jdk源码解析七之Lock
文章目录
- Lock
- ReentrantLock
- 构造
- lock
- unlock
- tryLock
- newCondition
- 非公平策略获取锁
- 总结
- 非公平和公平获取锁的区别?
- ReadWriteLock
- ReentrantReadWriteLock
- 构造
- 获取读写锁
- 读锁
- lock
- unlock
- 写锁
- lock
- unlock
- 锁降级
- 总结
- LockSupport
- AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
- Condition
- newCondition
- await
- signal
- signalAll
- 总结
- CAS例子
同步锁,是可重入锁,这样当访问本类或者超类其他加锁方法时,也能访问成功,从而避免死锁
加锁,可保证互斥,内存可见性,避免重排序
3种方式1:减少锁持有时间H_AttributeStore/I_BetterAttributeStore由于只有一个状态变量,可以使用其他容器类,如SyncMap/ConcurrentHashMap,这样无需显示同步,缩小了访问锁的范围,降低了代码维护风险缩小同步代码块不能影响需要原子的操作分解多个同步代码块时,可以将大量计算或阻塞操作从同步代码块中移除时,应该考虑缩小锁范围设置定时锁(Lock)F_CooperatingNoDeadlock:对一些方法公开调用,且缩小锁的使用粒度,极快释放,避免竞争.对一些耗时操作,copy一份副本,操作.2:降低锁请求频率减小锁粒度可采用如下2方法,其本质是采用多个相互独立的锁来保护独立的状态变量锁分解:J_ServerStatusBeforeSplit/K_ServerStatusAfterSplit锁分段:L_StripedMap场景:锁上的竞争频率>锁保护的数据上发生的竞争频率3:使用带有协调机制的独占锁,这些机制允许更高的并发放弃独占锁:使用并发容器,读写锁,不可变对象以及原子变量ReadWriteLock:多个读取以及单个写入的规则,读不需要加锁,写需要加锁原子变量:降低热点域时的开销,如静态计数器,序列发生器,AtomicLong等或者非独占锁
等待锁的时间长,选择阻塞.否则自旋
公平:等待时间最长的获取锁
非公平:随机获取锁
ABA问题无法确保当前值没有发生变化,V由A变成B,在由B变成A。可以使用AtomicStampedReference支持在2个变量上执行原子的条件更新,在引用上加版本号"避免ABA问题"AtomicMarkableReference:更新一个对象引用-布尔值二元组,通过二元组使节点保存在链表中同时又将其标记为"已删除的节点"
Lock


ReentrantLock
一个可重入的互斥锁 Lock
构造
public ReentrantLock() {//默认初始化非公平的AQSsync = new NonfairSync();}public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {//根据传入的值,选择公平还是非公平的策略sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();}
lock
public void lock() {//调用AQSsync.lock();}final void lock() {//更新state为1if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))//设置当前拥有独占访问权限的线程setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());else//以独占模式获取对象,忽略中断。acquire(1);}public final void acquire(int arg) {if (//是否能成功加锁!tryAcquire(arg) &&//阻塞获取锁acquireQueued(//将当前线程以及独占模式等待标记,存储到尾端节点addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))//获取锁的过程中,当出现中断时,会执行到这里selfInterrupt();}protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);}final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {//获取当前线程final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();//获取同步状态的值int c = getState();//说明锁空闲if (c == 0) {//这个在tryLock调用if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true;}}else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {//也就是这里支持重入锁//当前线程与当前拥有独占访问权限的线程一致//累加stateint nextc = c + acquires;if (nextc < 0) // overflowthrow new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");setState(nextc);return true;}return false;}final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {boolean failed = true;try {boolean interrupted = false;for (;;) {//返回前端节点final Node p = node.predecessor();/*如果是当前头节点且再次获取锁成功*/if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {//设置头结点为当前节点,以及清空当前节点的pre和threadsetHead(node);//释放GCp.next = null; // help GC//标记正常执行failed = false;return interrupted;}//检查并修改一个节点的状态,当该节点获取锁失败时。返回true如果线程需要阻塞。if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&//这里执行阻塞parkAndCheckInterrupt())//标记已中断interrupted = true;}} finally {if (failed)cancelAcquire(node);}}
unlock
public void unlock() {//释放锁sync.release(1);}public final boolean release(int arg) {if (//释放锁,成功则进入tryRelease(arg)) {//获取headNode h = head;//如果head不为空,且已经执行if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)//释放当前节点的下一个节点unparkSuccessor(h);return true;}//释放失败return false;}protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {//获取目前锁次数int c = getState() - releases;//如果当前线程不是当前拥有独占访问权限的线程,说明没有获取锁的情况下unlock,抛出异常if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();boolean free = false;//正常释放锁if (c == 0) {free = true;//清空当前拥有独占锁的线程setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);}//设置锁次数setState(c);return free;}private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {/** If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.*/int ws = node.waitStatus;//重置状态值if (ws < 0)compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);/** Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual* non-cancelled successor.*/Node s = node.next;//如果下一个节点为null,且状态取消了,则从尾端遍历,查找未取消的线程//所以当看到next字段为null时并不意味着当前节点是队列的尾部了。//无论如何,如果一个next字段显示为null,我们能够从队列尾向前扫描进行复核。if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {s = null;for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)if (t.waitStatus <= 0)s = t;}if (s != null)LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);}
