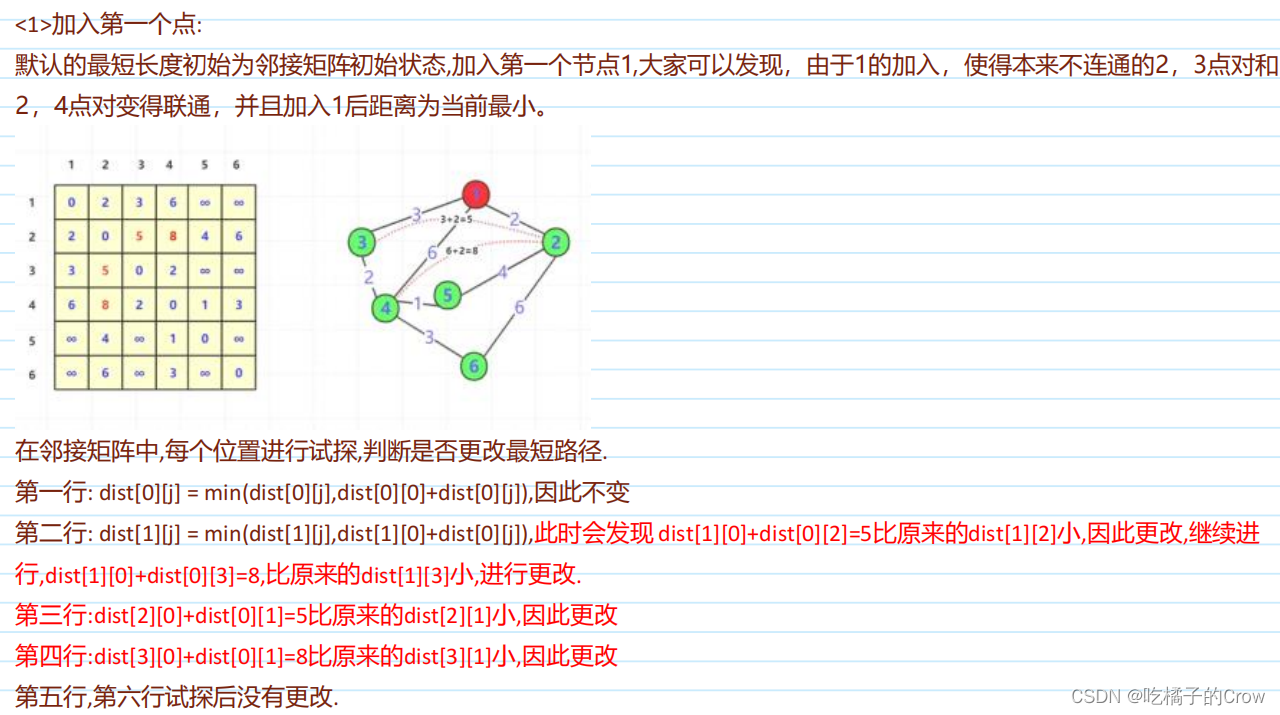
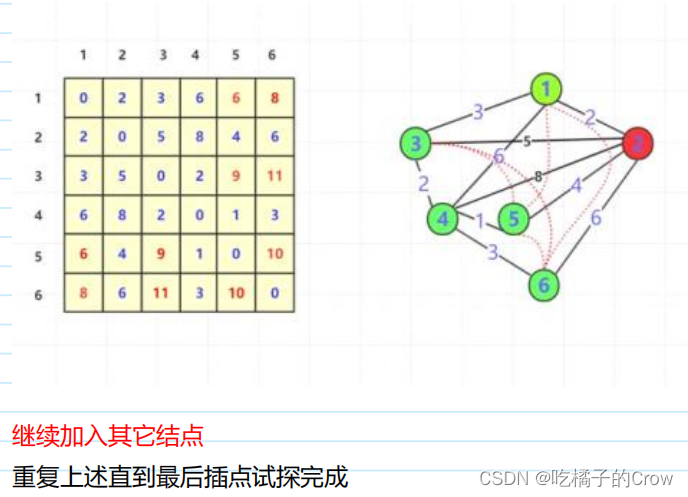
- 把第1个到第n个点依次加入图中。每个点加入进行试探是否有路径长度被更改。
- 而上述试探具体方法为遍历图中每一个点(i,j双重循环),判断每一个点对距离,是否因为加入的点而发生最小距离变化。如果发生改变,那么两点(i,j)距离就更改。
- 转移方程::dp[i][j]=min(dp[i][j],dp[i][k]+dp[k][j])

package graphtheory;import java.util.*;// 图的多源最最短路径-弗洛伊德算法Floyd(从任意顶点到图中各个顶点的最短距离)public class Graph05 {private char[] V;// 顶点数组private Vertex[] vertexs;private int N;// 邻接表private List<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>>[] adj; // key:顶点索引,val:权值private int[][] dists;public Graph05(char[] arr) { // {'A','E','F','G','H','P'}int length = arr.length;this.N = length;this.V = Arrays.copyOf(arr, length);// 构建图中的结点vertexs = new Vertex[length];for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {vertexs[i] = new Vertex(0, this.V[i]);}this.adj = new List[length];for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {this.adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();}this.dists = new int[this.N][this.N];for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < this.N; j++) {if (i == j) {this.dists[i][j] = 0;} else {this.dists[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;}}}}private class Vertex {char v;int index;public Vertex(int index, char v) {this.index = index;this.v = v;}}public void floyd() {// 对dists进一步初始化for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {List<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>> list = this.adj[i];for (int j = 0; j < list.size(); j++) {AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer> pair = list.get(j);int key = pair.getKey();int val = pair.getValue();this.dists[i][key] = val;}}// 将每个顶点加到二维数组中(是给每个二维数组中的每个元素都加) 相当于矩阵,给每个元素进行相同的操作for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) { // 表示的添加顶点的索引for (int m = 0; m < this.N; m++) {//同行不用进行操作if (m == i) {continue;}for (int n = 0; n < this.N; n++) {//距离无穷大也不用进行操作if (this.dists[m][i] != Integer.MAX_VALUE && this.dists[i][n] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {this.dists[m][n] = Math.min(this.dists[m][n], this.dists[m][i] + this.dists[i][n]);}}}}show();}private void show() {System.out.format("%-4s", " ");for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {System.out.format("%-4s", this.V[i]);}System.out.println();for (int i = 0; i < this.N; i++) {System.out.format("%-4s", this.V[i]);for (int j = 0; j < this.N; j++) {System.out.format("%-4s", this.dists[i][j] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "-" : this.dists[i][j] + "");}System.out.println();}}public static void main(String[] args) {char arr[] = {'A', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'P'};Graph05 graph05 = new Graph05(arr);// 邻接表List<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>>[] adj = graph05.adj;adj[0].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(1, 5));adj[0].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(2, 4));adj[0].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(5, 2));adj[1].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(0, 5));adj[1].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(5, 1));adj[1].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(4, 3));adj[2].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(0, 4));adj[3].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(4, 3));adj[3].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(5, 4));adj[4].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(1, 3));adj[4].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(5, 2));adj[4].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(3, 3));adj[5].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(0, 2));adj[5].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(1, 1));adj[5].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(4, 2));adj[5].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(3, 4));graph05.floyd();int sourceIndex = 1;int targetIndex = 3;}}





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...