【JUC并发编程】BlockingQueue实现原理(BlockingQueue接口/ Java阻塞队列)
目录
- 简单回顾数据结构
- 数组结构
- 链表结构
- Lock锁使用回顾
- 什么是阻塞队列
- BlockingQueue接口
- 有界与无界区别
- Java里的阻塞队列
- 8.1 ArrayBlockingQueue
- 8.2 ArrayBlockingQueue
- 8.3 ArrayBlockingQueue 实现生产者与消费者模型
- 8.4 纯手写ArrayBlockingQueue
- 8.5 LinkedBlockingQueue
- 8.6 ArrayBlockingQueue 与LinkedBlockingQueue 区别
1. 简单回顾数据结构
队列:基于数组或者链表实现,先进先出,后进后出规则。
2. 数组结构
连续固定的内存空间,对内存要求较高;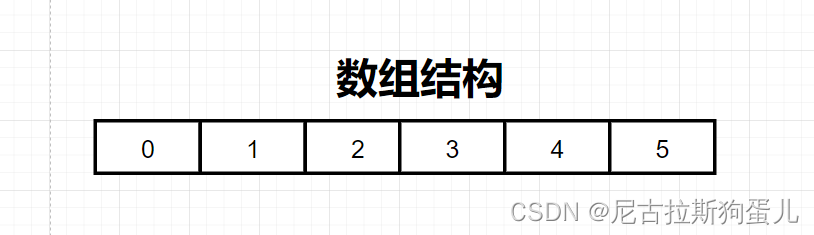
优点:可以直接根据下标查询 时间复杂度为0(1) 支持随机访问;
缺点:增加、删除元素效率慢;
3. 链表结构
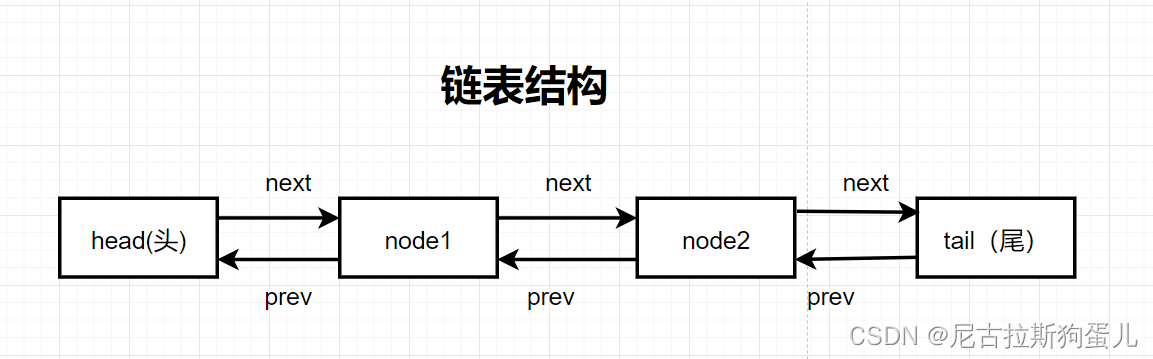
优点:插入删除速度快
缺点:不支持随机访问,需要从头查询到尾部 时间复杂度为o(n)
4. Lock锁使用回顾
ReentrantLock
lock():加锁操作,如果此时有竞争会进入等待队列中阻塞直到获取锁。
lockInterruptibly():加锁操作,但是优先支持响应中断。
tryLock():尝试获取锁,不等待,获取成功返回true,获取不成功直接返回false。
tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit):尝试获取锁,在指定的时间内获取成功返回true,获取失败返回false。
unlock():释放锁。
Condition
通常和ReentrantLock一起使用的
await():阻塞当前线程,并释放锁。
signal():唤醒一个等待时间最长的线程。
private static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();private static Condition condition = lock.newCondition();public static void main(String[] args) {new Thread(() -> {try {lock.lock();System.out.println("1");condition.await();System.out.println("2");} catch (Exception e) {} finally {lock.unlock();}}).start();try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (Exception e) {}new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {lock.lock();condition.signal();} catch (Exception e) {} finally {lock.unlock();}}}).start();}
5. 什么是阻塞队列
Java中的BlockingQueue接口是一个线程安全的存取队列,适用于生产者消费者的应用场景中,支持两个附加操作:
1.生产者线程会一直不断的往阻塞队列中放入数据,直到队列满了为止。队列满了后,生产者线程阻塞等待消费者线程取出数据。
2.消费者线程会一直不断的从阻塞队列中取出数据,直到队列空了为止。队列空了后,消费者线程阻塞等待生产者线程放入数据。
6. BlockingQueue接口
BlockingQueue提供四种不同的处理方法。
| 方法 | 抛出异常 | 返回特殊值 | 一直阻塞 | 超时退出 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 插入方法 | add(o) | offer(o) | put(o) | offer(o, timeout, timeunit) |
| 移除方法 | remove(o) | poll() | take(o) | poll(o, timeout, timeunit) |
| 检查方法 | element() | peek() | — | — |
抛出异常:
- add: 插入数据时,如果阻塞队列满,那么抛出异常IllegalStateException,否则插入成功返回true。当使用有界(capacity-restricted queue)阻塞队列时,建议使用offer方法。
llegalStateException - if the element cannot be added at this time due to capacity restrictions
ClassCastException - if the class of the specified element prevents it from being added to this queue
NullPointerException - if the specified element is null
IllegalArgumentException - if some property of the specified element prevents it from being added to this queue - remove: 删除数据时,如果队列中有此数据,删除成功返回true,否则返回false。如果包含一个或者多个object,那么只移除一个就返回true。注意:remove(o)是BlockingQueue接口的方法,remove()是Queue接口的方法。
- element: 如果队列为空,那么抛出异常NoSuchElementException。如果队列不为空,查询返回队列头部的数据,但是不移除数据,这点不同于remove(),element同样是Queue接口的方法。
返回特殊值:
- offer: 插入数据时,如果阻塞队列没满,那么插入成功返回true,否则返回false。当使用有界(capacity-restricted queue)阻塞队列时,建议使用offer方法,不建议会抛出异常的add方法。
