java——集合——List集合——List集合



List集合的概述与方法使用
java.util.List接口 extends Collection接口
List接口的特点:
1.有序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序是一致的(存储123 取出123)
2.有索引,包含了一些带索引的方法
3.允许存储重复的元素
List接口中带索引的方法(特有)
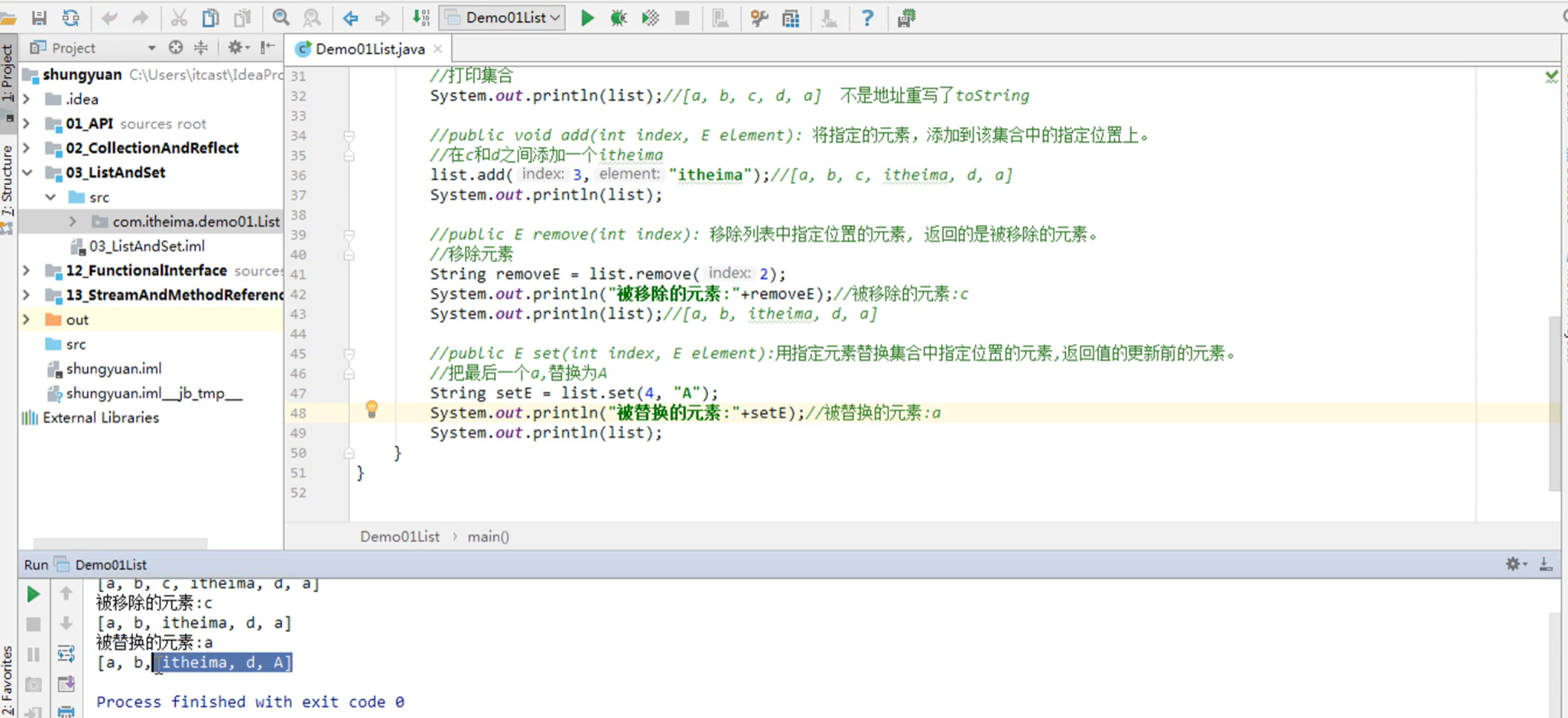
- public void add(int index, E element): 将指定的元素,添加到该集合中的指定位置上。
- public E get(int index):返回集合中指定位置的元素。
- public E remove(int index): 移除列表中指定位置的元素, 返回的是被移除的元素。
- public E set(int index, E element):用指定元素替换集合中指定位置的元素,返回值的更新前的元素。