tryLock
public boolean tryLock() {return sync.nonfairTryAcquire(1);}
newCondition
public Condition newCondition() {return sync.newCondition();}
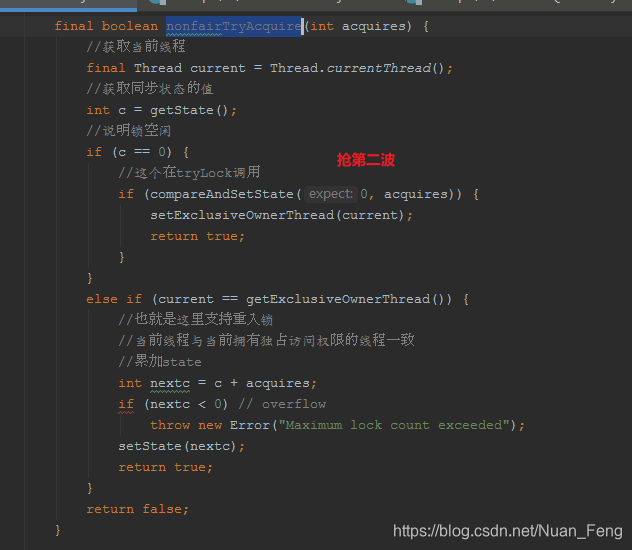
非公平策略获取锁
final void lock() {//以独占模式获取对象,忽略中断。acquire(1);}protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {//获取当前线程final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();int c = getState();//锁空闲if (c == 0) {//判断当前线程是否等待线程队列中的第二个线程//如果是说明等待最久if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {//设置当前拥有独占访问权限的线程setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true;}}else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {int nextc = c + acquires;if (nextc < 0)throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");setState(nextc);return true;}return false;}public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {// The correctness of this depends on head being initialized// before tail and on head.next being accurate if the current// thread is first in queue.Node t = tail; // Read fields in reverse initialization orderNode h = head;Node s;//判断当前线程是否是等待线程节点的下一个线程return h != t &&((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());}
总结
独占锁,支持可重入,每次重入时state+1
非公平和公平获取锁的区别?
非公平获取锁的时候,不管怎么说,先去抢一波.抢不到再去抢一波,是在抢不到才会添加AQS队列等待.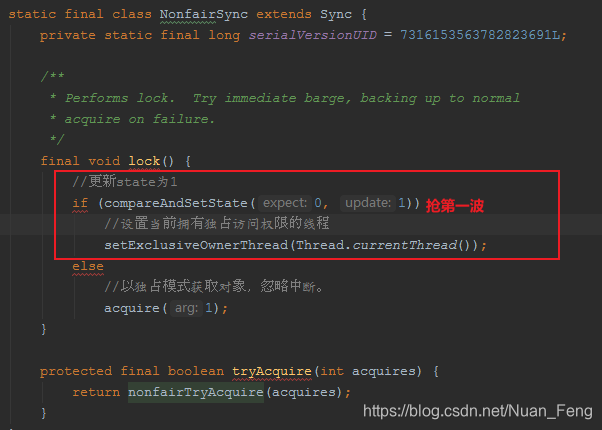
而公平锁先判断是不是等待最长的线程,如果是则去抢,否则加入队列抢.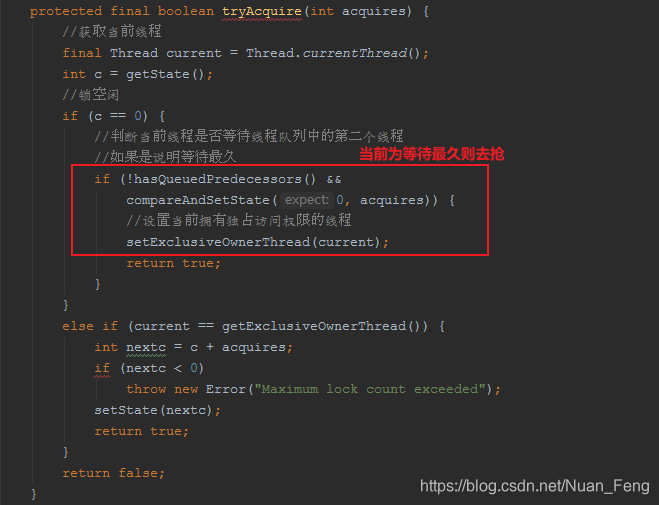
ReadWriteLock

分别维护2个锁,写锁是独占锁,读锁是共享锁,因为读的时间通常比写的时间长,所以写锁优先级比读锁高
ReentrantReadWriteLock
构造
public ReentrantReadWriteLock() {//默认独占this(false);}public ReentrantReadWriteLock(boolean fair) {sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();//静态内部类readerLock = new ReadLock(this);///静态内部类writerLock = new WriteLock(this);}//高16读锁,低16写锁static final int SHARED_SHIFT = 16;static final int SHARED_UNIT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT);static final int MAX_COUNT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1;static final int EXCLUSIVE_MASK = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1;/** Returns the number of shared holds represented in count *///返回共享个数static int sharedCount(int c) {return c >>> SHARED_SHIFT; }/** Returns the number of exclusive holds represented in count *///返回独占个数static int exclusiveCount(int c) {return c & EXCLUSIVE_MASK; }
获取读写锁
public ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writeLock() {return writerLock; }public ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readLock() {return readerLock; }
读锁
lock
public void lock() {sync.acquireShared(1);}protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {/** Walkthrough:* 1. If write lock held by another thread, fail.* 2. Otherwise, this thread is eligible for* lock wrt state, so ask if it should block* because of queue policy. If not, try* to grant by CASing state and updating count.* Note that step does not check for reentrant* acquires, which is postponed to full version* to avoid having to check hold count in* the more typical non-reentrant case.* 3. If step 2 fails either because thread* apparently not eligible or CAS fails or count* saturated, chain to version with full retry loop.*////获取当前线程Thread current = Thread.currentThread();//获取当前锁的数量int c = getState();//持有写锁失败if (//获取独占锁数量!=0exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&//且当前拥有独占访问权限的线程不等于当前线程,这里写锁可降级getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)return -1;//获取共享锁数量int r = sharedCount(c);/*第一次线程A读取,则记录第一个堵得线程以及个数第二次线程A读取,则当前访问线程个数+1第三次线程B读取,利用cachedHoldCounter缓存当前线程tid以及访问次数readHolds可以理解为一级缓存,绑定了每个线程的线程计数器cachedHoldCounter:二级缓存,缓存上一个线程执行重入锁的次数*/if (//线程是否应该被阻塞!readerShouldBlock() &&//共享锁数量<最大锁数量r < MAX_COUNT &&//更新共享锁数量compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {//如果是第一次读取if (r == 0) {//记录第一个读的线程firstReader = current;firstReaderHoldCount = 1;} else if (firstReader == current) {//如果当前访问的线程是第一个访问的线程,则访问线程数+1firstReaderHoldCount++;} else {//获取计数器HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;//计数器为null或者当前线程id不为正在运行线程idif (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))//获取当前计数线程对应计数器cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();else if (rh.count == 0)//设置线程计数器readHolds.set(rh);//线程重入次数+1rh.count++;}return 1;}//CAS尚未命中return fullTryAcquireShared(current);}final int fullTryAcquireShared(Thread current) {/** This code is in part redundant with that in* tryAcquireShared but is simpler overall by not* complicating tryAcquireShared with interactions between* retries and lazily reading hold counts.