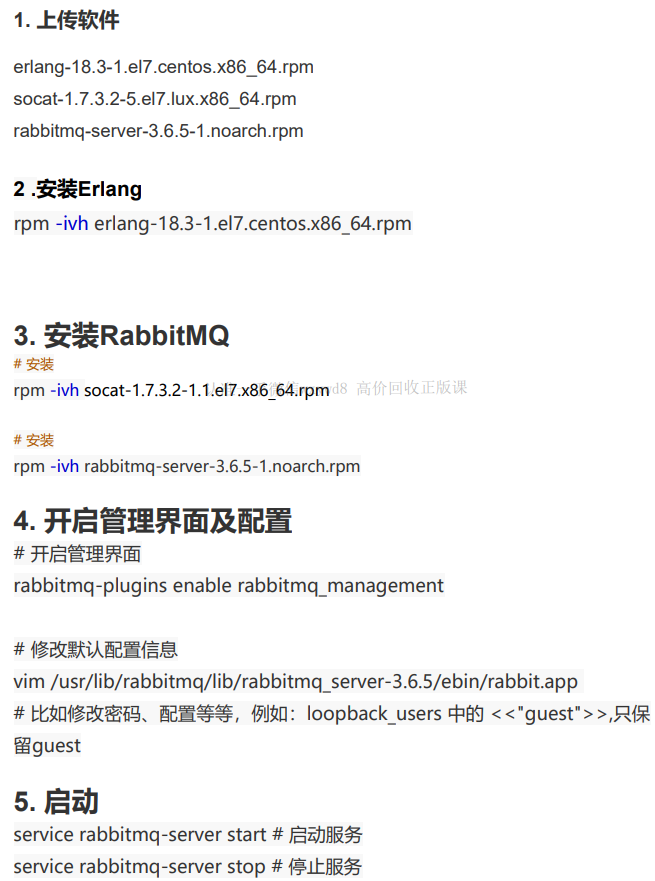
C语言回顾day6 (C控制语句:分支 跳转)
文章目录
- 分支
- if else
- 示例1
- getchar() putchar()
- 示例
- 可以把while的条件改为赋值表达式的值,进一步缩短程序
- ctype.h头文件中包含了原型的函数
- 示例2 电费
- 示例 判断是不是素数
- 示例 统计输入字符数,单词数,行数
- 条件运算符
- 示例 油漆需要几桶
- continue
- 示例 求多个分数的均值,用continue跳过不合法输入,也用了条件运算符
- 示例 continue;和空语句一样效果,跳过某些输入
- 示例 break
- switch
- 示例 对应不同输入给不同输出
- 示例 switch的多重标签 投票(同一个字母的大小写识别为同样输入)
- 跳转
- goto语句(不用!!!)
- 练习
- ‘b’>’a’ 是true
- switch(i++)
- 把==写成=,结果就是 will never end···
前面学了用循环重复执行任务,现在学习用分支根据测试条件执行相应行为
分支
if else
示例1
#include <stdio.h>int main(){int cold_days = 0, all_days = 0;const double FREEZING = 0.0;double temp;printf("Enter the list of daily temperatures:(enter q to quit)\n");while(scanf("%lf", &temp)==1){all_days++;if(temp<FREEZING)cold_days++;}if(all_days)printf("%d days total, and %4.2f%% were below freezing.\n", all_days, (double)cold_days/all_days*100.0);else if(all_days==0)printf("No data entered.\n");return 0;}Enter the list of daily temperatures:(enter q to quit)1.2 3.4 -2 -4q4 days total, and 50.00% were below freezing.
getchar() putchar()



示例
#include <stdio.h>#define SPACE ' 'int main(){char ch;ch = getchar();while(ch != '\n'){if(ch==SPACE)putchar(ch);//printf(" ");elseputchar(ch+1);//printf(ch+1);ch = getchar();}putchar(ch);//打印换行符return 0;}asdfghjkl;bteghiklm<
可以把while的条件改为赋值表达式的值,进一步缩短程序


#include <stdio.h>#define SPACE ' 'int main(){char ch;while((ch = getchar()) != '\n'){if(ch==SPACE)putchar(ch);//printf(" ");elseputchar(ch+1);//printf(ch+1);}putchar(ch);//打印换行符return 0;}
ctype.h头文件中包含了原型的函数


