MyBatis-3-MyBatis的sql映射文件
目录
SQL 映射文件有很少的几个顶级元素(按照它们应该被定义的顺序):
1:insert, update 和 delete
1.1获取自增主键的值
1.2:获取非自增主键的值
2:参数传递—-方法参数向sql映射语句映射
2.1:单个参数
2.2:多个参数
2.3:用@param指定参数(推荐)
2.4:传入pojo(javabean)
2.5:传入map
2.6:传入混合参数
3:参数处理—-设定参数的类型和$/#取值
1:参数也可以指定一个特殊的数据类型
2:#{属性名}和${属性名}的区别
4: 查询返回集合list
5: 查询返回map
5.1:查询返回一个map
5.2:查询返回多个map
6:resultMap—-自定义封装结果集
6.1:mybait封装结果集时会按照列名和属性名一一对应,如果对应不上就为null;
6.2:自定义resultMap封装结果集
6.3:封装复杂类型的对象(即对象里包含对象);
6.3.1:运用级联属性封装
6.3.2:运用association标签定义对象的封装规则
6.4:查询对象中的封装集合-Collection
7:分步查询和延迟加载(不推荐)
7.1:分部查询
7.1.1:association-分段查询
7.1.2:Collection—分段查询
7.2:延迟加载
8:动态sql
8.1:if
8.2:where
8.3:trim标签
8.4:foreach
8.5:choose分支选择
8.6:set标签动态修改
8.7:mybatis的ognl表达式以及_parameter参数和_databaseId参数
8.8:sql标签,可重用的标签
SQL 映射文件有很少的几个顶级元素(按照它们应该被定义的顺序):
- cache – 给定命名空间的缓存配置。
- cache-ref – 其他命名空间缓存配置的引用。
- resultMap – 是最复杂也是最强大的元素,用来描述如何从数据库结果集中来加载对象。
- parameterMap – 已废弃!老式风格的参数映射。内联参数是首选,这个元素可能在将来被移除,这里不会记录。
- sql – 可被其他语句引用的可重用语句块。
- insert – 映射插入语句
- update – 映射更新语句
- delete – 映射删除语句
- select – 映射查询语句
1:insert, update 和 delete
| id | 命名空间中的唯一标识符,可被用来代表这条语句。 |
| parameterType | 将要传入语句的参数的完全限定类名或别名。这个属性是可选的,因为 MyBatis 可以通过 TypeHandler 推断出具体传入语句的参数,默认值为 unset。 |
| parameterMap | 这是引用外部 parameterMap 的已经被废弃的方法。使用内联参数映射和 parameterType 属性。 |
| flushCache | 将其设置为 true,任何时候只要语句被调用,都会导致本地缓存和二级缓存都会被清空,默认值:true(对应插入、更新和删除语句)。 |
| timeout | 这个设置是在抛出异常之前,驱动程序等待数据库返回请求结果的秒数。默认值为 unset(依赖驱动)。 |
| statementType | STATEMENT,PREPARED 或 CALLABLE 的一个。这会让 MyBatis 分别使用 Statement,PreparedStatement 或 CallableStatement,默认值:PREPARED。对应原生jdbc的statement;callable为调用存储过程的; |
| useGeneratedKeys | (仅对 insert 和 update 有用)这会令 MyBatis 使用 JDBC 的 getGeneratedKeys 方法来取出由数据库内部生成的主键(比如:像 MySQL 和 SQL Server 这样的关系数据库管理系统的自动递增字段),默认值:false。 |
| keyProperty | (仅对 insert 和 update 有用)唯一标记一个属性,MyBatis 会通过 getGeneratedKeys 的返回值或者通过 insert 语句的 selectKey 子元素设置它的键值,默认:unset。如果希望得到多个生成的列,也可以是逗号分隔的属性名称列表。 |
| keyColumn | (仅对 insert 和 update 有用)通过生成的键值设置表中的列名,这个设置仅在某些数据库(像 PostgreSQL)是必须的,当主键列不是表中的第一列的时候需要设置。如果希望得到多个生成的列,也可以是逗号分隔的属性名称列表。 |
| databaseId | 如果配置了 databaseIdProvider,MyBatis 会加载所有的不带 databaseId 或匹配当前 databaseId 的语句;如果带或者不带的语句都有,则不带的会被忽略。 |
1.1获取自增主键的值
1:设置映射文件
<!--让mybatis自动的将自增的id赋值给employee的id属性useGeneratedKeys="true" 调用的是原生jdbc的获取自增主键的方法keyColumn,将自增主键赋值给哪个字段--><insert id="insertEmployee" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">insert into t_employee(name,email) VALUES(#{name},#{email})</insert>
2:测试
/*** 新增sql;结束后必须提交*/@Testpublic void test02() {//获取和数据库的一次会话;相当于getConnection();SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();try {//使用SqlSession操作数据库,获取到dao接口的实现EmployeeDao mapper = session.getMapper(EmployeeDao.class);//调用方法得出结果Employee abc = new Employee("abc", "aa@qq.com");Integer i = mapper.insertEmployee(abc);System.out.println("--->"+i);System.out.println("--->"+abc.getId());session.commit();} finally {//关闭连接session.close();}}
