【Java】String类的常用方法
 ✨博客主页: XIN-XIANG荣
✨博客主页: XIN-XIANG荣
✨系列专栏:【Java SE】
✨一句短话: 难在坚持,贵在坚持,成在坚持!
文章目录
- 一. String对象的比较
- ==比较是否引用同一个对象
- boolean equals(Object anObject)
- int compareTo(String s)
- int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
- 二. 字符串查找
- 三. 转化
- 数值和字符串转化
- 大小写转化
- 字符串和数组的转换
- 格式化
- 四. 字符串替换
- 五. 字符串拆分
- 六. 字符串截取
- 七. 其他操作方法
- String trim()
- boolean isEmpty ()
- int length()
- 判断字符串开头结尾
- boolean contains(String str)
一. String对象的比较
1. ==比较是否引用同一个对象
注意:
对于内置类型,==比较的是变量中的值;对于引用类型 , == 比较的是引用中的地址。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;int b = 20;int c = 10;// 对于基本类型变量,==比较两个变量中存储的值是否相同System.out.println(a == b); // falseSystem.out.println(a == c); // true// 对于引用类型变量,==比较两个引用变量引用的是否为同一个对象String s1 = new String("hello");String s2 = new String("hello");String s3 = new String("world");String s4 = s1;System.out.println(s1 == s2); // falseSystem.out.println(s2 == s3); // falseSystem.out.println(s1 == s4); // true
}
2. boolean equals(Object anObject)
按照字典序进行比较(字典序:字符大小的顺序)
String类重写了父类Object中equals方法,Object中equals默认按照==比较,String重写equals方法后,按照 如下规则进行比较,比如: s1.equals(s2)
String中的equals方法分析:
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {// 1. 先检测this 和 anObject 是否为同一个对象比较,如果是返回trueif (this == anObject) {return true;}// 2. 检测anObject是否为String类型的对象,如果是继续比较,否则返回falseif (anObject instanceof String) {// 将anObject向下转型为String类型对象String anotherString = (String)anObject;int n = value.length;// 3. this和anObject两个字符串的长度是否相同,是继续比较,否则返回falseif (n == anotherString.value.length) {char v1[] = value;char v2[] = anotherString.value;int i = 0;// 4. 按照字典序,从前往后逐个字符进行比较while (n-- != 0) {if (v1[i] != v2[i])return false;i++;}return true;}}return false;}
比较示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = new String("hello");String s2 = new String("hello");String s3 = new String("Hello");// s1、s2、s3引用的是三个不同对象,因此==比较结果全部为falseSystem.out.println(s1 == s2); // falseSystem.out.println(s1 == s3); // false// equals比较:String对象中的逐个字符// 虽然s1与s2引用的不是同一个对象,但是两个对象中放置的内容相同,因此输出true// s1与s3引用的不是同一个对象,而且两个对象中内容也不同,因此输出falseSystem.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // trueSystem.out.println(s1.equals(s3)); // false}
3. int compareTo(String s)
按照字典序进行比较