#include <stdio.h>#include <ctype.h>int main(){char ch;while(scanf("%c", &ch)==1){if(isalpha(ch)){if(islower(ch)){ch = toupper(ch);putchar(ch);putchar('\n'); // 极易写双引号!!!}}if(isblank(ch))putchar(' ');if(isdigit(ch))putchar(ch+1);}putchar('\n');return 0;}aAeE23
示例2 电费
#include <stdio.h>#define RATE1 0.13230#define RATE2 0.15040#define RATE3 0.30025#define RATE4 0.34025#define BREAK1 360.0#define BREAK2 468.0#define BREAK3 720.0#define BASE1 (RATE1*BREAK1)#define BASE2 (BASE1+RATE2*(BREAK2-BREAK2))#define BASE3 (BASE2+(BREAK3-BREAK2)*RATE3)int main(){double kwh=0, bill=0;printf("enter the kwh used:\n");scanf("%lf", &kwh);if(kwh<BREAK1)bill = kwh*RATE1;else if(kwh>=BREAK1 & kwh<BREAK2)bill = BASE1 + (kwh-BREAK1)*RATE2;else if(kwh>=BREAK2 & kwh<BREAK3)bill = BASE2 + (kwh-BREAK2)*RATE3;else if(kwh>=BREAK3)bill = BASE3 + (kwh-BREAK3)*RATE4;printf("The bill is $%4.3f.\n", bill);return 0;}enter the kwh used:500The bill is $57.236.
我觉得书上这个地方不对,不用再加BASE1
示例 判断是不是素数
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdbool.h>int main(){unsigned int num;_Bool isPrime = true;int i;//只需要循环检测到输入数字的平方根,不需要检测平方根后面的数字while(scanf("%u", &num)==1){for(i=2, isPrime=true;i*i<=num;i++){if(num%i==0){isPrime = false;if(i*i==num)printf("%u is divisible by %u.\n", num, i);elseprintf("%u is divisible by %u and %u.\n", num, i, num/i);}}if(isPrime)printf("%u is prime.\n", num);elseprintf("%u is not prime.\n", num);printf("enter another positive integer to decide if it is prime(enter q to quit):\n");}return 0;}11 is prime.enter another positive integer to decide if it is prime:22 is prime.enter another positive integer to decide if it is prime:33 is prime.enter another positive integer to decide if it is prime:44 is divisible by 2.4 is not prime.enter another positive integer to decide if it is prime:55 is prime.enter another positive integer to decide if it is prime:66 is divisible by 2 and 3.6 is not prime.enter another positive integer to decide if it is prime:77 is prime.enter another positive integer to decide if it is prime:88 is divisible by 2 and 4.8 is not prime.enter another positive integer to decide if it is prime:99 is divisible by 3.9 is not prime.enter another positive integer to decide if it is prime:1111 is prime.enter another positive integer to decide if it is prime:452738927852324219825 is divisible by 5 and 464843965.2324219825 is divisible by 25 and 92968793.2324219825 is not prime.enter another positive integer to decide if it is prime:


示例 统计输入字符数,单词数,行数
/*wordcnt.c*/#include <stdio.h>#include <stdbool.h> // bool, true, false#include <ctype.h> //isspace(),isalpha()原型#define STOP '|'int main(){char c;//n_lines完整的行(只要有换行符就认为是完整行)//p_lines不完整的行(最后一个字符不是换行符)int n_words=0, n_lines=0, p_lines=0, n_chars=0;//inword指输入的字符是一个单词的一部分,第一个字母和最后一个字母的inword是truebool inword = false;printf("enter text to be analyzed(| to terminate):\n");while((c = getchar())!=STOP){n_chars++;if(c=='\n')n_lines++;//只要输入字符不是空格并且inword现在是false,则认为开始一个新单词//(单引号双引号逗号等也会触发inword变为true,不过这个无所谓,因为并不影响最终单词总数)if(c!=' ' && !inword){inword = true;n_words++;}//相当于只有遇到空格就认为开始新单词,因为空格使单词之间断开if(c==' ' && inword)inword = false;}if(c!='\n')p_lines++; //最后一个输入字符printf("characters:%d\nwords:%d\nlines:%d\npartial lines:%d\n.",n_chars, n_words, n_lines, p_lines);return 0;}
但是这个程序有个问题:一行结束后输入换行符之前要先输入一个空格(即先敲空格再敲回车换行),这样新一行的第一个单词才会被检测到,否则Word数目就比真实数目少了完整行数个。
enter text to be analyzed(| to terminate):I have a pen.sd|characters:17words:5lines:1partial lines:1
但这样做的好处是一行没写完的单词不会被识别为两个词,而是仍然被识别为一个词。
enter text to be analyzed(| to terminate):I have a pen.|characters:14words:4lines:1partial lines:1
条件运算符



示例 油漆需要几桶

用while和scanf一起则可以一直输入新的值来使用程序,而不需要重新启动程序。很好。
while(scanf("%d", &square_feet)==1)#include <stdio.h>#define COVERAGE 350int main(){int square_feet, cans;printf("enter the square feet you need to paint:\n");while(scanf("%d", &square_feet)==1){cans = square_feet/COVERAGE;cans += (square_feet%COVERAGE==0)?0:1;printf("you need %d %s of paint.\n", cans, (cans==1)?"can":"cans");}return 0;}enter the square feet you need to paint:349you need 1 can of paint.351you need 2 cans of paint.700you need 2 cans of paint.701you need 3 cans of paint.
continue