1.2:获取非自增主键的值
• 而对于不支持自增型主键的数据库(例如 Oracle ),则可以使用 selectKey 子元素: selectKey 元素将会首先运行 , id 会被设置 , 然后插入语句会被调用
<!--非自增主键--><insert id="insertEmployee2" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"><selectKey order="BEFORE" resultType="int" keyProperty="id">select max(id)+1 from t_employee</selectKey>insert into t_employee(name,email) VALUES(#{name},#{email})</insert>
selectKey标签
| keyProperty | selectKey 语句结果应该被设置的目标属性。如果希望得到多个生成的列,也可以是逗号分隔的属性名称列表。 |
| keyColumn | 匹配属性的返回结果集中的列名称。如果希望得到多个生成的列,也可以是逗号分隔的属性名称列表。 |
| resultType | 结果的类型。MyBatis 通常可以推算出来,但是为了更加确定写上也不会有什么问题。MyBatis 允许任何简单类型用作主键的类型,包括字符串。如果希望作用于多个生成的列,则可以使用一个包含期望属性的 Object 或一个 Map。 |
| order | 这可以被设置为 BEFORE 或 AFTER。如果设置为 BEFORE,那么它会首先选择主键,设置 keyProperty 然后执行插入语句。如果设置为 AFTER,那么先执行插入语句,然后是 selectKey 元素 - 这和像 Oracle 的数据库相似,在插入语句内部可能有嵌入索引调用。 |
| statementType | 与前面相同,MyBatis 支持 STATEMENT,PREPARED 和 CALLABLE 语句的映射类型,分别代表 PreparedStatement 和 CallableStatement 类型。 |
2:参数传递—-方法参数向sql映射语句映射
2.1:单个参数
可以接受基本类型,对象类型,集合类型的值。这种情况 MyBatis 可直接使用这个参数,不需要经过任何处理 。
方法:public Employee getEmployee(Integer id);映射的sql:
<select id="getEmployee" resultType="com.wkl.bean.Employee">select * from t_employee where id =#{id}</select>甚至#{haha}都能取到
2.2:多个参数
– 任意多个参数,都会被MyBatis重新包装成一个Map 传入。 Map 的 key 是 param1 , param2 , … ,值就是参数的值 。
这时候#{参数名}就无效了;可以用#{param1}来获取参数,但是注意顺序不能乱
方法:public Employee getEmployee2(Integer id,String name);sql映射:
<select id="getEmployee2" resultType="com.wkl.bean.Employee">select * from t_employee where id =#{param1} and name = #{param2}</select>
2.3:用@param指定参数(推荐)
– 为参数使用 @Param 起一个名字, MyBatis 就会将这些参数封装进 map 中, key 就是我们自己指定的 名字
方法:public Employee getEmployee2(@Param("id") Integer id, @Param("name") String name);sql映射文件:
<select id="getEmployee2" resultType="com.wkl.bean.Employee">select * from t_employee where id =#{id} and name = #{name}</select>
2.4:传入pojo(javabean)
– 当这些参数属于我们业务 POJO 时,我们直接传递 POJO,sql取值就是#{pojo的参数名}
方法名:
public Employee getEmployee3(Employee ee);sql映射:
<select id="getEmployee3" resultType="com.wkl.bean.Employee">select * from t_employee where id =#{id} and name = #{name}</select>
2.5:传入map
– 我们也可以封装多个参数为 map ,直接传递;这样取值的时候就是#{我们自定义的key}
2.6:传入混合参数
public Employee getEmployee4(@Param("id")Integer id,String name, Employee ee);Integer id —->#{id}
name ——>#{param2}
Employee ee (取这里面的name)——>#{param3.name}
3:参数处理—-设定参数的类型和$/#取值
1:参数也可以指定一个特殊的数据类型
<select id="getEmployee" resultType="com.wkl.bean.Employee">select * from t_employee where id =#{id,jdbcType=numeric}</select>
• 参数位置支持的属性
– javaType 、 jdbcType 、 mode 、 numericScale 、
resultMap、typeHandler、jdbcTypeName、expression
•实际上**通常被设置的是**: 可能**为空的列名指定 jdbcType**
•实际上**通常被设置的是**: 可能**为空的列名指定 jdbcType**
2:#{属性名}和${属性名}的区别
1:#{属性名}支持参数预编译,参数位置用?代替;参数都数预编译设置进去的,安全,不会有sql注入
<select id="getEmployee3" resultType="com.wkl.bean.Employee">select * from t_employee where id =#{id} and name = #{name}</select>