与equals不同的是,equals返回的是boolean类型,而compareTo返回的是int类型。具体比较方式:
- 先按照字典次序大小比较,如果出现不等的字符,直接返回这两个字符的大小差值
如果前k个字符相等(k为两个字符长度最小值),返回值两个字符串长度差值
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("abc");String s2 = new String("ac");String s3 = new String("abc");String s4 = new String("abcdef");System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3)); // 相同输出 0System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3
}
4. int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
与compareTo方式相同,但是忽略大小写进行比较
public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = new String("abc");String s2 = new String("ac");String s3 = new String("ABc");String s4 = new String("abcdef");System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s3)); // 相同输出 0System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s4)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3}
二. 字符串查找
字符串查找也是字符串中非常常见的操作,String类提供的常用查找的方法,
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| char charAt(int index) | 返回index位置上字符,如果index为负数或者越界,抛出 IndexOutOfBoundsException异常 |
| int indexOf(int ch) | 返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int indexOf(String str) | 返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int lastIndexOf(int ch) | 从后往前找,返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找ch第一次出现的位置,没有返 回-1 |
| int lastIndexOf(String str) | 从后往前找,返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找str第一次出现的位置,没有返 回-1 |
public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "aaabbbcccaaabbbccc";System.out.println(s.charAt(3)); // 'b'System.out.println(s.indexOf('c')); // 6System.out.println(s.indexOf('c', 10)); // 15System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb")); // 3System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb", 10)); // 12System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c')); // 17System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c', 10)); // 8System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb")); // 12System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb", 10)); // 3}
注意:
- 上述方法都是实例方法,通过对象引用调用。
三. 转化
1. 数值和字符串转化
static String valueof() 数值转字符串
Integer.parseInt() 字符串整形
Double.parseDouble() 字符串转浮点型
