第六节:分布式配置中心SpringCloudConfig
一、项目准备
为了方便服务配置文件统一管理,实时更新,所以需要分布式配置中心组件。SpringCloudConfig组件的作用就是从GIT上加载配置文件。然后有一个Client,使用刚才读取到的配置文件。这样的话,就可以避免因为某个配置文件更新,导致需要重启一些微服务的麻烦。
需要在GIT上创建仓库,然后创建一个文件夹,里面放了三种不同的配置文件。https://github.com/hairdryre/Study\_SpringCloud 这是我的SpringCloud的学习的仓库。仓库有了,然后我再创建一个config/chapter6文件夹,用于放配置文件。我创建了三个配置文件,分别是开发环境的jay-config-dev.properties,测试环境的jay-config-test.properties与生产环境的jay-config-pro.properties。配置文件的内容也很简单。比如开发环境的键值对:jay.label = dev。

二、搭建Server端口
2.1 创建父项目main
首先创建一个maven项目,我习惯将其命名为main。导入依赖,父项目的依赖与以前的一样,比较长,可以参考源码。2.2 创建Server模块右击项目根目录,New--Module--选择左侧的Maven,点击next--输入新模块的名字config-server。为config-server子模块导入依赖。<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId></dependency></dependencies>
2.3 编写application.yml配置文件
在spring.cloud.config.server.git下,设置配置中心的相关路径。#项目部署的端口server:port: 8001spring:#当前项目的名字application:name: spring-cloud-config-server#配置中心的相关配置cloud:config:server:git:# 配置git仓库的URL地址uri: https://github.com/hairdryre/Study_SpringCloud# git仓库地址下的文件夹,可以配置多个,用“,”分割。search-paths: config/chapter6#公共仓库可不用配置帐号密码username:password:
2.4 编写启动类
使用@EnableConfigServer开启配置中心。
package com.safesoft.server;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer;/*** @author jay.zhou* @date 2019/1/27* @time 14:09*/@SpringBootApplication@EnableConfigServerpublic class ApplicationServer {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(ApplicationServer.class, args);}}
2.5 测试
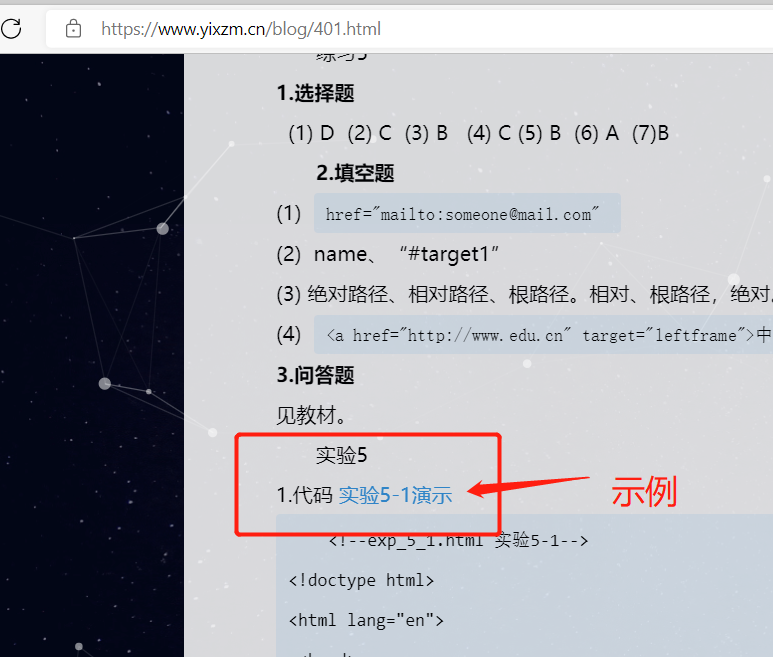
访问http://localhost:8001/jay-config/dev,也就是说访问git上的 jay-config-dev.properties。虽然我也不知道为什么就能访问到了这个配置文件,但是我想这应该也是一种约定吧。我本机的效果如下,我通过F12工具,看到了最关键的一条属性,就是配置文件中的键值对: jay.label = dev;