2:${属性名}不支持参数预编译,而是直接和sql’进行拼串;不安全;但是在表名;字段名等不支持参数预编译的地方会很方便
<select id="getEmployee2" resultType="com.wkl.bean.Employee">select * from ${tablename} where id =#{id} and name = #{name}</select>

4: 查询返回集合list
方法:
public List<Employee> getEmployeeALL();
sql映射:
<!--public List<Employee> getEmployeeALL();--><!--resultType,如果返回集合;里面写的是返回集合的元素的类型--><select id="getEmployeeALL" resultType="com.wkl.bean.Employee">select * from t_employee</select>
5: 查询返回map
5.1:查询返回一个map
<!--public Map<String,Object> getEmployeeResultMap(Integer id);--><!--resultType直接写map就行;到时候封装的时候就会将数据库字段名作为key;数据库字段值作为value--><select id="getEmployeeResultMap" resultType="map">select * from t_employee where id = #{id}</select>

5.2:查询返回多个map
方法:
/*必须指定那个字段作为主键;否则mybatis无法去对应*/@MapKey("id")public Map<Integer,Employee> getEmployeeAllResultMap();
sql映射文件:
<!--public Map<Integer,Employee> getEmployeeAllResultMap();--><select id="getEmployeeAllResultMap" resultType="com.wkl.bean.Employee">select * from t_employee</select>

6:resultMap—-自定义封装结果集
6.1:mybait封装结果集时会按照列名和属性名一一对应,如果对应不上就为null;
表:
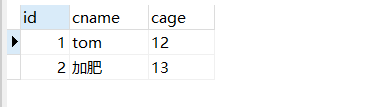
javabean
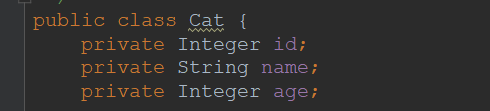
sql映射文件:
<!--public Cat getCat(Integer id);--><select id="getCat" resultType="com.wkl.bean.Cat">select * from t_cat where id = #{id}</select>
结果:

6.2:自定义resultMap封装结果集
sql映射:
<!--public Cat getCat(Integer id);--><!--想要使用自定义的结果集;那么就将resultType换成resultMap--><select id="getCat" resultMap="mycat">select * from t_cat where id = #{id}</select><!--id:唯一标识type:指定为那个javabean封装结果集,全类名--><resultMap id="mycat" type="com.wkl.bean.Cat"><!--指定主键的对应规则column="id" :指定那一列是主键列property="id" :指定cat的那个属性封装id的这一列数据--><id property="id" column="id"></id><!--普通列;字段规则一样--><result property="name" column="cname"></result><result property="age" column="cage"></result></resultMap>
结果:
6.3:封装复杂类型的对象(即对象里包含对象);
6.3.1:运用级联属性封装
javabean;


sql映射文件:

结果:

6.3.2:运用association标签定义对象的封装规则
sql映射文件
<!--public Cat getCat1(Integer id);--><select id="getCat1" resultMap="mycat2">select c.id as cid,c.cname,c.cage,c.person,e.id as eid,e.name,e.email from t_cat cLEFT JOIN t_employee e on c.person = e.idwhere c.id = #{id}</select><resultMap id="mycat2" type="com.wkl.bean.Cat"><id property="id" column="cid"></id><result property="name" column="cname"></result><result property="age" column="cage"></result><!--接下来的属性是一个对象,自定义这个对象的封装规则,使用association表示联合一个对象javaType表示指定这个属性的类型--><association property="employee" javaType="com.wkl.bean.Employee"><id property="id" column="eid"></id><result property="name" column="name"></result><result property="email" column="email"></result></association></resultMap>
6.4:查询对象中的封装集合-Collection
表关系:一个人有多个猫

javabean:

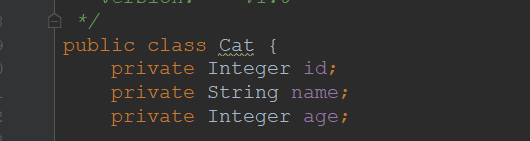
sql映射文件:
<!--public Employee getEmployeeCats(Integer id);--><select id="getEmployeeCats" resultMap="mycat3">select c.id as cid,c.cname,c.cage,c.person,e.id as eid,e.name,e.email from t_cat cLEFT JOIN t_employee e on c.person = e.idwhere e.id = #{id}</select><resultMap id="mycat3" type="com.wkl.bean.Employee"><id property="id" column="eid"></id><result property="name" column="name"></result><result property="email" column="email"></result><!--collection定义集合元素的封装property:指定那个属性是几个元素ofType:指定几个元素里面的封装规则--><collection property="cats" ofType="com.wkl.bean.Cat"><id property="id" column="cid"></id><result property="name" column="cname"></result><result property="age" column="cage"></result></collection></resultMap>
结果:

7:分步查询和延迟加载(不推荐)
7.1:分部查询
目的:就是将复杂的链接查询变成多个简单的查询;然后用前一个的结果集给第二个查询做参数
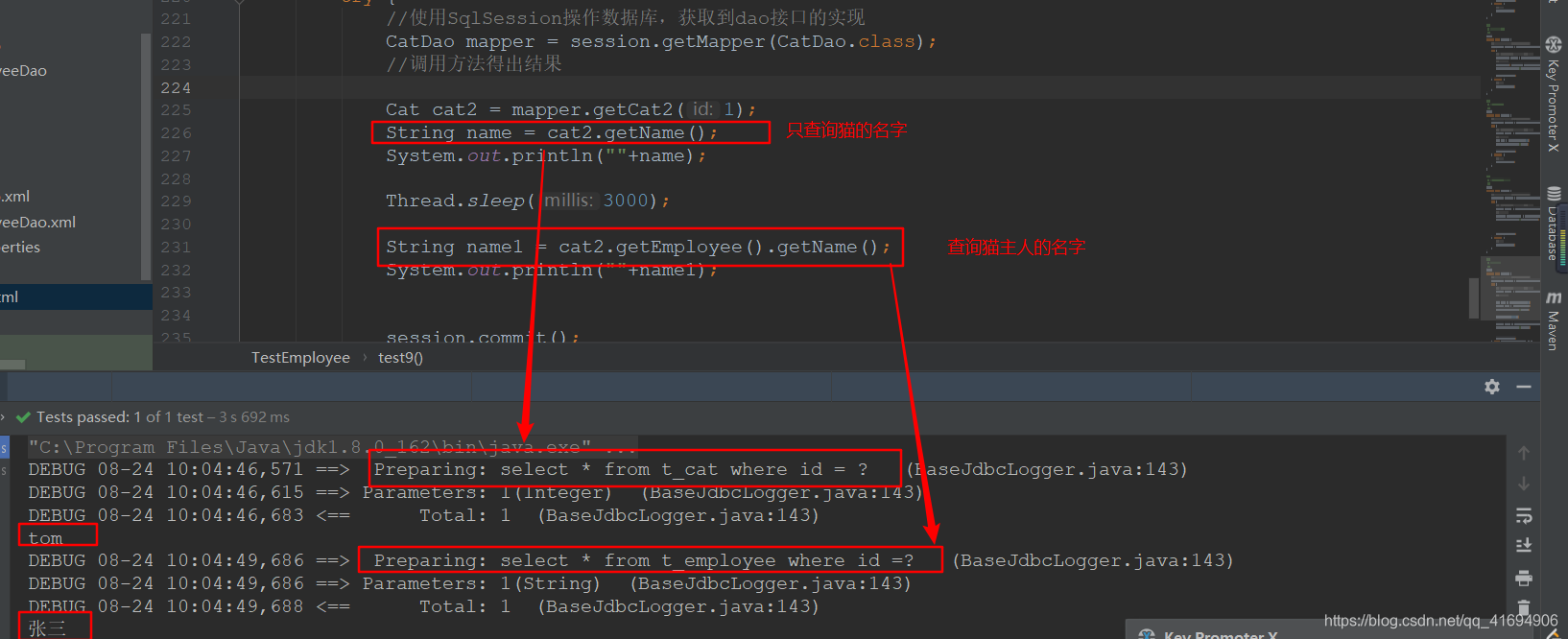
7.1.1:association-**分段查询**
说明:一个猫有一个主人;
sql映射:
这是另一个方法;专门利用人员id查询人员信息
<!--public Employee getEmployee(Integer id);--><select id="getEmployee" resultType="com.wkl.bean.Employee">select * from t_employee where id =#{id}</select>查询猫的信息;因为猫拥有一个主人,所以在association中利用分部查询进行主人的信息;<!--public Cat getCat2(Integer id);--><select id="getCat2" resultMap="myassciation">select * from t_cat where id = #{id}</select><resultMap id="myassciation" type="com.wkl.bean.Cat"><id property="id" column="id"></id><result property="name" column="cname"></result><result property="age" column="cage"></result><!--告诉mybatis自己去查主人的信息select = "执行一个查询猫主人的唯一标识,mybatis将自动调用指定的sql将employee查出来";com.wkl.dao.EmployeeDao.getEmployee:需要传入人员idcolumn:指定那一列的数据值传过去--><association property="employee" select="com.wkl.dao.EmployeeDao.getEmployee"column="person"></association></resultMap>
结果;