*/HoldCounter rh = null;for (;;) {int c = getState();//如果当前有独占锁,且独占线程非当前线程,则返回if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0) {if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)return -1;// else we hold the exclusive lock; blocking here// would cause deadlock.} else if (readerShouldBlock()) {//写锁没有被获取,且读线程被阻塞// Make sure we're not acquiring read lock reentrantly//当前第一个线程为读线程,说明当前线程重入if (firstReader == current) {// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;} else {if (rh == null) {//获取缓存的计数器rh = cachedHoldCounter;//没有缓存计数器,或者计数器线程tid非当前线程tid(也就是说非上一个获取锁的线程)//对写锁的让步,如果第一个获取锁的线程是写锁,那么后续所有线程AQS排队if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current)) {//获取线程计数器rh = readHolds.get();//重入锁数量为0if (rh.count == 0)//删除计数器readHolds.remove();}}//重入锁数量为0if (rh.count == 0)//AQS排队return -1;}}//读锁数量超过上限,异常if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT)throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");//设置读锁数量//当前线程是第一个获取读锁的线程,或是上一个执行任务的线程会执行到这里//也就是说重入获取读锁的线程才会执行到这里if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {//if (sharedCount(c) == 0) {firstReader = current;firstReaderHoldCount = 1;} else if (firstReader == current) {firstReaderHoldCount++;} else {if (rh == null)rh = cachedHoldCounter;if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))rh = readHolds.get();else if (rh.count == 0)readHolds.set(rh);//重入数量累加rh.count++;//缓存计数器cachedHoldCounter = rh; // cache for release}return 1;}}}final boolean readerShouldBlock() {//下一个锁是否是独占锁return apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive();}final boolean apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive() {Node h, s;return (h = head) != null &&(s = h.next) != null &&!s.isShared() &&s.thread != null;}
unlock
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int unused) {//获取当前线程Thread current = Thread.currentThread();//当前线程为第一个获取读锁的线程if (firstReader == current) {// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;//如果是最后一次释放锁,则直接置空firstReaderif (firstReaderHoldCount == 1)firstReader = null;else//头锁重入次数-1firstReaderHoldCount--;} else {//获取上一个获取读锁的线程计数器HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))//非上一次执行的线程,则获取当前线程计数器rh = readHolds.get();int count = rh.count;if (count <= 1) {//删除当前线程计数器readHolds.remove();//说明没有之前获取锁,直接释放则异常if (count <= 0)throw unmatchedUnlockException();}//线程重入次数-1--rh.count;}for (;;) {int c = getState();int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT;if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))// Releasing the read lock has no effect on readers,// but it may allow waiting writers to proceed if// both read and write locks are now free.//锁为0说明正确释放return nextc == 0;}}
写锁
lock
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {//获取当前线程Thread current = Thread.currentThread();///获取当前线程状态int c = getState();//获取独占锁重入数量int w = exclusiveCount(c);//如果有线程获取读写锁if (c != 0) {// (Note: if c != 0 and w == 0 then shared count != 0)//写锁没被占用,或当前拥有独占访问权限的线程不等于当前线程,说明有读锁被占用,返回falseif (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread())return false;//读写锁数量超过最大数量,异常if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT)throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");// Reentrant acquire//执行到这里,说明写锁被重入setState(c + acquires);return true;}//执行到这里说明没有读写锁占用if (//写锁是否阻塞writerShouldBlock() ||//修改状态!compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires))//如果写锁没有被阻塞,且修改状态失败,则返回falsereturn false;//设置锁被当前线程独占setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true;}
非公平获取锁是否阻塞
final boolean writerShouldBlock() {return false; // writers can always barge}
公平获取锁是否阻塞