示例 求多个分数的均值,用continue跳过不合法输入,也用了条件运算符
#include <stdio.h>#define MIN 0.0f#define MAX 100.0fint main(){float score, max=MIN, min=MAX, total=0.0;int n = 0;//分数的个数printf("enter the first score:\n");while(scanf("%f", &score)==1){if(score < MIN || score > MAX){printf("The input score is invalid.\n");continue;}max = (score>max)?score:max;min = (score<min)?score:min;total += score;n++;printf("enter next score(enter q to end the input):\n");}if(n>0){printf("The average score is %4.2f\nThe total score is %4.2f\n", total/n, total);printf("lowest: %4.2f\nhighest:%4.2f\n", min, max);}elseprintf("No valid scores were entered.\n");return 0;}enter the first score:2.3enter next score(enter q to end the input):4.5enter next score(enter q to end the input):5.6enter next score(enter q to end the input):qThe average score is 4.13The total score is 12.40lowest: 2.30highest:5.60
注意必须把n初始化为0,否则后面n++,最终得到的均值会完全错误
int n = 0;//分数的个数
另一点,注意max初始化为MIN,而不是MAX哦!把max初始化为比较小的值,然后后面只要比他大的就替换他
还有一点,scanf对float用的转换说明是%f,千万别写成double的%lf咯,不然也会错误
示例 continue;和空语句一样效果,跳过某些输入
#include <stdio.h>int main(){char c;while((c=getchar())!='\n');printf("%u", c);return 0;}werf,d sad dsd10
;空语句换为 continue;效果是一毛一样的
#include <stdio.h>int main(){char c;while((c=getchar())!='\n')continue;printf("%u", c);return 0;}qw dwkljk..sx10
跳过制表符
#include <stdio.h>int main(){char c;while((c=getchar())!='\n'){//除了制表符以外的都打印出来其ascii码if(c=='\t')continue;elseprintf("%u ", c);}return 0;}
我输入了空格,d,制表符,f,然后只打印了3个码
d f32 100 102
示例 break
#include <stdio.h>int main(){float length, width;printf("enter the length of the rectangle:\n");while(scanf("%f", &length)==1){printf("length = %0.2f\n", length);printf("enter its width:\n");if(scanf("%f", &width)!=1)break;printf("width=%0.2f\n", width);printf("area=%0.2f\n", length*width);printf("enter the length of the rectangle(enter q to quit):\n");}printf("Done.\n");return 0;}enter the length of the rectangle:12length = 12.00enter its width:23width=23.00area=276.00enter the length of the rectangle(enter q to quit):qDone.
其实我没懂上面程序的那两句代码
现在懂了,看后面的练习部分,有一道题用在switch语句中break;实现了和continue一毛一样的功能:跳过
这里应该也一样,就是跳过,什么也不做
if(scanf("%f", &width)!=1)break;
可以用while(scanf(“%f %f”, &length, &width)==2)简化上面的程序
#include <stdio.h>int main(){float length, width;printf("enter the length and width of the rectangle:\n");while(scanf("%f %f", &length, &width)==2){printf("length = %0.2f\n", length);printf("width=%0.2f\n", width);printf("area=%0.2f\n", length*width);printf("enter the length of the rectangle(enter q to quit):\n");}printf("Done.\n");return 0;}enter the length and width of the rectangle:12 23length = 12.00width=23.00area=276.00enter the length of the rectangle(enter q to quit):qDone.
switch
示例 对应不同输入给不同输出
#include <stdio.h>int main(){char ch;printf("Type in a letter in lowercase, type # to end my act.\n");while((ch = getchar())!='#'){if(ch=='\n')continue;elseswitch(ch){case 'a':printf("argali\n");break;case 'b':printf("babirusa\n");break;case 'c':printf("coati\n");break;case 'd':printf("desman\n");break;default:printf("That's a stumper!\n");}}printf("Bye!\n");return 0;}Type in a letter in lowercase, type # to end my act.aargaligThat's a stumper!sThat's a stumper!2That's a stumper!hThat's a stumper!bbabirusa# Bye!

