【数据结构】---栈和队列的实现【C语言实现】
目录
栈的实现
队列的实现
1. 栈的实现
栈是一种先进后出的数据结构。
栈(stack)是限定仅在表的一端进行操作的数据结构,只有一个入口和出口,只能从这个口子,进去或者出去。
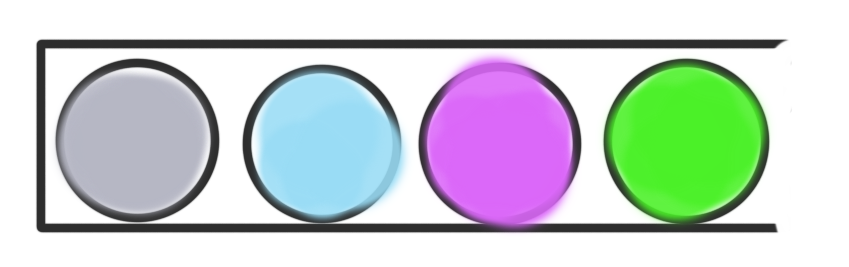
如图:栈就像一个放球的单管桶,只允许球从桶的开口这一端取出,并且球先放入桶中则后从桶中拿出。
栈的节点的设计
栈分为数组栈和链表栈,其区别是数组栈使用数组进行功能的模拟,实现较为快速和便利,
而链表栈使用链表的思路去设计,实现较为麻烦,但是其稳定不易出错;
在链表栈中又分为静态链表栈和动态链表栈,静态链表栈给定栈的空间大小,不允许超过存储超过给定数据大小的元素,
而动态栈使用的是自动创建空间的方法进行创建,只要符合机器的硬件要求以及编译器的控制,其理论上是极大的。
我们以链表栈的动态链表栈为例子,
先设计2 个结构体,
一个作为保存节点数值和指向下一个节点的指针,
另一个用于节点数量和指向最顶端的节点指针
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>// 栈的实现,一种先进后出的数据结构// 定义 2 个结构体typedef struct node{int data;struct node *next;}Node;typedef struct stack{int count;// 用于计算栈的大小Node *top; // 用于指向最顶端的节点}Link_stack;
初始化头部节点
// 初始化头部节点Link_stack *init(){Link_stack *head;head = (Link_stack *)malloc(sizeof(Link_stack ));if (head == NULL){printf("无法创建--- \n");exit(0);}head->count = 0;head->top = NULL;return head;}
将元素 push 进链表,并更新头部节点的指针
void stack_push(Link_stack *head, int value){if (head == NULL){printf("请先创建一个头部节点---- \n");return NULL;}Node *temp = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));temp->data = value;temp->next = head->top;head->top = temp; // 更新头部节点head->count++;}
打印栈的大小
int stack_size(Link_stack *head){return head->count;}
将元素 pop 出链表,返回删除了的元素的数值
int stack_pop(Link_stack *head){if (head == NULL) return -1;Node *temp = head->top;int res = temp->data;head->top = temp->next; // 指向下一个节点就可以,记得free tempfree(temp);head->count--;return res;}
遍历栈 链表结构
void show_stack(Link_stack *head){if (stack_size(head) == 0){printf("stack data is empty \n");}Node *temp = head->top;while (temp != NULL){printf("stack data is : %d \n", temp->data);temp = temp->next;}}
测试代码:
int main(){printf("starting ------ \n");Link_stack *head = init();for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){stack_push(head, i+1);}show_stack(head);printf("delete stack node : %d \n", stack_pop(head));printf("delete stack node : %d \n", stack_pop(head));printf("stack size : %d \n", stack_size(head));show_stack(head);return 0;}
2. 队列的实现
队列是一个先进先出的数据结构。
队列(queue)是限定在表的一端进行插入,表的另一端进行删除的数据结构,如同栈的学习,请联系前文所学链表,试想一个单链表,我们只能对他的链表表尾进行插入,而只能对链表的表头进行结点的删除,其余一切的操作均不允许,这样强限制性的“链表“,就是我们所说的队列。
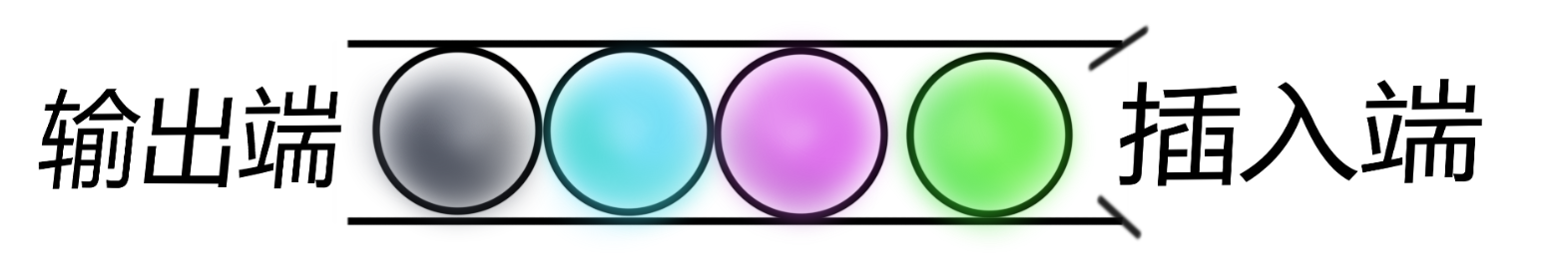
如图:队列就像一个两端相通的水管,只允许一端插入,另一端取出,先放入管中的球先从管中拿出。
设定2 个结构体