final boolean writerShouldBlock() {return hasQueuedPredecessors();}public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {// The correctness of this depends on head being initialized// before tail and on head.next being accurate if the current// thread is first in queue.Node t = tail; // Read fields in reverse initialization orderNode h = head;Node s;//判断当前线程是否是等待线程节点的下一个线程return h != t &&((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());}
unlock
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {//拥有独占锁的不是当前线程,则异常if (!isHeldExclusively())throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();int nextc = getState() - releases;boolean free = exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0;//独占锁数量为0,则清空锁的持有者if (free)setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);//设置锁数量setState(nextc);return free;}
锁降级

* class CachedData {* Object data;* volatile boolean cacheValid;* final ReentrantReadWriteLock rwl = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();** void processCachedData() {* rwl.readLock().lock();* if (!cacheValid) {* // Must release read lock before acquiring write lock* rwl.readLock().unlock();* rwl.writeLock().lock();* try {* // Recheck state because another thread might have* // acquired write lock and changed state before we did.* if (!cacheValid) {* data = ...* cacheValid = true;* }* // Downgrade by acquiring read lock before releasing write lock* rwl.readLock().lock();* } finally {* rwl.writeLock().unlock(); // Unlock write, still hold read* }* }** try {* use(data);* } finally {* rwl.readLock().unlock();* }* }* }}
总结
当获取写锁的情况下,当前线程依旧能获取读锁,这称之为锁降级
当获取读锁情况下,不能获取写锁
这里始终保证了写锁>读锁等级.
避免了锁等级一样,出现获取锁的乱序问题.
读锁添加的State是SHARED_UNIT的倍数
这里分别用firstReader记录第一个获取读锁的线程
cachedHoldCounter获取上一个获取读锁的线程计数器
readHolds记录每个线程锁对应的计数器
如果下一个锁是独占锁,且非公平模式下,则后续所有线程都进入AQS等待锁,只有已经获取读锁的依旧可以执行
final boolean readerShouldBlock() {//下一个锁是否是独占锁return apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive();}protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {/if (//线程是否应该被阻塞!readerShouldBlock() &&{//...}//CAS尚未命中return fullTryAcquireShared(current);}final int fullTryAcquireShared(Thread current) {HoldCounter rh = null;for (;;) {int c = getState();//如果当前有独占锁,且独占线程非当前线程,则返回if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0) {if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)return -1;/} else if (readerShouldBlock()) {/}//读锁数量超过上限,异常if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT)throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");//设置读锁数量//当前线程是第一个获取读锁的线程,或是上一个执行任务的线程会执行到这里//也就是说重入获取读锁的线程才会执行到这里if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {//if (sharedCount(c) == 0) {firstReader = current;firstReaderHoldCount = 1;} else if (firstReader == current) {firstReaderHoldCount++;} else {if (rh == null)rh = cachedHoldCounter;if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))rh = readHolds.get();else if (rh.count == 0)readHolds.set(rh);//重入数量累加rh.count++;//缓存计数器cachedHoldCounter = rh; // cache for release}return 1;}}}
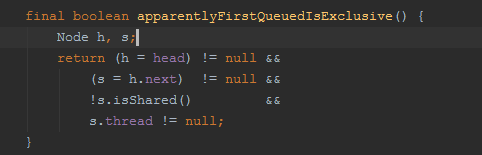
公平模式下直接让下一个线程获取锁
final boolean readerShouldBlock() {return hasQueuedPredecessors();}public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {// The correctness of this depends on head being initialized// before tail and on head.next being accurate if the current// thread is first in queue.Node t = tail; // Read fields in reverse initialization orderNode h = head;Node s;return h != t &&((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());}
LockSupport
park:为了线程调度,禁用当前线程,除非许可可用。
unpark:如果给定线程的许可尚不可用,则使其可用。
class FIFOMutex {private final AtomicBoolean locked = new AtomicBoolean(false);private final Queue<Thread> waiters= new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Thread>();public void lock() {boolean wasInterrupted = false;Thread current = Thread.currentThread();waiters.add(current);// Block while not first in queue or cannot acquire lockwhile (waiters.peek() != current ||!locked.compareAndSet(false, true)) {LockSupport.park(this);if (Thread.interrupted()) // ignore interrupts while waitingwasInterrupted = true;}waiters.remove();if (wasInterrupted) // reassert interrupt status on exitcurrent.interrupt();}public void unlock() {locked.set(false);LockSupport.unpark(waiters.peek());}}
