node koa常用属性、方法和常用中间件
request
常用API:
例子:http://localhost:4000/index?name=lxc&age=20
ctx.request.query -> 获取简析的查询字符串,无则返回空对象 { name: ‘lxc’, age: ‘20’ }
ctx.request.querystring -> 获取原始查询字符串 *name=lxc&age=20*
ctx.request.url -> 获取请求的url /index?name=lxc&age=20
ctx.request.path -> 获取path路径名 /index
ctx.request.method -> 获取请求方法 GET
ctx.request.host -> 获取主机 localhost:4000
ctx.request.hostname -> 获取主机名 localhost
例子:http://localhost:4000/index/:id
ctx.request.params-> 获取动态请求参数 { id: xxx }
ctx.request.header -> 设置请求头 (等于ctx.request.headers)
ctx.request.originalUrl -> 获取原始的URL(与ctx.request.url 相同)
ctx.request.href-> 获取完整的请求url http://localhost:4000/index?name=lxc&age=20
ctx.request.search -> 获取原始的查询字符串 ?name=lxc&age=20
ctx.request.type -> 获取请求的 content-type,不含 ‘charset’等参数 application/json
ctx.request.protocol -> 获取请求协议 http 或 https
post请求 {username: ‘lxc’, password: ‘123456’}
ctx.request.body-> 获取请求body ( 前提需要安装koa-bodyparser ) {username: ‘lxc’, password: ‘123456’}
#
response
ctx.response.status -> 设置响应状态(默认为404 - Not Found ,原生node的res.statusCode为200)
ctx.response.header -> 设置响应头对象 (等于ctx.response.headers)
ctx.response.body -> ,设置响应体内容 === ctx.body 可设置以下类型:
· string (Content-Type 默认为
text/html或text/plain, 同时默认字符集是 utf-8)· Buffer (Content-Type 默认为
application/octet-stream)· Stream管道 * (Content-Type 默认为
application/octet-stream)*· Object || Array (需要JSON.stringify( ) ,Content-Type 默认为
application/json)· null 无响应内容
tips: 如果未设置ctx.response.status,koa自动设置状态为200或204
ctx.response.redirect( url, [alt] )-> 设置重定向 参数二可选
ctx.response.set( ‘key’, ‘value’ )-> 设置响应头, 参数也可以是一个对象,设置多个响应头
ctx.response.append( ‘link’, ‘http://127.0.0.1‘ )-> 附加额外的消息头
ctx.response.type = xxx -> 设置响应的content-type
ctx.type = 'text/plain; charset=utf-8';
实例属性:
app.context -> 它就是创建ctx的原型,可以通过编辑app.context 为ctx添加属性或方法(就是在ctx的原型上添加属性)
上下文:
koa中的上下文封装了Request对象和Response对象,详情见koa源码或者我写的一个简易的koa:
https://github.com/lvxingchenGit/LKoa
ctx.state -> 命名空间,传递信息的。
// eg:ctx.state.user = await User.find(id)ctx.app -> 实例的引用(就是实例)
多个中间件组合成单一中间件:
koa-compose - 包
// npm i koa-compose --saveconst compose = require('koa-compose')async function m1(ctx, next){console.log('1')await next()}async function m2(ctx, next){console.log('2')await next()}async function m3(ctx, next){console.log('3')await next()}const all = componse([m1, m2, m3])app.use(all) // 总之中间件最后需要挂载到app.use()中小案例:
前端请求 - 计算服务器响应时间
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {const prevTime = new Date().getTime()await next()const nowTime = new Date().getTime()console.log('time:', nowTime - prevTime + 'ms') // 4msctx.body = {name: 'lxc'}})app.use(async (ctx, next) => {console.log('1')})
补充:
koa中使用原生的node request对象、response对象,还有几个常用属性:
- ctx.request: koa 封装的 request 对象,中间件应该尽量使用
- ctx.req:Node.js 原生的 request 对象
- ctx.response:koa 封装的 response 对象,中间件应该尽量使用
- ctx.res:Node.js 原生的 response 对象
- ctx.state:koa 推荐的命名空间,用于通过中间件传递信息到前端视图
- ctx.app:对应用实例 app 的引用
常用的koa中间件
koa-bodyparser
这个中间件可以将post请求的参数转为json格式返回。
koa接收到的post请求参数并不是json格式,我们需要将其转换为json
使用方法:安装后直接在ctx.request.body内获取POST请求参数,中间件自动给我们解析为json
// 解析post请求中的参数const bdparser = require('koa-bodyparser')app.use(bdparser()) // 加载koa-bodyparser中间件
koa-router
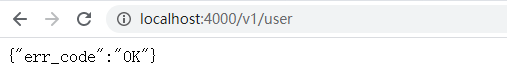
// koaRouter.js 路由请求const Router= require('koa-router')const user = new Router({prefix: '/v1'}) // prefix 可在prefix定义公共前缀路径user.get('/user', ctx => {ctx.body = {err_code = 'OK'}})user.post('/addOne', ctx => {})module.exports = {user}// --------------------------------------------// app.jsconst koa = require('koa')const { user } = require('./koaRouter')const app = koa()app.use(user.routes()) // 加载user中间件
#
nodemon
// 自动加载服务: Terminal 运行:nodemon projectName.js
require-directory
// 自动查找文件夹 - 加载文件路径// 在项目开发过程中,往往各个路由模块会有多个文件,使用require 导入路由很麻烦,require-derectory可自动查找一个文件夹下的所有模块const requireDirectory = require('require-directory')const ABSOLUTE_URL = `${proccess.cwd()}/user`requireDirectory(module, ABSOLUTE_URL, {visit(){}})/**参数一:module 不需要修改参数二:要查找的文件夹,绝对路径,proccess.cwd()输出当前项目的绝对路径;__dirname:输出当前文件所在文件夹的绝对路径。参数三:对象options配置项,如下:*//**{include: /name+\.js/g, // 白名单,只加载符合条件的,可使用正则或函数(参数为path - 模块的绝对路径)// include 值也可以是一个函数,返回true表示符合加载条件:include(path) {if(/.+\.js$/g.test(path)) {return true}},exclude(path){ // 黑名单,不加载的模块return /name+\.js/g.test(path) // 返回Boolean},visit(obj) { // 每个模块加载时执行的加载函数,参数为 module.exports 导出的模块app.use(obj) // 在这里边通常会把所有路由中间件挂载到app.use()中},rename: function(name) { // 重命名键名console.log(name) 会把所有的文件夹名及文件名打印出来!!!return name.toUpperCase()},recurse: true // 是否遍历文件夹,默认为true,嵌套文件夹下的模块也会被加载}*/
封装自动导出路由文件
const Router = require('koa-router')const requireDirectory = require('require-directory')const baseULR = process.cwd()class InitRouter {static InitRouterFn(app) {InitRouter.app = appInitRouter.runRouterMounting()}static runRouterMounting() {let whiteRulesReg = /.+\.js/g // 正则制定规则 - 哪些js文件可以导出requireDirectory(module, `${baseULR}/api`, {include(path) {if(whiteRulesReg.test(path)) {console.log('path', path) // 这里可以打印出符合匹配规则的文件路径return true // 返回true为白名单;返回false为黑名单}},visit(exportRouters) { // 兼容 module.exports = xxx 和 module.exports = {}if(exportRouters instanceof Router) {InitRouter.app.use(exportRouters.routes())}else {Object.keys(exportRouters).forEach(ele => {if(exportRouters[ele] instanceof Router) {InitRouter.app.use(exportRouters[ele].routes())}})}}})}}// 导出类module.exports = {InitRouter}






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...