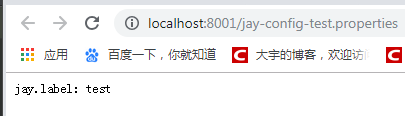
直接访问配置文件的内容:发送http://localhost:8001/jay-config-test.properties
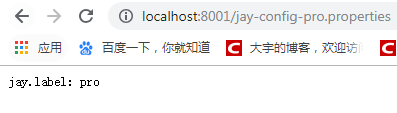
直接访问配置文件的内容:发送http://localhost:8001/jay-config-pro.properties
搜集的资料:SpringBoot的核心思想就是约定优于配置,所以仓库中的配置文件会被转换成web接口,访问可以参照以下的规则:
/{application}/{profile}[/{label}]
/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{application}-{profile}.properties
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.properties
我们的配置文件是 jay-config-dev.properties,所以符合第四条,因此就有了如下映射
application = jay-config
profile = dev
三、搭建Client端
右击项目根目录,New--Module--选择左侧的Maven,点击next--输入新模块的名字**config-client,效果如下。**
2.1 导入依赖
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope></dependency></dependencies>
2.2 编写配置文件
有两个配置文件,一个application.properites,另外一个是bootstrap.properties。bootstrap.properties的加载优先级别要高于application.properties。application.properties配置文件就是配置当前项目的部署的端口号,还有当前项目的名称。内容比较简单。
spring.application.name=spring-cloud-config-client
server.port=8002
bootstrap.properties就很重要了。它指明了要去哪个Server端去获取此Server从GIT上获取的配置文件内容。
我在配置文件中使用生产环境的配置文件:jay-config-pro.properties,所以就像下面那样配置就好了。#对应{application}部分spring.cloud.config.name=jay-config#对应{profile}部分。如果想使用别的配置,修改这里成#spring.cloud.config.profile=dev 或者 spring.cloud.config.profile=testspring.cloud.config.profile=pro#配置中心的具体地址,即Server的端口spring.cloud.config.uri=http://localhost:8001/#git分支spring.cloud.config.label=master
2.3 编写Controller
使用@Value("$\{...\}")注解获取读取到的配置文件的内容package com.safesoft.client.web;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;/*** @author jay.zhou* @date 2019/1/27* @time 14:19*/@RestControllerpublic class IndexController {@Value("${jay.label}")private String label;@RequestMapping("/hello")public String test() {return label;}}
2.4 编写启动类
package com.safesoft.client;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;/*** @author jay.zhou* @date 2019/1/27* @time 14:18*/@SpringBootApplicationpublic class ApplicationClient {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(ApplicationClient.class, args);}}
2.5 测试
访问:http://localhost:8001/jay-config-pro.properties,我本机得到的结果
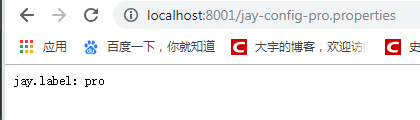
再从部署在8002端口的Client访问数据,访问:http://localhost:8002/hello
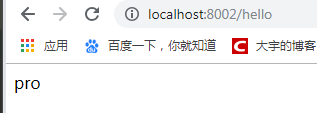
获取到jay-config-pro.properties里面的配置文件的内容,说明测试成功。
四、源码下载
https://github.com/hairdryre/Study\_SpringCloud
参考文章: 史上最简单的SpringCloud教程 | 第六篇: 分布式配置中心(Spring Cloud Config)(Finchley版本)springcloud(六):配置中心git示例 纯洁的微笑参考文章:[https://blog.csdn.net/yanluandai1985/article/details/86665973][https_blog.csdn.net_yanluandai1985_article_details_86665973]






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...