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizerextends AbstractOwnableSynchronizerimplements java.io.Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 7373984972572414691L;static final class Node {/** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in shared mode */static final Node SHARED = new Node();/** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in exclusive mode */static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;/** waitStatus value to indicate thread has cancelled *///这个节点由于超时或中断被取消了。节点不会离开(改变)这个状态。尤其,一个被取消的线程不再会被阻塞了static final int CANCELLED = 1;/** waitStatus value to indicate successor's thread needs unparking *//* 这个节点的后继(或者即将被阻塞)被阻塞(通过park阻塞)了,所以当前节点需要唤醒它的后继当它被释放或者取消时。为了避免竞争,获取方法必须首先表示他们需要一个通知信号,然后再原子性的尝试获取锁,如果失败,则阻塞。也就是说,在获取锁的操作中,需要确保当前node的preNode的waitStatus状态值为’SIGNAL’,才可以被阻塞,当获取锁失败时。(『shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire』方法的用意就是这)*/static final int SIGNAL = -1;/** waitStatus value to indicate thread is waiting on condition *//* 这个节点当前在一个条件队列中。它将不会被用于当做一个同步队列的节点直到它被转移到同步队列中,转移的同时状态值(waitStatus)将会被设置为0。(这里使用这个值将不会做任何事情与该字段其他值对比,只是为了简化机制)。*/static final int CONDITION = -2;//一个releaseShared操作必须被广播给其他节点。(只有头节点的)该值会在doReleaseShared方法中被设置去确保持续的广播,即便其他操作的介入。static final int PROPAGATE = -3;}private Node enq(final Node node) {//(自旋+CAS)for (;;) {Node t = tail;//初始化,头和尾为空节点if (t == null) {// Must initializeif (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))tail = head;} else {///设置尾部节点node.prev = t;if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {//这里可能出现next=null短暂现象.t.next = node;return t;}}}}private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {//包装当前线程以及表示该节点正在共享或独占模式下等待Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failureNode pred = tail;if (pred != null) {//将当前节点添加到尾部节点node.prev = pred;if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {pred.next = node;return node;}}enq(node);return node;}private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {int ws = node.waitStatus;//重置状态值if (ws < 0)compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);Node s = node.next;//如果下一个节点为null,且状态取消了,则从尾端遍历,查找未取消的线程//所以当看到next字段为null时并不意味着当前节点是队列的尾部了。//无论如何,如果一个next字段显示为null,我们能够从队列尾向前扫描进行复核。if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {s = null;for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)if (t.waitStatus <= 0)s = t;}if (s != null)LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);}private void doReleaseShared() {//广播释放所有阻塞的锁for (;;) {Node h = head;if (h != null && h != tail) {int ws = h.waitStatus;//更新默认值0,且解除parkif (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))continue; // loop to recheck casesunparkSuccessor(h);}else if (ws == 0 &&!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))continue; // loop on failed CAS}if (h == head) // loop if head changedbreak;}}private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate) {Node h = head; // Record old head for check below//设置当前节点为头节点,以及清空当前线程和前置节点setHead(node);//如果闭锁是开的,且头为null,且waitStatus//如果标识了广播(propagate>0),if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ||(h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0) {Node s = node.next;//如果当前节点为null或者当前节点为共享等待标记,则释放,执行//enq初始化时,会有短暂为null现象if (s == null || s.isShared())doReleaseShared();}}private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {// Ignore if node doesn't existif (node == null)return;node.thread = null;// Skip cancelled predecessors//将node的prev属性指向一个在它之前的有效的节点Node pred = node.prev;while (pred.waitStatus > 0)node.prev = pred = pred.prev;// predNext is the apparent node to unsplice. CASes below will// fail if not, in which case, we lost race vs another cancel// or signal, so no further action is necessary./* 这个predNext是pred表面上的下一个连接的节点(即,无需考虑该节点是否被取消了)。下面的CAS操作将会失败(『compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);』or『compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next);』),如果和其他的取消或通知操作发生竞争时,这时不需要进一步的操作。因为如果产生竞争,说明pred的next已经被修改了,并且是最新的值了,而我们的操作也就没有要执行的必要了。*/Node predNext = pred.next;// Can use unconditional write instead of CAS here.// After this atomic step, other Nodes can skip past us.