- poll: 此方法是Queue接口的。如果队列不为空,查询、移除并返回队列头部元素。如果队列为空,那么返回null。
- peek: 此方法是Queue接口的。如果队列为空,返回null,这点不同于poll。如果队列不为空,查询返回队列头部的数据,但是不移除数据,这点不同于remove()。
一直阻塞:
- put: 插入数据时,如果队列已满,那么阻塞等待队列可用,等待期间如果被中断,那么抛出InterruptedException。
- take: 查询、删除并返回队列头部元素,如果队列为空,那么阻塞等待队列可用,等待期间如果被中断,那么抛出InterruptedException。
超时退出:
- offer: 插入数据时,如果队列已满,那么阻塞指定时间等待队列可用,等待期间如果被中断,那么抛出InterruptedException。如果插入成功,那么返回true,如果在达到指定时间后仍然队列不可用,那么返回false。
- poll: 查询、删除并返回队列头部元素,如果队列为空,那么阻塞指定时间等待队列可用,等待期间如果被中断,那么抛出InterruptedException。如果删除成功,那么返回队列头部元素,如果在达到指定时间后仍然队列不可用,那么返回null。
Queue队列不能插入null,否则会抛出NullPointerException。
7. 有界与无界区别
有界就是队列有容量限制;
无界就是队列没有容量限制;—
如果当前队列容量限制是为(Integer.MAX_VALUE)
该队列容量是为无界队列
8. Java里的阻塞队列
ArrayBlockingQueue :一个由数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列。
LinkedBlockingQueue :一个由链表结构组成的有界阻塞队列。
PriorityBlockingQueue :一个支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列。
DelayQueue:一个使用优先级队列实现的无界阻塞队列。
SynchronousQueue:一个不存储元素的阻塞队列。
LinkedTransferQueue:一个由链表结构组成的无界阻塞队列。
LinkedBlockingDeque:一个由链表结构组成的双向阻塞队列。
8.1 ArrayBlockingQueue
ArrayBlockingQueue是基于数组(array-based)的先进先出(FIFO)有界(bounded)阻塞队列。
- ArrayBlockingQueue是基于数组实现
- 存入方法 采用lock锁保证存取线程安全问题
- ArrayBlockingQueue 属于有界队列 默认的情况下 会创建指定
大小的数组创建一个数组 名称=items
如果现在设置队列容量限制过大的话,(缺陷 有可能会引发内存溢出的问题) - ArrayBlockingQueue 读写都会使用到同一把锁
2个线程 A线程做写的操作 B线程做读的操作
8.2 ArrayBlockingQueue
ArrayBlockingQueue是基于数组(array-based)的先进先出(FIFO)有界(bounded)阻塞队列。
- ArrayBlockingQueue是基于数组实现
- 存入方法 采用lock锁保证存取线程安全问题
- ArrayBlockingQueue 属于有界队列 默认的情况下 会创建指定
大小的数组创建一个数组 名称=items
如果现在设置队列容量限制过大的话,(缺陷 有可能会引发内存溢出的问题) ArrayBlockingQueue 读写都会使用到同一把锁
2个线程 A线程做写的操作 B线程做读的操作// 有界
BlockingQueuestrings = new ArrayBlockingQueue (1);
strings.offer(“xiaowang”);
strings.offer(“xiaochao”);
// 先进先出原则 取出xiaowang同时从队列中删除
System.out.println(strings.poll());
// 先进先出原则 取出xiaochao同时从队列中删除
System.out.println(strings.poll());
// 先进先出原则 null
System.out.println(strings.poll());
strings.poll(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)—如果3s内没有从队列中获取到内容,则当前线程会阻塞等待,超时时间为3s。
当队列满了,继续投递数据在队列中 当前线程会阻塞等待。
strings.offer(“xiaowang”, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
8.3 ArrayBlockingQueue 实现生产者与消费者模型
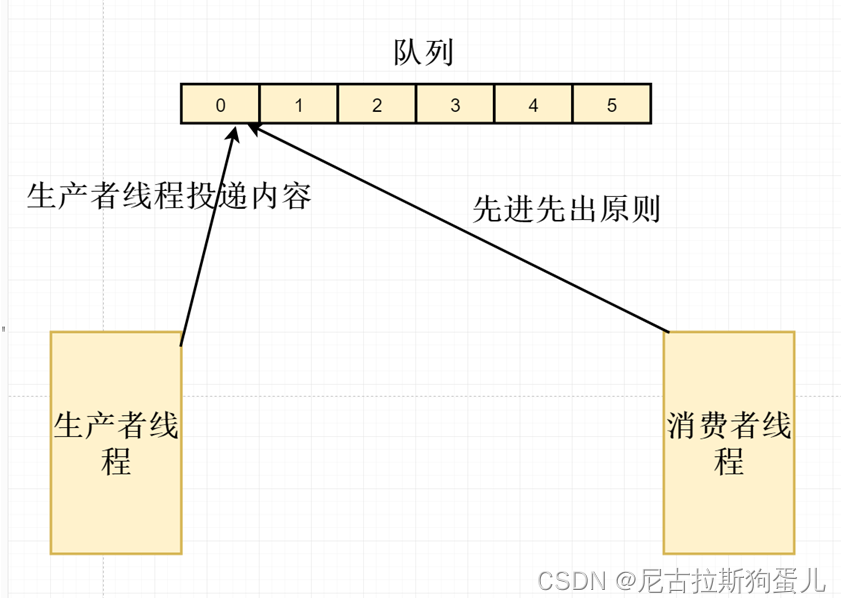
private static ArrayBlockingQueue<String> arrayBlockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(20);public static void main(String[] args) {new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i <= 30; i++) {try {// 模拟生产者存入的线程速率 30毫秒Thread.sleep(30);String msg = i + "";boolean result = arrayBlockingQueue.offer(msg, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "生产者线程存入" + msg + "," + (result ? "成功" : "失败"));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "生产者线程").start();new Thread(() -> {while (true) {String msg = arrayBlockingQueue.poll();if (msg != null)System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "消费者消费:" + msg);try {// 模拟处理消费者线程处理业务逻辑的时间3sThread.sleep(3000);} catch (Exception e) {}}}, "消费者线程").start();}