7.1.2:Collection—分段查询
<!--public Employee getEmployee5(Integer id);--><select id="getEmployee5" resultMap="hahah">select * from t_employee where id = #{id}</select><resultMap id="hahah" type="com.wkl.dao.EmployeeDao"><id property="id" column="name"></id><result property="name" column="name"></result><result property="email" column="email"></result><!--通过主人查猫--><collection property="cats" select="com.wkl.dao.CatDao.getCat"column="id"></collection></resultMap>• 分步查询 的时候通过 column 指定,将对应的列的数据传递过去,我们有时需要传递多列数据 。
• 使用column= {key1=column1,key2=column2…} 的形式
7.2:延迟加载
当猫对象有一个属性是Employee类;那么如果只需要查询猫名字的时候,在分步查询时不需要mybatis将猫主人信息查出来;这就是延迟加载
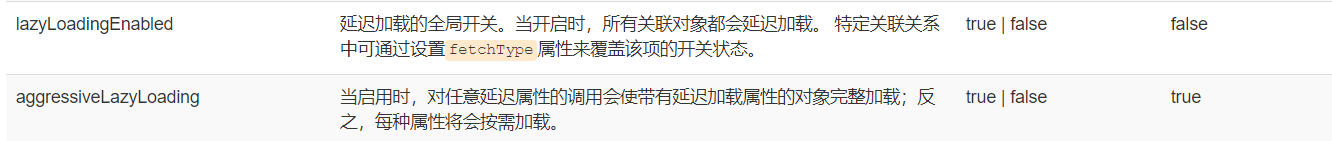
<!--重要的配置--><settings><setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/><setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/><setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/></settings>