// Before, we are free of interference from other threads./* 将node的waitStatus设置为’CANCELLED’。这里可以使用无条件的写代替CAS(注意,node的waitStatus是volatile的)。在这个原子操作之后,其他节点会跳过我们(即,跳过waitStatus被置位CANCELLED的节点),在这个原子操作之前,我们不受其他线程的干扰。也就是说,无论其他线程对node的waitStatus是否有在操作,在当前的情况下我们都需要将这个node的waitStatus置为’CANCELLED’。*/node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;// If we are the tail, remove ourselves./* 如果待取消的node节点是队列尾节点的话(即,『node == tail』),那么删除node自己即可。使用CAS将tail节点设置成前面得到的第一个有效前驱节点(即,『compareAndSetTail(node, pred)』)。并且CAS操作成功的话,执行『compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);』也就是将tail的next置为null的意思。如果该CAS操作失败的话,没关系。说明此时tail已经被修改了。*/if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) {compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);} else {// If successor needs signal, try to set pred's next-link// so it will get one. Otherwise wake it up to propagate.int ws;if (//pred不是head节点pred != head &&//pred.waitStatus为SIGNAL” 或者((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||//“pred.waitStatus <= 0”时且通过CAS将pred.waitStatus设置为SIGNAL”成功(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&//pred的thread非空pred.thread != null) {Node next = node.next;/* 当node的next节点非空,且next节点的waitStatus<=0(说明next节点未被取消)时,通过CAS将pred的next执行node的next(即,pred.next = node.next)。同时,如果该CAS操作失败是没关系的,说明有其他线程操作已经修改了该pre的next值。*/if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0)compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next);} else {//释放当前这个待取消节点的下一个节点。//当prev是head节点,或者prev也被取消的话,会执行『unparkSuccessor(node);』来释放node的下一个节点,其实也就是pred的下一个节点)unparkSuccessor(node);}//释放GCnode.next = node; // help GC}}private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {int ws = pred.waitStatus;//则说明node的前驱节点已经被要求去通知释放它的后继节点,所以node可以安全的被挂起(park)if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)/** This node has already set status asking a release* to signal it, so it can safely park.*/return true;if (ws > 0) {//则说明node的前驱节点被取消了。那么跳过这个前驱节点并重新标志一个有效的前驱节点(即,// waitStatus <= 0 的节点可作为有效的前驱节点),然后,退出方法,返回false。/** Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and* indicate retry.*/do {node.prev = pred = pred.prev;} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);pred.next = node;} else {//其他情况下,即pred.waitStatus为’0’或’PROPAGATE’。// 表示我们需要一个通知信号(即,当前的node需要唤醒的通知),// 但是当前还不能挂起node。// 调用『compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL)』方法通过CAS的方式来修改前驱节点的waitStatus为“SIGNAL”。// 退出方法,返回false。/** waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.*///等待状态值指示后续线程需要断开连接compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);}return false;}private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {//为了线程调度,在许可可用之前禁用当前线程。LockSupport.park(this);//测试当前线程是否已经中断。return Thread.interrupted();}final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {boolean failed = true;try {boolean interrupted = false;for (;;) {//返回前端节点final Node p = node.predecessor();/*如果是当前头节点且再次获取锁成功*/if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {//设置头结点为当前节点,以及清空当前节点的pre和threadsetHead(node);//释放GCp.next = null; // help GC//标记正常执行failed = false;return interrupted;}//检查并修改一个节点的状态,当该节点获取锁失败时。返回true如果线程需要阻塞。if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&//这里执行阻塞parkAndCheckInterrupt())//标记已中断interrupted = true;}} finally {if (failed)cancelAcquire(node);}}/*** Acquires in shared interruptible mode.* @param arg the acquire argument*/private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)throws InterruptedException {//将当前线程以及共享模式等待标记,存储到尾端节点final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);//标记是否正常处理,如果出现中断,则取消执行boolean failed = true;try {for (;;) {//返回前端节点final Node p = node.predecessor();//如果是当前头节点/*经过发现,只有head节点,执行完后,才会执行下一个节点*/if (p == head) {//判断闭锁是否是开的int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);//如果闭锁是开的if (r >= 0) {//设置node为head,以及清空node的pre和threadsetHeadAndPropagate(node, r);//释放GCp.next = null; // help GC//标记正确执行failed = false;return;}}//检查并修改一个节点的状态,当该节点获取锁失败时。返回true如果线程需要阻塞。