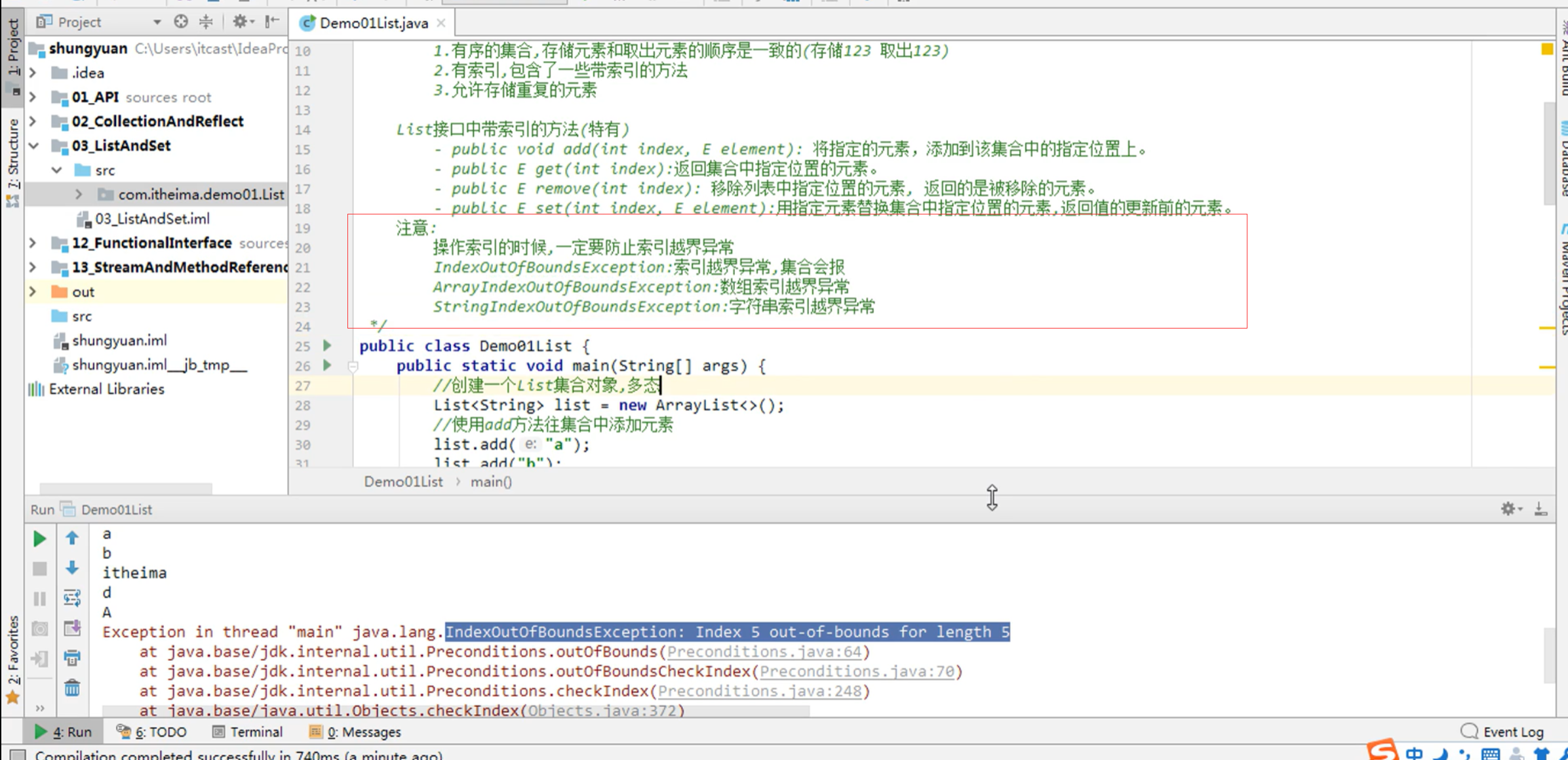
注意:
操作索引的时候,一定要防止索引越界异常
- IndexOutOfBoundsException:索引越界异常,集合会报
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:数组索引越界异常
- StringIndexOutOfBoundsException:字符串索引越界异常
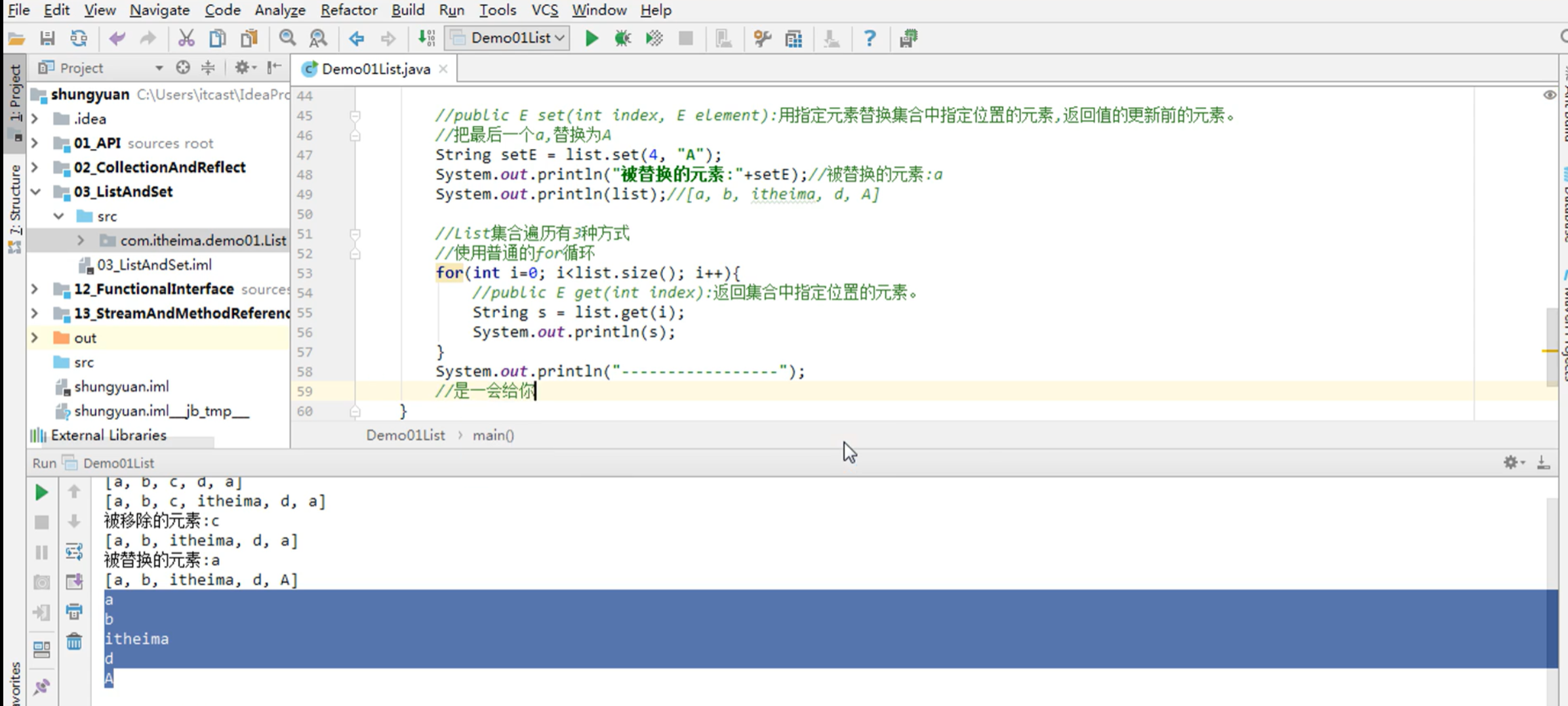
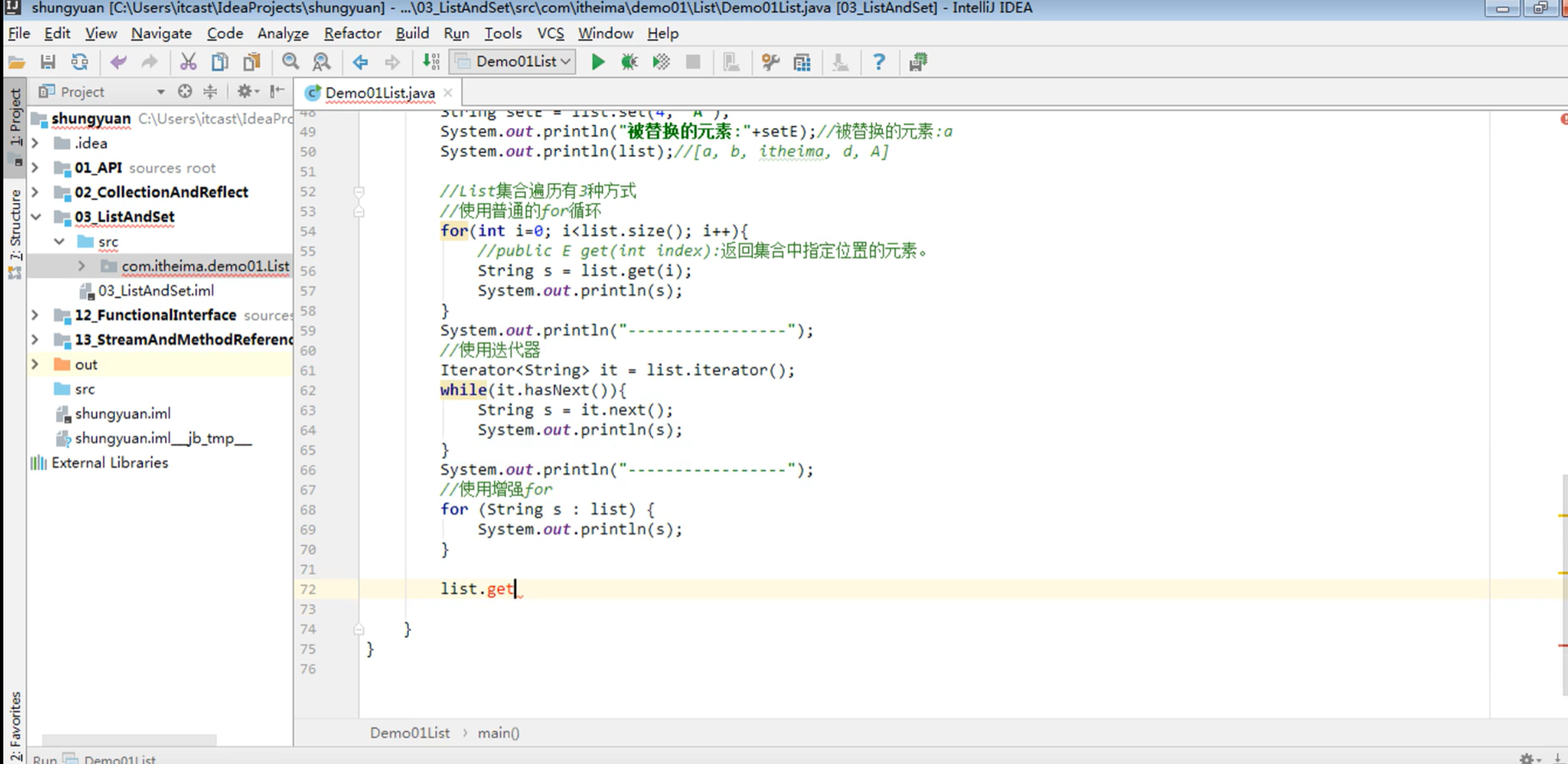
public classDemo01List {public static void main(String[] args) { //创建一个List集合对象,多态 List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); //使用add方法往集合中添加元素 list.add("a"); list.add("b"); list.add("c"); list.add("d"); list.add("a"); //打印集合 System.out.println(list);//[a, b, c, d, a] 不是地址重写了toString //public void add(int index, E element): 将指定的元素,添加到该集合中的指定位置上。 //在c和d之间添加一个itheima list.add(3,"itheima");//[a, b, c, itheima, d, a] System.out.println(list); //public E remove(int index): 移除列表中指定位置的元素, 返回的是被移除的元素。 //移除元素 String removeE = list.remove(2); System.out.println("被移除的元素:"+removeE);//被移除的元素:c System.out.println(list);//[a, b, itheima, d, a] //public E set(int index, E element):用指定元素替换集合中指定位置的元素,返回值的更新前的元素。 //把最后一个a,替换为A String setE = list.set(4, "A"); System.out.println("被替换的元素:"+setE);//被替换的元素:a System.out.println(list);//[a, b, itheima, d, A] //List集合遍历有3种方式 //使用普通的for循环 for(int i=0; i<list.size(); i++){ //public E get(int index):返回集合中指定位置的元素。 String s = list.get(i); System.out.println(s); } System.out.println("-----------------"); //使用迭代器 Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ String s = it.next(); System.out.println(s);



































还没有评论,来说两句吧...