4.4-node-web
1 模块查找机制
require('./a'); // a.js
1.1 模块有路径没有后缀名
1 首先找同名js 找到则执行
2 找不到则找同名js文件夹
3 假如找到同名js文件夹,会找package.json文件main选项指定的入口文件
4 假如package.json文件main选项指定的入口文件不存在或者没配置,则会
找有没有index.js
5 没有index.js会报错
require('a'); // require('fs') require('mime')
1.2没有路径也没有后缀
1 首先会假设这是系统模块
2 node会去node_modules文件夹
3 首先看有没有该名字的js
4 再看有没有该名字的文件夹
5 假如找到同名js文件夹,会找package.json文件main选项指定的入口文件
6 假如package.json文件main选项指定的入口文件不存在或者没配置,则会
找有没有index.js
7 没有index.js会报错
node-web
客户端
服务器端 处理数据和业务逻辑
请求
客户端 ——————> 服务器端
<——————
响应
ip地址/域名 http://www.baidu.com
端口 如: 9999
URL http://www.baidu.com
https://www.baidu.com/index.html
本地ip 127.0.0.1 本地域名localhost
报文 请求和响应的过程中传递的数据块
响应报文
1 HTTP状态码
200 OK 请求成功
404 请求资源不存在
500 服务器错误
400 客户端请求有语法错误
2 内容类型
text/html
text/css
text/javascript
image/jepg
application/json
怎样创建一个服务器
// http 创建服务器模块const http = require('http');/* 创建一个服务器*/const app = http.createServer();// 监听客户端请求app.on('request', (req, res) => {console.log(req);// 请求报文console.log(req.headers);// 请求地址console.log('请求地址', req.url) // /favicon.ico// 请求方法console.log('请求方法', req.method); // GET// 响应 给客户端回写res.end('<h1>hello</h1>');});// 监听端口app.listen(9999);console.log('服务器已经启动,请访问localhost:9999');/* 方法二 const app = http.createServer((req, res) => { console.log(111); res.writeHead(200, { 'content-type': 'text/html;charset=utf8' }); res.end('<h1>hi,小鲜肉</h1>'); }); app.listen(6688); */
HTTP请求处理与响应处理
1 请求参数
get请求参数
http://localhost:9999/?username=admin&pwd=123456
参数回访制在浏览器地址栏中,可以借用url模块parese处理
get请求 1 浏览器直接输入网址 2 link 3 script 4 img 5 form表单