if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&//这里执行阻塞parkAndCheckInterrupt())throw new InterruptedException();}} finally {if (failed)cancelAcquire(node);}}public final void acquire(int arg) {if (//是否能成功加锁!tryAcquire(arg) &&//阻塞获取锁acquireQueued(//将当前线程以及独占模式等待标记,存储到尾端节点addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))//获取锁的过程中,当出现中断时,会执行到这里selfInterrupt();}public final boolean release(int arg) {if (//释放锁,成功则进入tryRelease(arg)) {//获取headNode h = head;//如果head不为空,且已经执行if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)//释放当前节点的下一个节点unparkSuccessor(h);return true;}//释放失败return false;}public final void acquireShared(int arg) {//共享模式获取锁,忽略中断if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)doAcquireShared(arg);}public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)throws InterruptedException {//中断检测if (Thread.interrupted())throw new InterruptedException();//个数是否消耗完,消耗完则直接跳过,直接执行//否则执行下列方法if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);}public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {//检测闭锁是否开启if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {//释放doReleaseShared();return true;}return false;}public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {Node t = tail; // Read fields in reverse initialization orderNode h = head;Node s;//判断当前线程是否是等待线程节点的下一个线程return h != t &&((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());}}
Condition

主要看java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject
newCondition
public Condition newCondition() {return sync.newCondition();}final ConditionObject newCondition() {return new ConditionObject();}
await
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {//中断处理if (Thread.interrupted())throw new InterruptedException();//添加下一个节点到等待队列Node node = addConditionWaiter();//阻塞时候,会释放锁int savedState = fullyRelease(node);//1) 当在被通知前被中断则将中断模式设置为THROW_IE;// 2) 当在被通知后则将中断模式设置为REINTERRUPT(因为acquireQueued不会响应中断)。int interruptMode = 0;//如果不在同步队列,则阻塞while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {//阻塞当前线程//在另一个线程调用sign和unlock之后唤醒//调用sign,将当前等待线程添加到同步线程//然后调用unlock释放同步线程LockSupport.park(this);//如果中断,确保节点添加到同步队列,并跳出循环if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)break;}//阻塞竞争锁,如果被通知或者中断的话.获取锁的话会重新计入重入次数if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;if (node.nextWaiter != null) // clean up if cancelled//删除状态不为CONDITION的节点unlinkCancelledWaiters();//根据中断模式抛出异常if (interruptMode != 0)reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);}private Node addConditionWaiter() {//获取上一个等待节点Node t = lastWaiter;// If lastWaiter is cancelled, clean out.if (t != null && t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) {unlinkCancelledWaiters();t = lastWaiter;}//创建一个新的节点,并标记CONDITIONNode node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), Node.CONDITION);//如果上一个等待节点为空,则设置为第一个节点if (t == null)firstWaiter = node;else//否则设置为下一个节点t.nextWaiter = node;lastWaiter = node;return node;}final int fullyRelease(Node node) {boolean failed = true;try {int savedState = getState();//释放所有锁?if (release(savedState)) {failed = false;//返回保存状态return savedState;} else {throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();}} finally {//失败,则标记状态为取消if (failed)node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;}}final boolean isOnSyncQueue(Node node) {//如果节点在条件队列或者节点前置为null,则阻塞//prev为null的时候,说明是头节点,而头结点一般是空node,所以不可能是头结点//name也就是处于transferForSignal方法中compareAndSetWaitStatus和enq之间的中间状态if (node.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION || node.prev == null)return false;//如果有后续任务,说明被其他线程修改,已经入队if (node.next != null) // If has successor, it must be on queuereturn true;/** node.prev can be non-null, but not yet on queue because* the CAS to place it on queue can fail. So we have to* traverse from tail to make sure it actually made it. It* will always be near the tail in calls to this method, and* unless the CAS failed (which is unlikely), it will be* there, so we hardly ever traverse much.*///状态不是CONDITION,且前置节点不为null,后置节点为null,可能是尾节点,则从后查找//从后到前查找是否有node,如果没有说明还正在添加则阻塞//也就是enq调用compareAndSetTail存在并发修改失败return findNodeFromTail(node);}//尾部查找node节点private boolean findNodeFromTail(Node node) {Node t = tail;for (;;) {if (t == node)return true;if (t == null)return false;t = t.prev;}}private int checkInterruptWhileWaiting(Node node) {/*没有异常,返回0中断在通知之前,THROW_IE中断在通知之后,REINTERRUPT*/return Thread.interrupted() ?