SpringBoot项目规范(1)| 异常统一处理以及自定义异常处理
SpringBoot项目规范(1)| 异常统一处理以及自定义异常处理
文章目录 SpringBoot项目规范(1)| 异常统一处理以及自定义异常处理 @[TOC] 前言 一、自定义异常 1.自定义异常(ExploException) 2.定义错误码(HttpCode) 3.全局异常捕获 4.业务层异常处理 二、效果演示 1.请求失败返回结果 2.请求成功返回结果 总结
前言
在业务层代码中,当方法层层嵌套,对最深处的代码进行不满足的数据或者调价做判断时,直接返回响应体并不是很合适(这个时候就需要抛出自定义异常)
一、自定义异常
1.自定义异常(ExploException)
按照异常类型,自定义RuntimeException类型的异常,主要用于在业务处理过程中判断参数、响应、逻辑等是否满足条件,当不满足的时候直接抛出异常,并将异常原因放回前端提示。自定义异常代码如下
import com.oak.monitor.response.HttpCode;import lombok.Data;@Datapublic class ExploException extends RuntimeException {/*** 错误码*/private HttpCode retCode = HttpCode.UNKNOWN_ERROR;/*** 错误详情*/private String errorInfo;public ExploException(String errorInfo) {super(errorInfo);}public ExploException(HttpCode retCode) {this.retCode = retCode;this.errorInfo = errorInfo;}public ExploException(HttpCode retCode, String errorInfo) {super(errorInfo);this.retCode = retCode;this.errorInfo = errorInfo;}}
2.定义错误码(HttpCode)
错误码定义分不同的类别,这样的好处是便于管理,并且如果有国际化需求可以很快的切换
public enum HttpCode {// 成功状态码SUCCESS(00000, "成功"),UNKNOWN_ERROR(99999, "服务未知异常"),// 系统500错误UNAUTHORIZED(10401, "签名验证失败"),// 参数错误:10001-19999PARAM_IS_INVALID(10001, "参数无效"),// 用户错误:20001-29999USER_NOAUTH(20000,"用户未登录"),USER_HAS_EXISTED(20001, "用户名已存在"),USER_NOT_FIND(20002, "用户名不存在"),USER_PASS_ERROR(20003,"密码不正确"),USER_LOCKED(20004,"账户已锁定"),USER_PASS_OUT(20005,"用户名或密码错误次数过多"),USER_NOTFIND_ERROR(20006,"没有找到用户"),USER_ERROR(20007,"用户名或密码不正确"),// ES错误:30001-39999ES_INDEX_ERROR(30001,"索引已经存在");private Integer code;private String message;HttpCode(Integer code, String message) {this.code = code;this.message = message;}public Integer code() {return this.code;}public String message() {return this.message;}}