8:动态sql
MyBatis 的强大特性之一便是它的动态 SQL。如果你有使用 JDBC 或其他类似框架的经验,你就能体会到根据不同条件拼接 SQL 语句有多么痛苦。拼接的时候要确保不能忘了必要的空格,还要注意省掉列名列表最后的逗号。利用动态 SQL 这一特性可以彻底摆脱这种痛苦。
通常使用动态 SQL 不可能是独立的一部分,MyBatis 当然使用一种强大的动态 SQL 语言来改进这种情形,这种语言可以被用在任意的 SQL 映射语句中。
- if
- choose (when, otherwise)
- trim (where, set)
- foreach
8.1:if
<!--根据传入的对象,加入employee中某属性有值,就按照该属性取值--><!--public Employee getEmployeeByCondition(Employee ee);--><select id="getEmployeeByCondition" resultMap="employeeMap">select * from t_employee where 1=1/*test="" 编写判断条件id!=null取出javabean中的id属性值*/<if test="id!=null">and id > #{id}</if>/*ognl表达式,第一个name是数据库字段,第二个是传入的javabean的属性*/<if test="name!='' and name!=null">and name like #{name}</if></select>
8.2:where
where标签可以自动的为我们减去不需要的and链接符合增加where判断关键字
<!--根据传入的对象,加入employee中某属性有值,就按照该属性取值--><!--public Employee getEmployeeByCondition(Employee ee);--><select id="getEmployeeByCondition" resultMap="employeeMap">select * from t_employee<!--test="" 编写判断条件id!=null取出javabean中的id属性值--><where><if test="id!=null">and id > #{id}</if><!--ognl表达式,第一个name是数据库字段,第二个是传入的javabean的属性--><if test="name!='' and name!=null">and name like #{name}</if></where></select>
8.3:trim标签
<!--prefix="" 前缀;为我们的sql整体填一个前缀prefixOverrides="" 去除整体字符前边多余的前缀suffix="" 后缀;为sql整体加一个后缀suffixOverrides="" 去除整体字符后边多余的后缀--><trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and" suffix="" suffixOverrides=""><if test="id!=null">and id > #{id}</if><!--ognl表达式,第一个name是数据库字段,第二个是传入的javabean的属性--><if test="name!='' and name!=null">and name like #{name}</if></trim>
8.4:foreach
动态 SQL 的另外一个常用的必要操作是需要对一个集合进行遍历,通常是在构建 IN 条件语句的时候 。
<!--public List<Employee> getEmployeeByIds(@Param("ids") List ids);--><select id="getEmployeeByIds" resultMap="employeeMap">select * from t_employee where id in<!--collection="ids" :标识遍历的集合close="":以什么结束;open="":以什么开始index="i":索引如果遍历的是一个list:index:指定当前的变量保存了当前的索引item:保存当前遍历的变量的值如果遍历的是一个map:index:指定的变量就是保存了当前遍历的元素的key;item:就是保存当前遍历元素的valueitem="变量名":每次便利店额元素的值;separator:每次遍历的分隔符--><foreach collection="ids" close=")" item="id" open="(" separator=",">#{id}</foreach></select>

