netty实现http客户端请求远程http服务
一般http请求,我们会使用httpclient来实现连接池方式的连接,根据请求的类型,封装get,post等请求,设置参数,设置请求头,调用方法,发送请求之后等待请求返回结果,根据结果解析出我们需要的数据。netty也可以实现httpclient类似的功能,只不过,很多时候,我们使用netty构建tcp的连接,要么使用netty构建http服务端,很少用来构建http客户端,其实和tcp客户端类似,构建http客户端也很简单,但是需要注意的是,请求以及响应的相对关系处理。使用netty构建http客户端,我们需要在pipeline这里加入请求编码器,响应解码器,以及发送请求和处理响应的handler。在发送请求的时候,我们需要构造FullHttpRequest,设置uri,header等信息,然后就可以通过ctx.writeAndFlush(request)调用即可。另外当我们处理channelRead()即获取响应的时候,需要对响应体做类型转换,一般来说我们得到的msg是FullHttpResponse。本人在编写netty实现http客户端程序的时候,发现当我使用http1.1类型的时候,无论如何,都无法正确请求springboot项目的方法,channelRead()方法倒是会收到数据,请求状态码总是400,很纳闷,这不是参数错误么,后来就把http1.1改为了http1.0,请求正常,返回了正确结果,但是结果里显示http1.1,也是很奇怪。准备工作,如下所示,本机开启一个springboot服务,开启一个接口http://localhost:8081/user/get,在命令行下,模拟发送请求,响应如下:![20191108231557650.png][]代码如下所示,主要的方法中一个简单的group,bootstrap,然后设置childHandler,在childHandler中再设置处理请求和响应相关的decoder,encoder,handler。
HttpClient.java
package com.xxx.http.client;import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;import io.netty.channel.Channel;import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpClientCodec;import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpContentDecompressor;import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator;import com.xxx.http.client.handler.HttpClientHandler;public class HttpClient {public static void start(String host,int port){EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();try {bootstrap.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true).handler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(Channel channel)throws Exception {//channel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpRequestEncoder());//channel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpResponseDecoder());channel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpClientCodec());channel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(65536));channel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpContentDecompressor());channel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpClientHandler());}});ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync();future.channel().closeFuture().sync();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally{group.shutdownGracefully();}}public static void main(String[] args) {//start("127.0.0.1", 8000);start("127.0.0.1", 8081);}}
HttpClientHandler.java
package com.xxx.http.client.handler;import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;import io.netty.handler.codec.http.DefaultFullHttpRequest;import io.netty.handler.codec.http.FullHttpRequest;import io.netty.handler.codec.http.FullHttpResponse;import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaderNames;import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaderValues;import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpMethod;import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpVersion;import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;import java.net.URI;public class HttpClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {@Overridepublic void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {URI uri = new URI("/user/get");FullHttpRequest request = new DefaultFullHttpRequest(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_0, HttpMethod.GET, uri.toASCIIString());request.headers().add(HttpHeaderNames.CONNECTION,HttpHeaderValues.KEEP_ALIVE);request.headers().add(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH,request.content().readableBytes());ctx.writeAndFlush(request);}@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)throws Exception {System.out.println("msg -> "+msg);if(msg instanceof FullHttpResponse){FullHttpResponse response = (FullHttpResponse)msg;ByteBuf buf = response.content();String result = buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);System.out.println("response -> "+result);}}}
运行HttpClient.java主程序,控制台打印信息如下所示:
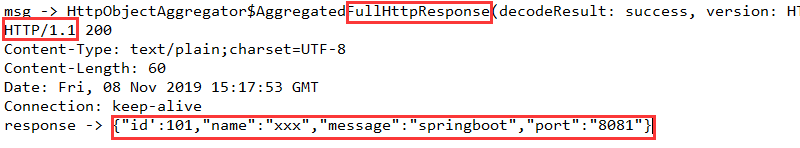
这里有几个重要的信息,一个是msg原始信息,我们打印出来,有几行,第一行就是明确显示FullHttpResponse,第二行折行显示了返回的http版本信息以及http状态码200,后面几行显示了响应体数据格式、响应体长度、响应时间、以及连接状态。最后一句打印的是response经过类型转换获取的ByteBuf的字符串值。也就是我们在命令行下通过curl获取的结果是一样的。我们将HttpClientHandler类中channelActive()方法中的构造请求体的参数HttpVersion.HTTP\_1\_0,改为HttpVersion.HTTP\_1\_1,我们再来运行一下,会发生什么?![watermark_type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk_shadow_10_text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L2ZlaW5pZmk_size_16_color_FFFFFF_t_70][]这个问题很奇怪,不知道如何解释,为什么我们的http1.0改为http1.1竟然就不正确,还报了400错误码,如果有同学遇到了编写http客户端,获取结果不正确的或者报错,可以留意一下。另外一个问题,就是有可能,我们的handler中请求编写的都是正确的, 服务端也响应了,但就是channelRead()方法好像不执行,可以检查一下我们在pipeline这里设置编解码是否正确,他们的顺序也很重要。再一个就是,当我们使用netty构建一个http服务端的时候,我们也可以通过http客户端来调用服务端的接口,这时候http1.0和http1.1都可以,没有那么多的限制。这一点也很奇怪。



































还没有评论,来说两句吧...