3.全局异常捕获
用于捕获代码层抛出的异常,对捕获的异常进行个性化逻辑处理。
@ControllerAdvicepublic class GlobalExceptionHandle {private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.OK)@ExceptionHandler(ExploException.class)@ResponseBodypublic ResponseHandle handleException(ExploException e) {ResponseHandle response = new ResponseHandle();response.setDesc(e.getMessage());response.setStatus(e.getRetCode().code());return response;}@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) // 此处是为了设置http的响应码@ExceptionHandler(ArithmeticException.class)@ResponseBodypublic ResponseHandle handleException(ArithmeticException e) {ResponseHandle response = new ResponseHandle();response.setDesc(e.getMessage());response.setStatus(HttpCode.SYSTEM_ERROR.code());return response;}}
说明:
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.OK)这个定义了捕获的异常返回前端的http请求状态
@ExceptionHandler(ExploException.class) 这个定义捕获的异常类型
4.业务层异常处理
业务层对于不满足条件的逻辑进行异常抛出
if (StringUtils.equals("小明", employe.getName())) {throw new ExploException(HttpCode.EUSER_ERROR);}else{return ResponseHandle.SUCCESS(employe);}
二、效果演示
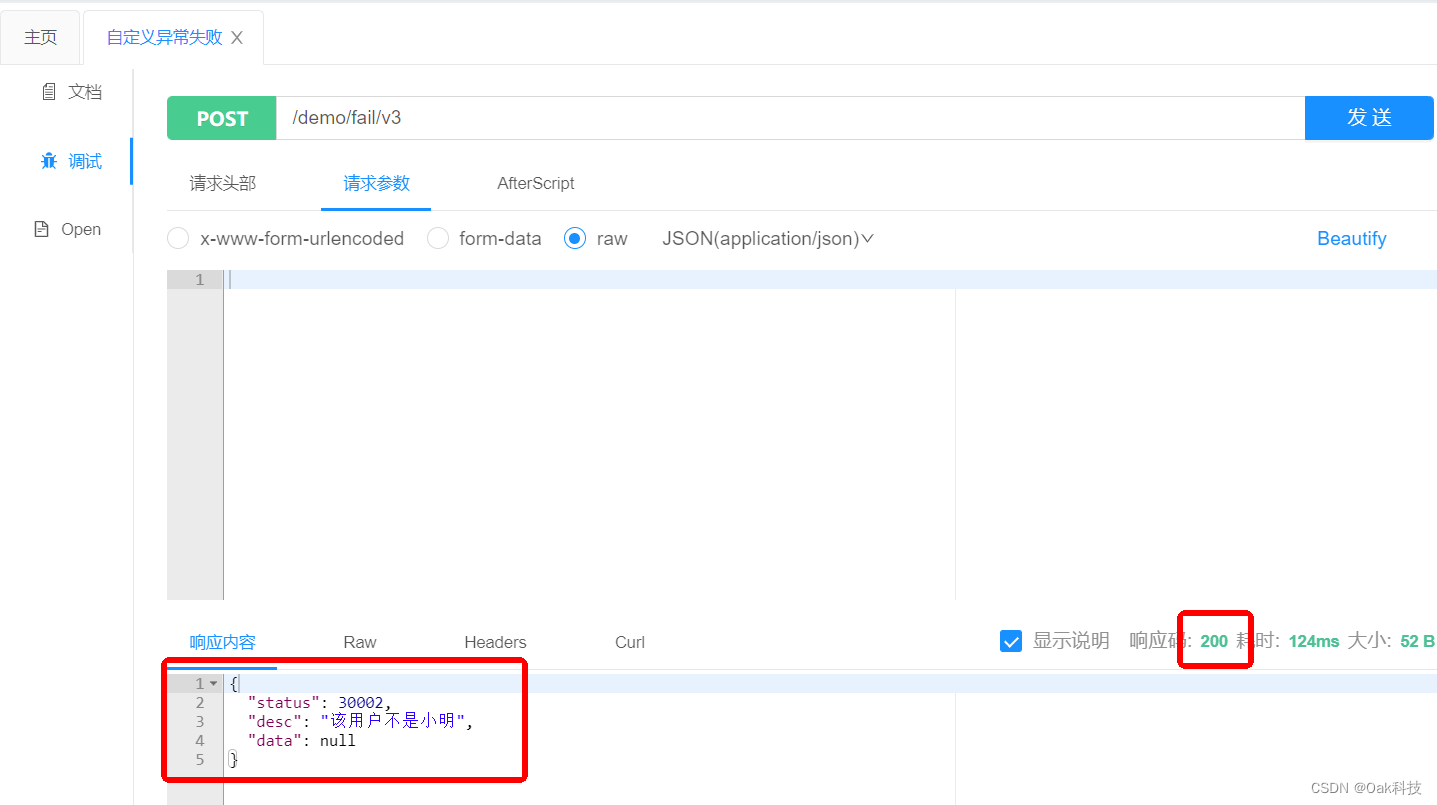
1.请求失败返回结果
业务抛出异常结果,http的响应码是200,业务抛出的状态码是status:30002,这样客户端拿到改状态码就可以进行提示
2.请求成功返回结果
成功返回状态码为status:0

总结
以上就是SpringBoot规范化异常处理,这样异常情况下返回给客户端的格式将会统一,便于前端业务逻辑的判断。


































还没有评论,来说两句吧...