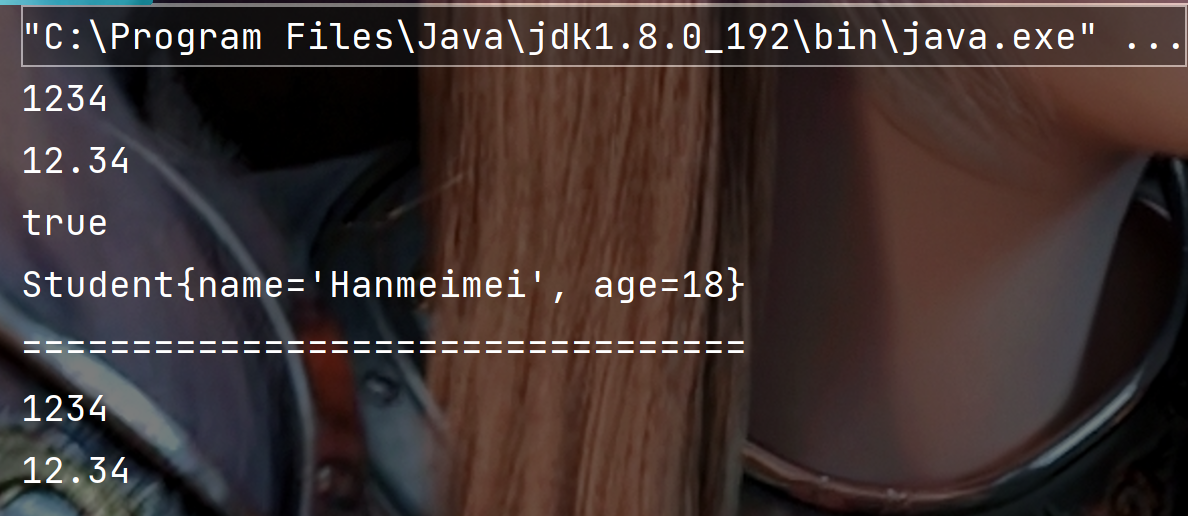
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// 值转字符串String s1 = String.valueOf(1234);String s2 = String.valueOf(12.34);String s3 = String.valueOf(true);String s4 = String.valueOf(new Student("Hanmeimei", 18));System.out.println(s1);System.out.println(s2);System.out.println(s3);System.out.println(s4);System.out.println("=================================");// 字符串转数字//Integer、Double等是Java中的包装类型int data1 = Integer.parseInt("1234");double data2 = Double.parseDouble("12.34");System.out.println(data1);System.out.println(data2);}}class Student{String name;int age;public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}}
执行结果:
2. 大小写转化
String toUpperCase() 转大写
String toLowerCase() 转小写
这两个函数只转换字母。
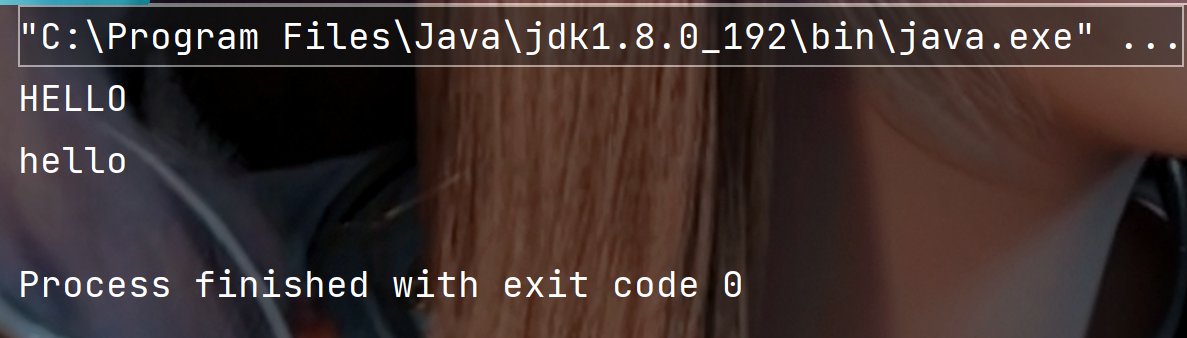
public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = "hello";String s2 = "HELLO";// 小写转大写System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase());// 大写转小写System.out.println(s2.toLowerCase());}
执行结果:
3. 字符串和数组的转换
char[ ] toCharArray() 字符串转数组
new String(数组引用) 数组转字符串
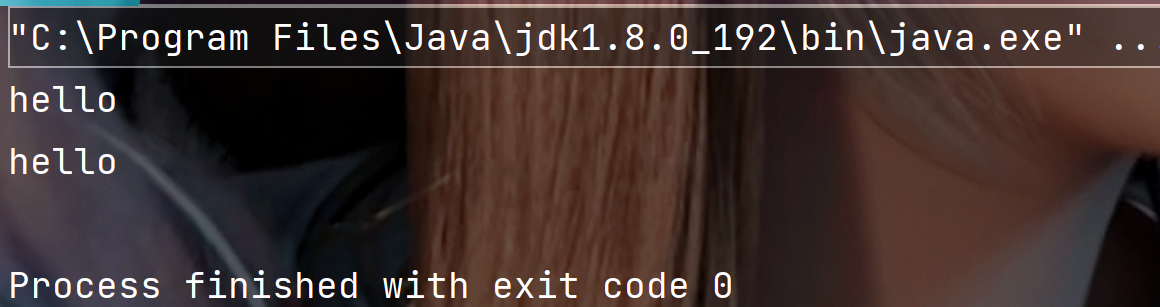
public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "hello";// 字符串转数组char[] ch = s.toCharArray();for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {System.out.print(ch[i]);}System.out.println();// 数组转字符串String s2 = new String(ch);System.out.println(s2);}
执行结果:
4. 格式化
static String format( );
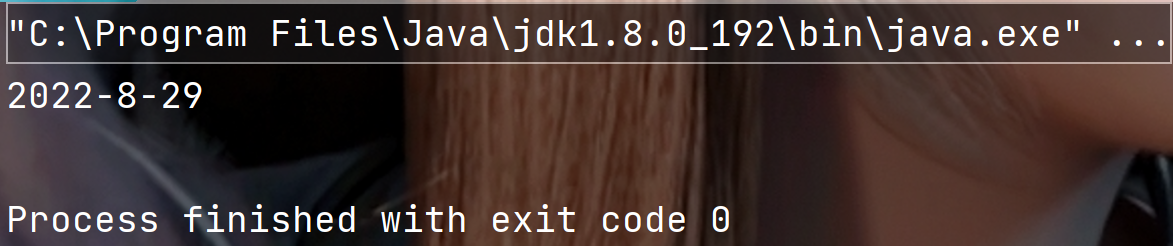
public static void main(String[] args) {String s = String.format("%d-%d-%d", 2022, 8, 29);System.out.println(s);}
执行结果:
四. 字符串替换
使用一个指定的新的字符串替换掉已有的字符串数据,可用的方法如下:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) | 替换所有的指定内容 |
| String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) | 替换首个指定内容 |
代码示例:
字符串的替换处理:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld" ;System.out.println(str.replaceAll("l", "_"));System.out.println(str.replaceFirst("l", "_"));
}
执行结果:

注意事项:
- 由于字符串是不可变对象, 替换不修改当前字符串, 而是产生一个新的字符串.
五. 字符串拆分
可以将一个完整的字符串按照指定的分隔符划分为若干个子字符串。
可用方法如下:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| String[] split(String regex) | 将字符串全部拆分 |
| String[] split(String regex, int limit) | 将字符串以指定的格式,拆分为limit组 |
如果一个字符串中有多个分隔符,可以用”|”作为连字符.
