Java基础知识之字符编码
一.字符编码的发展历程:
字符编码的发展历程:
阶段1:
计算机只认识数字,我们在计算机里一切数据都是以数字来表示,因为英文符号有限,
所以规定使用的字节的最高位是0.每一个字节都是以0~127之间的数字来表示,比如A对应65,a对应97.
这就是美国标准信息交换码-ASCII.
阶段2:
随着计算机在全球的普及,很多国家和地区都把自己的字符引入了计算机,比如汉字.
此时发现一个字节能表示数字范围太小,不能包含所有的中文汉字,那么就规定使用两个字节来表示一个汉字.
规定:原有的ASCII字符的编码保持不变,仍然使用一个字节表示,为了区别一个中文字符与两个ASCII码字符,
中文字符的每个字节最高位规定为1(中文的二进制是负数).这个规范就是GB2312编码,
后来在GB2312的基础上增加了更多的中文字符,比如汉字,也就出现了GBK.
阶段3:
新的问题,在中国是认识汉字的,但是如果把汉字传递给其他国家,该国家的码表中没有收录汉字,其实就显示另一个符号或者乱码.
为了解决各个国家因为本地化字符编码带来的影响,咱们就把全世界所有的符号统一进行编码-Unicode编码.
此时某一个字符在全世界任何地方都是固定的,比如’哥’,在任何地方都是以十六进制的54E5来表示.
Unicode的编码字符都占有2个字节大小.
常见的字符集:
ASCII: 占一个字节,只能包含128个符号. 不能表示汉字
ISO-8859-1:(latin-1):占一个字节,收录西欧语言,.不能表示汉字.
ANSI:占两个字节,在简体中文的操作系统中 ANSI 就指的是 GB2312.
GB2312/GBK/GB18030:占两个字节,支持中文.
UTF-8:是一种针对Unicode的可变长度字符编码,称万国码,是Unicode的实现方式之一。
编码中的第一个字节仍与ASCII兼容,这使得原来处理ASCII字符的软件无须或只须做少部份修改,即可继续使用。
因此,它逐渐成为电子邮件、网页及其他存储或传送文字的应用中,优先采用的编码。互联网工程工作小组(IETF)要求所有互联网协议都必须支持UTF-8编码。
UTF-8 BOM:是MS搞出来的编码,默认占3个字节,不要使用这个.
存储字母,数字和汉字:
存储字母和数字无论是什么字符集都占1个字节.
存储汉字: GBK家族占两个字节,UTF-8家族占3个字节.
不能使用单字节的字符集(ASCII/ISO-8859-1)来存储中文.
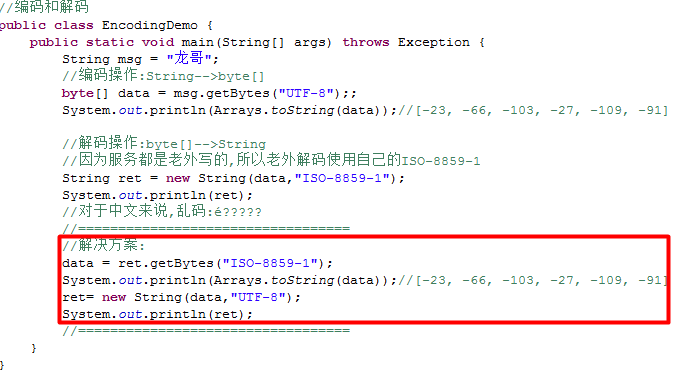
二.字符的编码和解码操作:
编码: 把字符串转换为byte数组.
解码: 把byte数组转换为字符串.
一定要保证编码和解码的字符相同,否则乱码.
三.工具类
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;/** * 字符编码工具类 */public class CharTools {/** * 转换编码 ISO-8859-1到GB2312 * @param text * @return */public static final String ISO2GB(String text) {String result = "";try {result = new String(text.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"), "GB2312");}catch (UnsupportedEncodingException ex) {result = ex.toString();}return result;}/** * 转换编码 GB2312到ISO-8859-1 * @param text * @return */public static final String GB2ISO(String text) {String result = "";try {result = new String(text.getBytes("GB2312"), "ISO-8859-1");}catch (UnsupportedEncodingException ex) {ex.printStackTrace();}return result;}/** * Utf8URL编码 * @param s * @return */public static final String Utf8URLencode(String text) {StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();for (int i = 0; i < text.length(); i++) {char c = text.charAt(i);if (c >= 0 && c <= 255) {result.append(c);}else {byte[] b = new byte[0];try {b = Character.toString(c).getBytes("UTF-8");}catch (Exception ex) {}for (int j = 0; j < b.length; j++) {int k = b[j];if (k < 0) k += 256;result.append("%" + Integer.toHexString(k).toUpperCase());}}}return result.toString();}/** * Utf8URL解码 * @param text * @return */public static final String Utf8URLdecode(String text) {String result = "";int p = 0;if (text!=null && text.length()>0){text = text.toLowerCase();p = text.indexOf("%e");if (p == -1) return text;while (p != -1) {result += text.substring(0, p);text = text.substring(p, text.length());if (text == "" || text.length() < 9) return result;result += CodeToWord(text.substring(0, 9));text = text.substring(9, text.length());p = text.indexOf("%e");}}return result + text;}/** * utf8URL编码转字符 * @param text * @return */private static final String CodeToWord(String text) {String result;if (Utf8codeCheck(text)) {byte[] code = new byte[3];code[0] = (byte) (Integer.parseInt(text.substring(1, 3), 16) - 256);code[1] = (byte) (Integer.parseInt(text.substring(4, 6), 16) - 256);code[2] = (byte) (Integer.parseInt(text.substring(7, 9), 16) - 256);try {result = new String(code, "UTF-8");}catch (UnsupportedEncodingException ex) {result = null;}}else {result = text;}return result;}/** * 编码是否有效 * @param text * @return */private static final boolean Utf8codeCheck(String text){String sign = "";if (text.startsWith("%e"))for (int i = 0, p = 0; p != -1; i++) {p = text.indexOf("%", p);if (p != -1)p++;sign += p;}return sign.equals("147-1");}/** * 判断是否Utf8Url编码 * @param text * @return */public static final boolean isUtf8Url(String text) {text = text.toLowerCase();int p = text.indexOf("%");if (p != -1 && text.length() - p > 9) {text = text.substring(p, p + 9);}return Utf8codeCheck(text);}}
































还没有评论,来说两句吧...