const http = require('http');// url模块,处理url地址const url = require('url');const app = http.createServer();app.on('request', (req, res) => {//console.log(req.url); // /?username=admin&pwd=123456// let urlStr = url.parse(req.url, true);// 第二个参数‘true’可以把参数解析成对象形式// 不写此参数时username=admin&pwd=123456// console.log(urlStr); //{ username: 'admin', pwd: '123456' }let { query } = url.parse(req.url, true);res.end(`${ query.username}-${ query.pwd}`);// res.end('welcome');})app.listen(9999);console.log('已经启动');
POST请求
1 参数是被放在请求体中进行传输
2 node处理POST请求,需要使用data和end事件
3 使用querystring模块处理
const http = require('http');const qs = require('querystring');const app = http.createServer();app.on('request', (req, res) => {//console.log(req.url); // 输出/let postData = '';// 监听,数据变化拼接req.on('data', (chunk) => {postData += chunk;});// 监听结束返回req.on('end', () => {console.log(postData); //username=admin&pwd=11111let { username, pwd } = qs.parse(postData); // {uername:**, pwd:**}console.log(username, pwd);});})app.listen(9999);console.log('已经启动');
其他前端界面
<body><!-- 默认method=get --><!-- <form action="http://localhost:9999"> --><!-- 用户名:<input type="text" name="username"> --><!-- 密码:<input type="password" name="pwd"> --><!-- <input type="submit" value="登陆"> --><!-- 提交后地址变化=> http://localhost:9999/?username=admin&pwd=123456 --><!-- </form> --><!-- post请求 --><form action="http://localhost:9999" method="POST">用户名:<input type="text" name="username">密码:<input type="password" name="pwd"><input type="submit" value="登陆"></form></body>
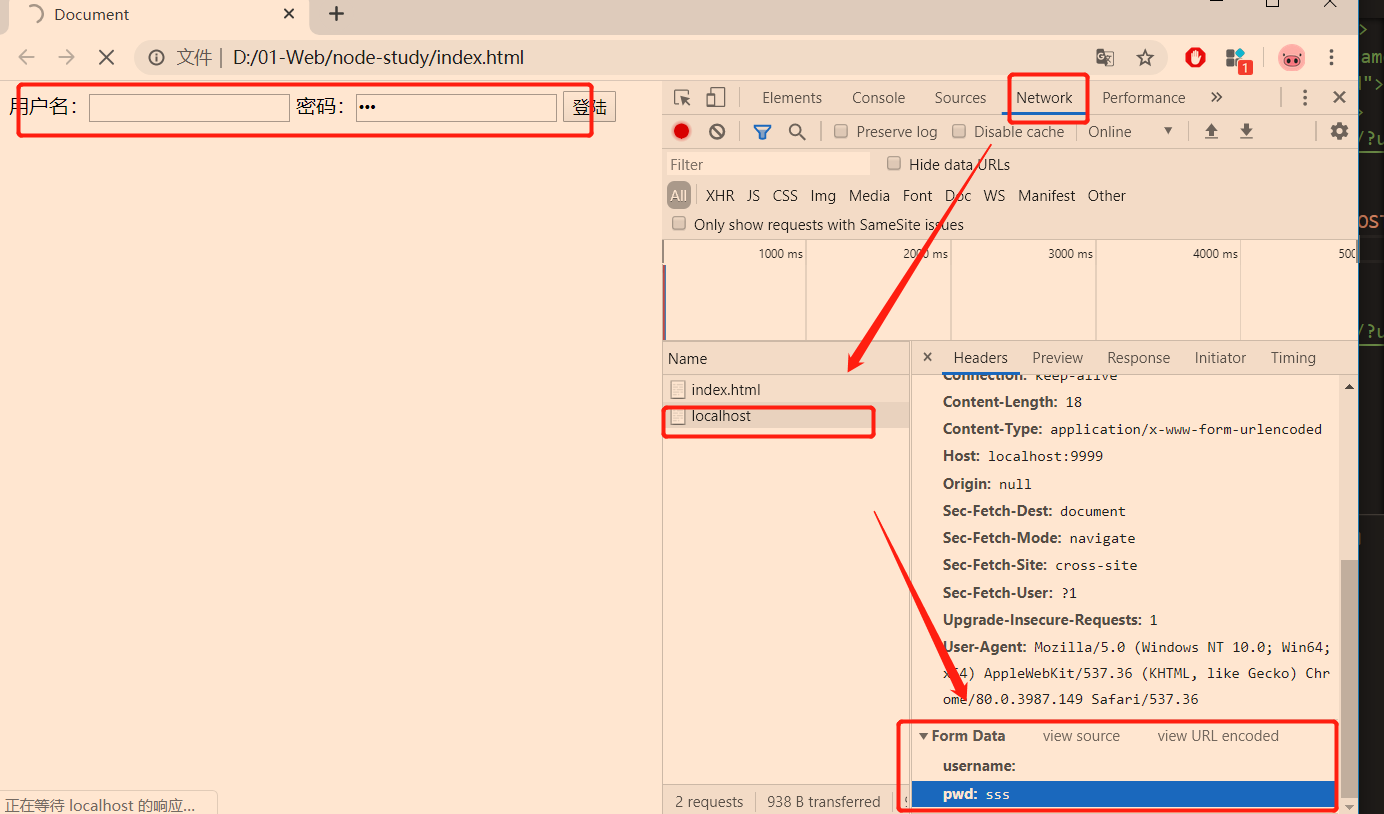
路由 客户端请求地址与服务端程序代码的对应关系
静态资源: 服务器不需要处理,可以直接响应给客户端
动态资源: 相同的请求地址,不同的响应资源
/blog/article?id=1
/blog/article?id=2































还没有评论,来说两句吧...