8.4 纯手写ArrayBlockingQueue
public class DemoArrayBlockingQueue<E> {/*** 基于数组形式实现队列*/private ArrayList<E> blockingQueue;private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();private Condition condition = lock.newCondition();/*** 初始化队列容量*/private int items;public DemoArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) {this.items = capacity;blockingQueue = new ArrayList<E>(capacity);}public boolean offer(E e) {lock.lock();try {if (blockingQueue.size() == items)return false;else {blockingQueue.add(e);return true;}} finally {lock.unlock();}}/*** 阻塞队列** @param e* @param timeout* @param unit* @return*/public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {lock.lock();try {long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);while (blockingQueue.size() == items) {// 如果当前队列满了 则阻塞等待if (nanos <= 0) {return false;}nanos = condition.awaitNanos(nanos);}blockingQueue.add(e);return true;} finally {lock.unlock();}}public E poll() {lock.lock();try {return (blockingQueue.size() == 0) ? null : dequeue();} finally {lock.unlock();}}public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {lock.lock();try {long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);// 没有获取到内容 则阻塞等待while (blockingQueue.size() == 0) {if (nanos <= 0) {return null;}nanos = condition.awaitNanos(nanos);}return dequeue();} finally {lock.unlock();}}private E dequeue() {E e = blockingQueue.get(0);// 取出该元素blockingQueue.remove(0);// 同时删除该元素return e;}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {DemoArrayBlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new DemoArrayBlockingQueue<String>(2);blockingQueue.offer("xiaowang");blockingQueue.offer("xiaochao");// blockingQueue.offer("xiaodan", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);System.out.println(">2<<");System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println("结束");}}
8.5 LinkedBlockingQueue
LinkedBlockingQueue是基于链表(linked nodes)的先进先出(FIFO)的可选界(optionally-bounded)的阻塞队列。
//LinkedBlockingDeque默认是无界队列 底层采用链表实现LinkedBlockingDeque<String> strings = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>();strings.offer("xiaowang");strings.offer("xiaochao");System.out.println(strings.poll());System.out.println(strings.poll());System.out.println(strings.poll());
8.6 ArrayBlockingQueue 与LinkedBlockingQueue 区别
ArrayBlockingQueue 与LinkedBlockingQueue 区别:
- ArrayBlockingQueue 底层基于数组实现;
- LinkedBlockingQueue 底层基于链表实现;
- ArrayBlockingQueue 默认是有界队列;
- LinkedBlockingQueue 默认是无界队列 容量为 Integer.MAX_VALUE;
- ArrayBlockingQueue 读写采用同一把锁, LinkedBlockingQueue 锁是读写分离;
- LinkedBlockingQueue clear方法 同时清理两把锁
- LinkedBlockingQueue使用AtomicInteger计入个数,ArrayBlockingQueue int count计数

































还没有评论,来说两句吧...