代码示例:
实现字符串的拆分处理
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello world hello rong";String[] result = str.split(" ") ; // 按照空格拆分for(String s: result) {System.out.println(s);}System.out.println("==============");String str1 = "xin&xin=xiang&rong";String[] str2 = str1.split("&|=");//按照=和&拆分for(String s: str2) {System.out.println(s);}
}
执行结果:
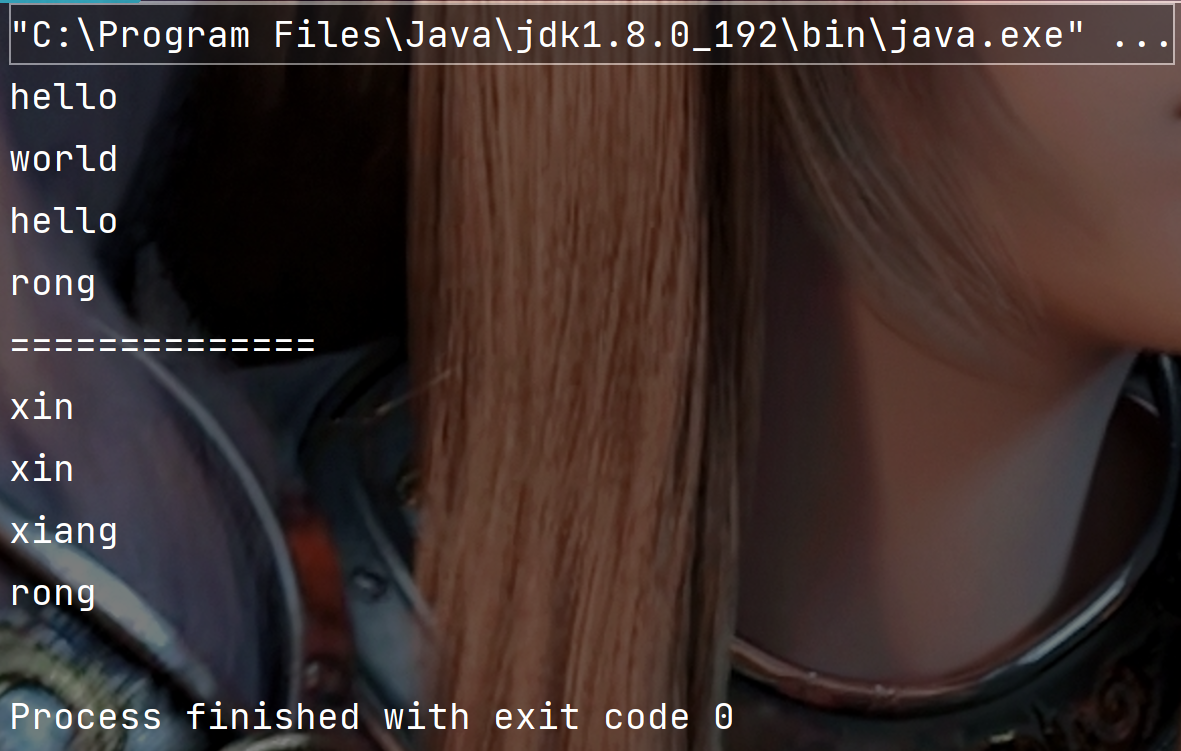
代码示例:
字符串的部分拆分
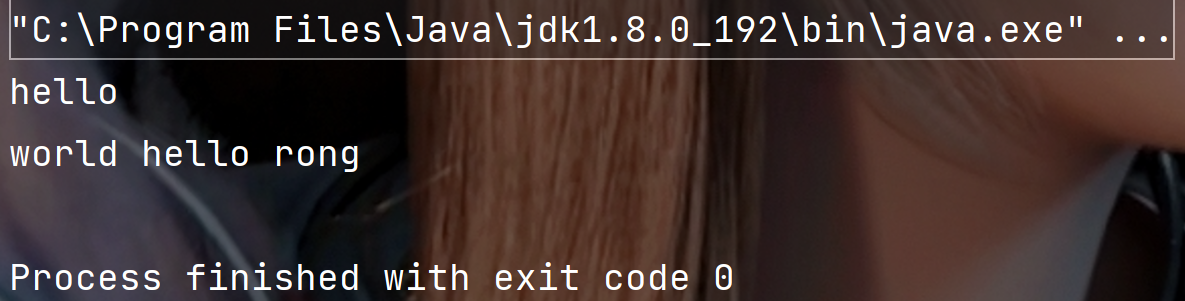
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello world hello rong" ;String[] result = str.split(" ",2) ;for(String s: result) {System.out.println(s);}
}
执行结果:
有些特殊字符作为分割符可能无法正确切分, 需要加上转义.
- 字符”|“,”*“,”+“,”.”都得加上转义字符,前面加上 “ \ “ .