删除上面程序的switch语句的所有break,输入一个a,会把case a后面 的语句全部执行一遍
Type in a letter in lowercase, type # to end my act.aargalibabirusacoatidesmanThat's a stumper!
continue不可用于switch语句
示例 switch的多重标签 投票(同一个字母的大小写识别为同样输入)
#include <stdio.h>int main(){unsigned short a_cnt, e_cnt, i_cnt, o_cnt, u_cnt;a_cnt = e_cnt = i_cnt = o_cnt = u_cnt = 0;char ch;printf("vote for the five letters a e i o u:(enter # to end voting.)\n");while((ch=getchar())!= '#'){switch(ch){case 'a':case 'A':a_cnt++;break;case 'E':case 'e':e_cnt++;break;case 'i':case 'I':i_cnt++;break;case 'o':case 'O':o_cnt++;break;case 'u':case 'U':u_cnt++;break;default:break;}}printf("\nEnd of voting! The number of vowels:\na:%u\ne:%u\ni:%u\no:%u\nu:%u\n", a_cnt, e_cnt, i_cnt, o_cnt, u_cnt);return 0;}vote for the five letters a e i o u:(enter # to end voting.)aaaoooiiiuueehj#End of voting! The number of vowels:a:3e:2i:3o:3u:2
上面的多重标签代码可以被改进地更短更简单,即统一转换为大写或小写:
#include <stdio.h>#include <ctype.h>int main(){unsigned short a_cnt, e_cnt, i_cnt, o_cnt, u_cnt;a_cnt = e_cnt = i_cnt = o_cnt = u_cnt = 0;char ch;printf("vote for the five letters a e i o u:(enter # to end voting.)\n");while((ch=getchar())!= '#'){switch(tolower(ch))//加这么一点就可以不用多重标签了{case 'a':a_cnt++;break;case 'e':e_cnt++;break;case 'i':i_cnt++;break;case 'o':o_cnt++;break;case 'u':u_cnt++;break;default:break;}}printf("\nEnd of voting! The number of vowels:\na:%u\ne:%u\ni:%u\no:%u\nu:%u\n", a_cnt, e_cnt, i_cnt, o_cnt, u_cnt);return 0;}

跳转
goto语句(不用!!!)


练习
‘b’>‘a’ 是true
#include <stdio.h>int main(){if('b'>'a')printf("char can be compared.\n");return 0;}char can be compared.
switch(i++)

还真是没想到输出这个,主要是没注意到没有break,所以后面的都会输出一次
fat hat cat oh no!hat cat oh no!cat oh no!
加上break的话
#include <stdio.h>int main(){int i = 0;while(i<3){switch(i++){case 0: printf("fat ");break;case 1: printf("hat ");break;case 2: printf("cat ");break;default: printf("oh no!");}putchar('\n');}return 0;}fathatcat
把==写成=,结果就是 will never end···


改好后
You are 40. Here is a raise.You are 60. Here is a raise.You are 65. Here is your gold watch.#include <stdio.h>int main(){char ch;while((ch=getchar())!='#'){if(ch=='\n')continue;printf("step 1\n");if(ch=='c')continue;else if(ch=='b')break;else if(ch=='h')goto laststep;printf("step 2\n");laststep: printf("step 3\n");}printf("Done!\n");return 0;}astep 1step 2step 3cstep 1hstep 1step 3bstep 1Done!
如果以下列顺序输入呢,会输出什么
和我的a c h b一毛一样,因为除了定义的几个字母以外的字母都会打印三句
qstep 1step 2step 3cstep 1hstep 1step 3bstep 1Done!
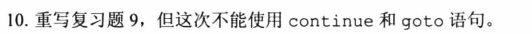
复习题9就是上面这个,不是很好改呢,小花了3分钟
由于不用goto又要跳转就只好用switch了,用default输出上面程序本来就要输出的三句;
输入换行符什么也不做所以直接break;起到了和continue一样的效果
记住每个case一定要break,这大概是switch语句最容易出错的地方了
#include <stdio.h>int main(){char ch;while((ch=getchar())!='#'){switch(ch){case '\n':break;case 'c':printf("step 1\n");break;case 'b':printf("step 1\n");break;case 'h':printf("step 1\n");printf("step 3\n");break;default:printf("step 1\n");printf("step 2\n");printf("step 3\n");break;}if(ch=='b')break;}printf("Done!\n");return 0;}

#include <stdio.h>int main(){char ch;int space_cnt=0, n_lines=0, other_cnt=0;printf("enter # to quit.\n");while((ch=getchar())!='#'){if(ch==' ')space_cnt++;else if(ch=='\n')n_lines++;elseother_cnt++;}printf("spaces:%d\nlines:%d\nother characters:%d\n", space_cnt, n_lines, other_cnt);return 0;}enter # to quit.sd sdsj ,./';]ddddhtuo r w# spaces:8lines:6other characters:22
如果把提示语放在while里面,就会这样,每输入一个字符打印一次
sdenter # to quit.enter # to quit.enter # to quit.denter # to quit.enter # to quit.fenter # to quit.enter # to quit.


































还没有评论,来说两句吧...