next指针表示,下一个的指针,其指向下一个结点,通过next指针将各个结点链接。
我们也额外添加一个结构体,其包括了两个分别永远指向队列的队尾和队头的指针,由于队列只能从头节点删除,尾节点插入,所以需要保存 2 个节点
// 定义 2 个结构体typedef struct node{int data;struct node *next;}Node;typedef struct my_q{Node *front; // 保存指向头节点的指针Node *rear; // 保存指向尾部节点的指针int size;}queue;
入队操作:
- 进行入队(push)操作的时候,我们首先需要特判一下队列是否为空,如果队列为空的话,需要将头指针和尾指针一同指向第一个结点
- 当如果队列不为空的时候,我们只需要将尾结点向后移动,通过不断移动next指针指向新的结点构成队列即可
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>// 队列的实现,一种先进先出的数据结构,// 定义 2 个结构体typedef struct node{int data;struct node *next;}Node;typedef struct my_q{Node *front; // 保存指向头节点的指针Node *rear; // 保存指向尾部节点的指针int size;}queue;// 初始化队列queue *init_queue(){queue *q = (queue*)malloc(sizeof(queue));if (q == NULL){printf("无法创建----- \n");exit(0);}q->front = NULL;q->rear = NULL;q->size = 0;return q;}// 判断是否为空:int isEmpty(queue* q){return q->front == NULL;}// 将元素 push 进链表队列中void queue_push(queue *q, int value){Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));temp->data = value;temp->next = NULL; // 设置最后指针指向空,否则遍历无法终止// 如果是为空情况下if (isEmpty(q)){q->front = temp;q->rear = temp;q->size++;}else{q->rear->next = temp; // 将队列连接起来q->rear = temp; // 更新尾部节点q->size++;}}// 队列的大小int queue_size(queue *q){return q->size;}// 将元素 pop 出链表,返回删除了的元素的数值int queue_pop(queue *q){if (isEmpty(q)){printf("queue is empty -- \n");return 0;}else{Node *temp = q->front;int res = temp->data;q->front = q->front->next; // 删除节点q->size--;free(temp);return res;}}// 遍历队列结构void show_queue(queue *q){if (q->front == NULL){printf("queue is empty --- \n");}else{Node *node = q->front;while (node != NULL){printf("node data is : %d \n", node->data);node = node->next;}printf(" over --- \n");}}int main(){printf("starting ------2222 \n");queue *q = init_queue();for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){queue_push(q, i + 1);}show_queue(q);printf("size of queue is : %d \n", queue_size(q));printf("delete node: %d \n", queue_pop(q));printf("delete node: %d \n", queue_pop(q));show_queue(q);printf("size of queue is : %d \n", queue_size(q));return 0;}
项目推荐:
2000多G的计算机各行业电子资源分享(持续更新)
2020年微信小程序全栈项目之喵喵交友【附课件和源码】
Spring Boot开发小而美的个人博客【附课件和源码】
Java微服务实战296集大型视频-谷粒商城【附代码和课件】
Java开发微服务畅购商城实战【全357集大项目】-附代码和课件
最全最详细数据结构与算法视频-【附课件和源码】






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...