- 而如果是 “ \ “ ,那么就得写成 “ \ \ “ ; 使用split来切分字符串时,遇到以反斜杠\作为切分的字符串,split后传入的内容是 \ \ \ \,这么写是因为第一和第三是个斜杠是字符串的转义符。转义后的结果是\ \,split函数解析的不是字符串而是正则,正则表达式中的\ \结果对应\,所以分隔反斜杠的时候要写四个反斜杠。
代码示例:
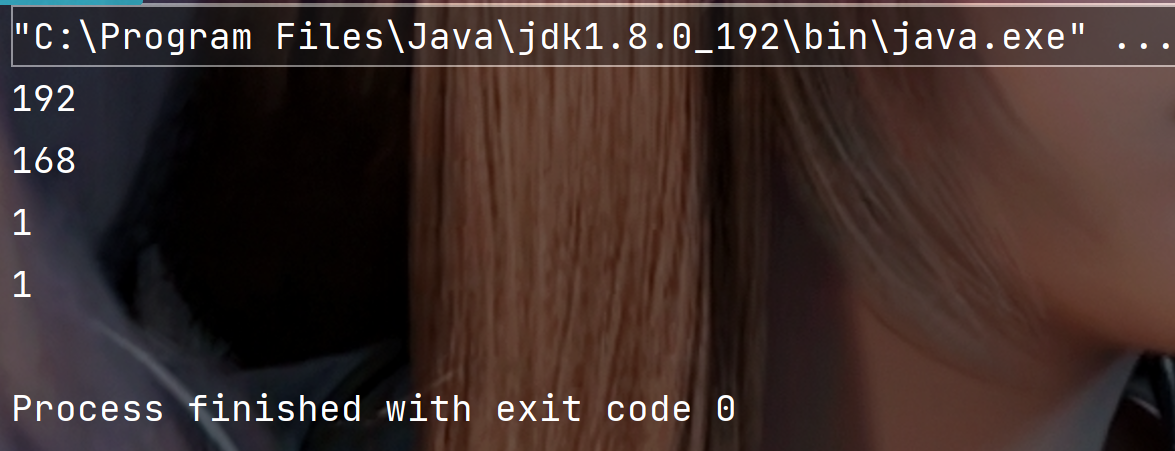
拆分IP地址
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "192.168.1.1" ;String[] result = str.split("\\.") ;for(String s: result) {System.out.println(s);}
}
执行结果:
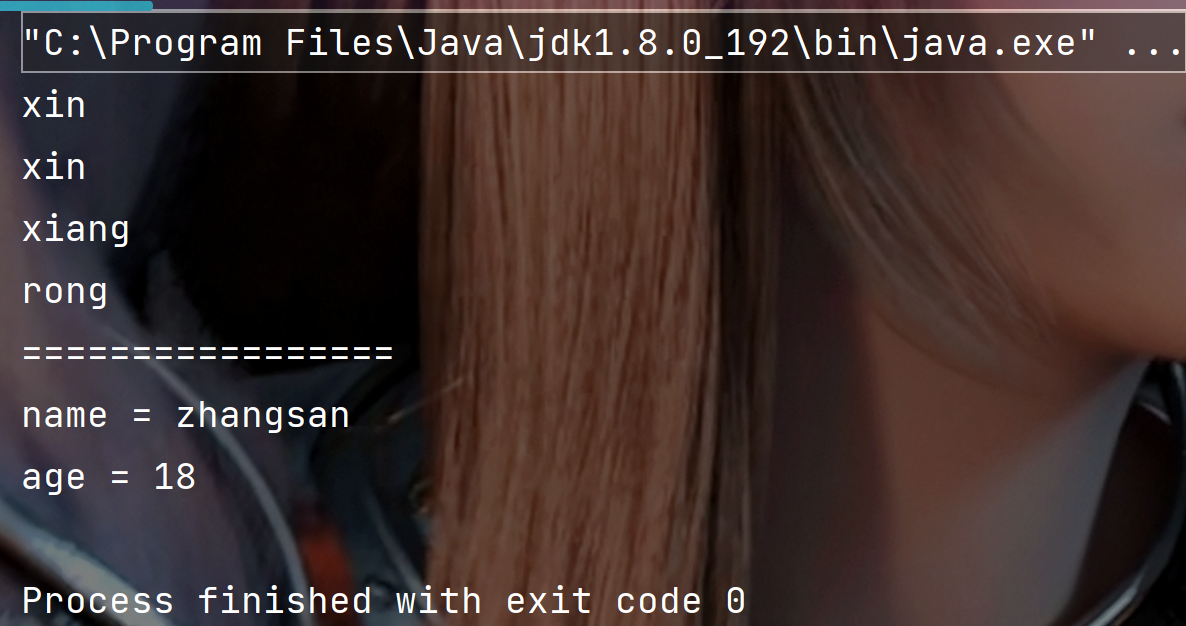
代码中的多次拆分:
ppublic static void main(String[] args) {//字符串多次拆封String str = "xin&xin=xiang&rong";String[] str1 = str.split("&");for (int i = 0; i < str1.length; i++) {String[] str2 = str1[i].split("=");for (String x:str2) {System.out.println(x);}}String s = "name=zhangsan&age=18" ;String[] result = s.split("&") ;for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {String[] temp = result[i].split("=") ;System.out.println(temp[0]+" = "+temp[1]);}}
执行结果:
六. 字符串截取
从一个完整的字符串之中截取出部分内容。可用方法如下 :
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| String substring(int beginIndex) | 从指定索引截取到结尾 |
| String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | 截取部分内容 |
代码示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "helloworld" ;System.out.println(str.substring(5));System.out.println(str.substring(0, 5));}
执行结果:
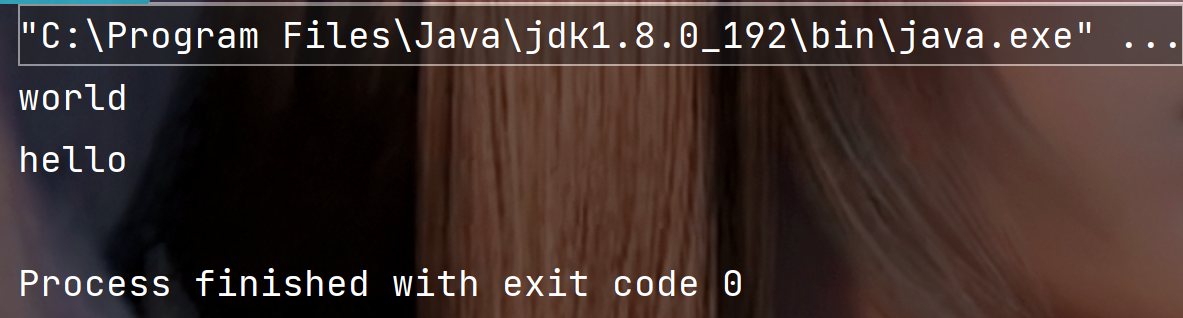
注意事项:
- 索引从0开始
- 注意前闭后开区间的写法, substring(0, 5) 表示包含 0 号下标的字符, 不包含 5 号下标,即(0,4)
七. 其他操作方法
1. String trim()
去掉字符串中的左右空格,保留中间空格
trim 会去掉字符串开头和结尾的空白字符(空格, 换行, 制表符等).