8.5:choose分支选择
相当于if—-elase
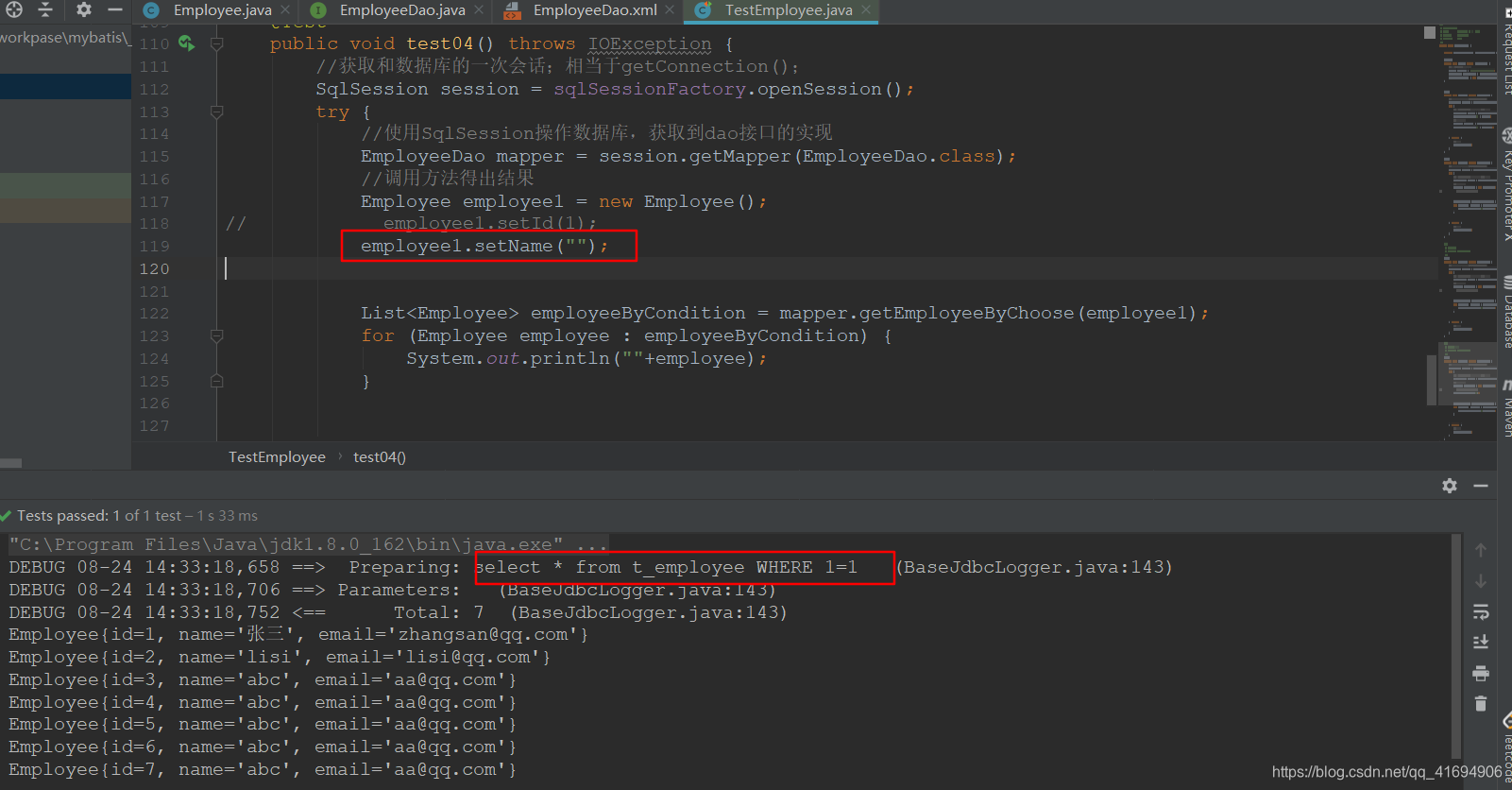
<!--public List<Employee> getEmployeeByChoose(Employee ee);--><select id="getEmployeeByChoose" resultMap="employeeMap">select * from t_employee<where><choose><when test="id!=null">id = #{id}</when><when test="name!=null and !name.equals("")">name =#{name}</when><otherwise>1=1</otherwise></choose></where></select>
8.6:set标签动态修改
<!--public List<Employee> getEmployeeByIds(@Param("ids") List ids);--><update id="updateEmployee">update t_employee<!--set标签可以动态的将修改的语句最后的逗号去掉--><set><if test="name!='' and name!=null">name=#{name},</if><if test="email!='' and email!=null">email = #{email},</if></set><where>id = #{id}</where></update>

8.7:mybatis的ognl表达式以及_parameter参数和_databaseId参数
OGNL**( Object Graph Navigation Language )对象图导航语言,这是一种强大的表达式语言,通过它可以非常方便的来操作对象属性。 类似于我们的EL,SpEL等**
访问对象属性: person.name
调用方法: person.getName()
调用静态属性/方法: @java.lang.Math@PI
@java.util.UUID@randomUUID()
调用构造方法: new com.atguigu.bean.Person(‘admin’).name
运算符: +,-*,/,%
逻辑运算符: in,not in,>,>=,<,<=,==,!=
注意:xml中特殊符号如”,>,<等这些都需要使用转义字符
访问集合属性:
| 类型 | 伪属性 | 伪属性对应的 Java 方法 |
| List、Set、Map | size、isEmpty | List/Set/Map.size(),List/Set/Map.isEmpty() |
| List、Set | iterator | List.iterator()、Set.iterator() |
| Map | keys、values | Map.keySet()、Map.values() |
| Iterator | next、hasNext | Iterator.next()、Iterator.hasNext() |
_parameter:代表传入的参数;
传入单个参数;_parameter就代表这个参数
传入多个参数:_parameter就代表多个参数集合起来的map
_databaseId:代表当前环境
这样就可以根据不同的数据库厂商构建特定的语句

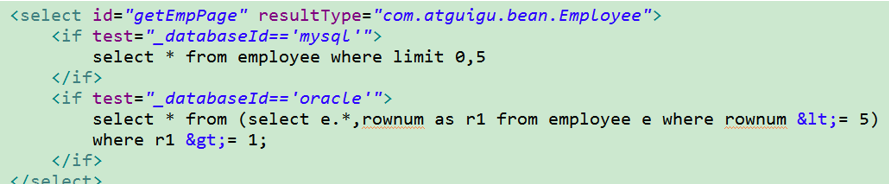
8.8:sql标签,可重用的标签
<!--提取可重用的sql--><sql id="selectsql">select * from t_employee</sql>






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...