示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {String str = " hello world " ;System.out.println("["+str+"]");System.out.println("["+str.trim()+"]");}
执行结果:
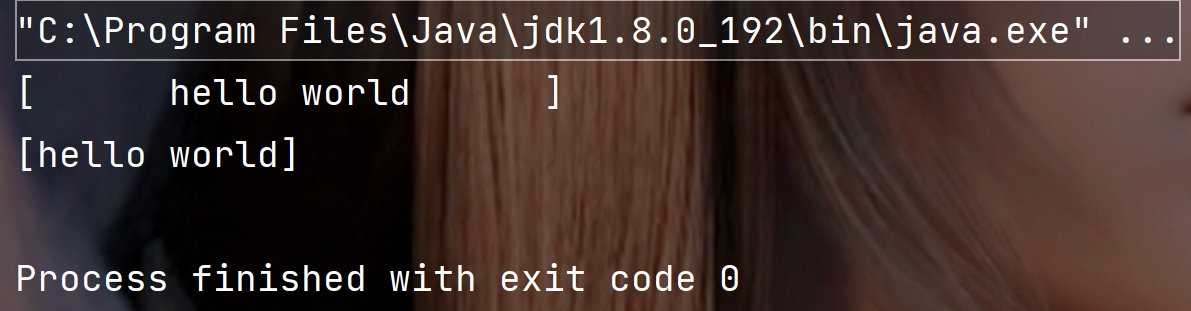
2. boolean isEmpty ()
isEmpty() 方法用于判断字符串是否为空
示例代码:
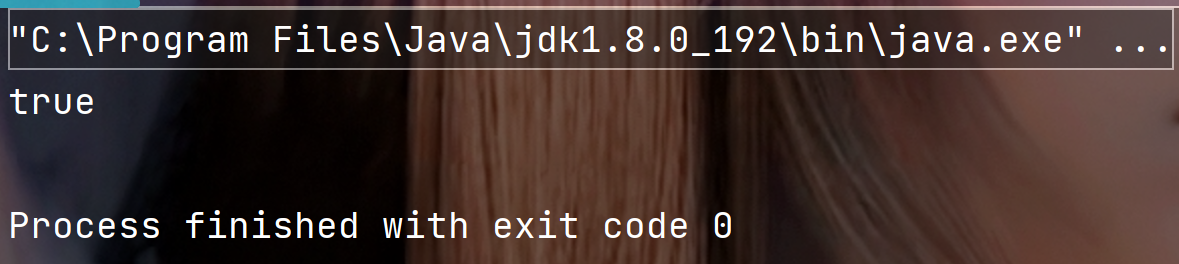
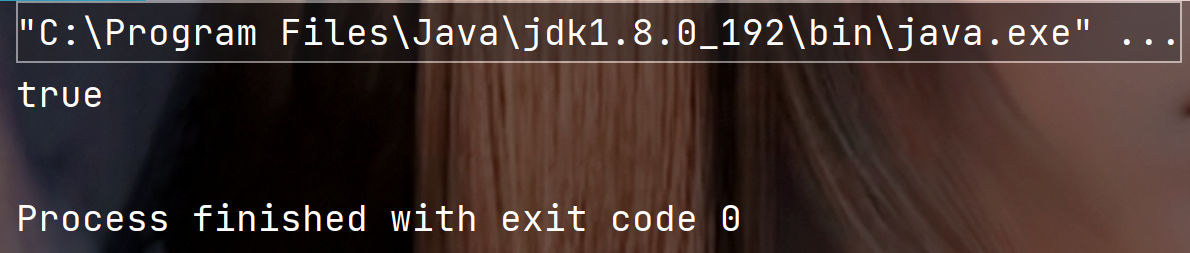
public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "";System.out.println(str.isEmpty());}
执行结果:
3. int length()
用于求字符串的长度
示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "xinxinxiangrong";System.out.println(str.length());}
执行结果:
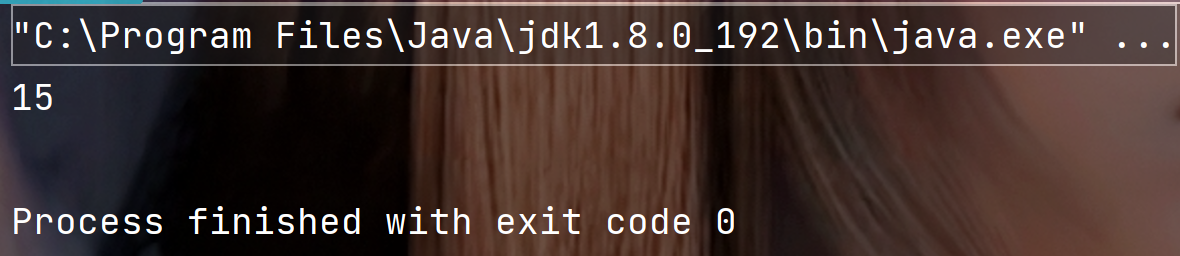
4. 判断字符串开头结尾
boolean startsWith(String prefix) 判断字符串是否以某个字符串开头的
boolean endWith(String sufix) 判断字符串是否以某个字符串结尾的
示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "xinxinxianrong";System.out.println(str.startsWith("xin"));System.out.println(str.endsWith("rong"));}
执行结果:

5. boolean contains(String str)
判断字符串中是否包含某个字符串
示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "xinxinxianrong";System.out.println(str.contains("inx"));}
执行结果:


































还没有评论,来说两句吧...