(transferAfterCancelledWait(node) ? THROW_IE : REINTERRUPT) :0;}final boolean transferAfterCancelledWait(Node node) {//当前节点状态为CONDITION,中断在通知之前//设置状态为0,将取消的线程添加到同步队列中if (compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0)) {enq(node);return true;}/** If we lost out to a signal(), then we can't proceed* until it finishes its enq(). Cancelling during an* incomplete transfer is both rare and transient, so just* spin.*//*节点不是CONDITION状态,这说明中断在通知之后自旋添加到队列中*/while (!isOnSyncQueue(node))Thread.yield();//线程在通知之后被取消return false;}final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {boolean failed = true;try {boolean interrupted = false;for (;;) {//返回前端节点final Node p = node.predecessor();/*如果是当前头节点且再次获取锁成功*/if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {//设置头结点为当前节点,以及清空当前节点的pre和threadsetHead(node);//释放GCp.next = null; // help GC//标记正常执行failed = false;return interrupted;}//检查并修改一个节点的状态,当该节点获取锁失败时。返回true如果线程需要阻塞。if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&//这里执行阻塞parkAndCheckInterrupt())//标记已中断interrupted = true;}} finally {if (failed)cancelAcquire(node);}}private void unlinkCancelledWaiters() {//删除状态不为CONDITION的节点//trail ->t->nextNode t = firstWaiter;//记录上一个状态为CONDITION的节点Node trail = null;while (t != null) {Node next = t.nextWaiter;if (t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) {t.nextWaiter = null;if (trail == null)firstWaiter = next;else//删除t节点trail.nextWaiter = next;if (next == null)lastWaiter = trail;}elsetrail = t;t = next;}}private void reportInterruptAfterWait(int interruptMode)throws InterruptedException {//抛出中断异常if (interruptMode == THROW_IE)throw new InterruptedException();else if (interruptMode == REINTERRUPT)//中断selfInterrupt();}
signal
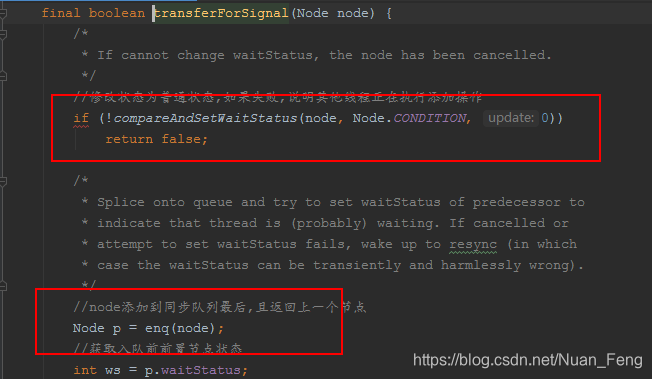
public final void signal() {//发送信号的是否是当前线程,如果不是则异常//确保signal在lock之后,且同一个线程if (!isHeldExclusively())throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();//获取第一个等待节点Node first = firstWaiter;if (first != null)//发送信号doSignal(first);}private void doSignal(Node first) {do {//删除first节点,并设置firstWaiter为下一个节点//如果下一个节点为null,则清空lastWaiterif ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null)lastWaiter = null;//清空first下一个节点first.nextWaiter = null;} while (//将删除的first节点添加到同步队列//如果添加失败,说明已经有其他线程添加成功了//却白first不为null,再次遍历!transferForSignal(first) &&(first = firstWaiter) != null);}final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {/** If cannot change waitStatus, the node has been cancelled.*///修改状态为普通状态,如果失败,说明其他线程正在执行添加操作if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))return false;/** Splice onto queue and try to set waitStatus of predecessor to* indicate that thread is (probably) waiting. If cancelled or* attempt to set waitStatus fails, wake up to resync (in which* case the waitStatus can be transiently and harmlessly wrong).*///node添加到同步队列最后,且返回上一个节点Node p = enq(node);//获取入队前前置节点状态int ws = p.waitStatus;//前置节点为取消状态的时候,也就是说他不会在被唤醒,如果当前线程执行unlock执行unpark操作的时候,唤醒的是一个取消节点//而这不是我们愿意看到的,我们希望唤醒的是一个正常节点,这里提前唤醒下一个正常节点线程.在正常节点被唤醒后,会竞争锁,竞争锁成功后,会删除取消的节点//前置节点为取消状态,直接唤醒//或者为非取消状态则修改为SIGNAL,如果失败则唤醒if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL))//唤醒当前线程LockSupport.unpark(node.thread);//添加同步队列成功return true;}
signalAll
public final void signalAll() {//非当前获取独占锁线程异常if (!isHeldExclusively())throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();//获取第一个等待节点Node first = firstWaiter;if (first != null)//遍历添加所有等待节点到同步队列doSignalAll(first);}private void doSignalAll(Node first) {lastWaiter = firstWaiter = null;do {Node next = first.nextWaiter;first.nextWaiter = null;transferForSignal(first);first = next;} while (first != null);}
总结
await时,会释放锁
await有2个阻塞状态,第一个阻塞状态等待当前节点添加到同步队列
第二个阻塞状态是竞争锁.
ConditionObject维护了2个节点,当await时将节点添加到等待队列中
当signal时,将队列节点添加到同步队列head和tail中.在执行unlock的时候被唤醒.
但是在signal时,如果上一个节点出现取消状态或者上一个同步队列节点修改状态失败,则提前唤醒当前节点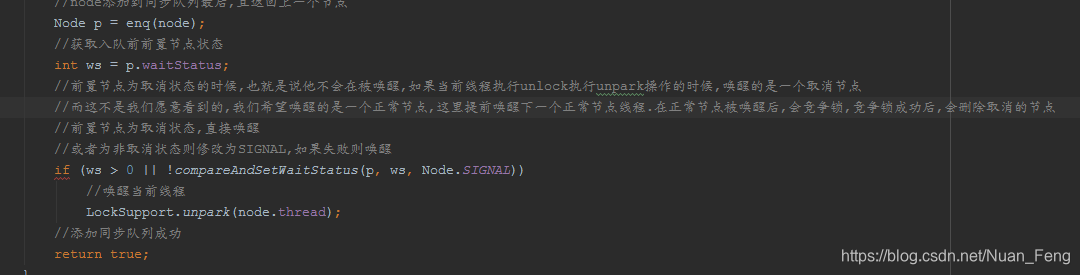

对CAS中间状态的维护
CAS例子
package concurrent.D;import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;/*** LinkedQueue* <p/>* Insertion in the Michael-Scott nonblocking queue algorithm线程安全* Michael-Scott非阻塞链接队列算法中的插入算法** ConcurrentLinkedQueue使用原子域更新器AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater来代替AtomicReference,从而提升性能* @author Brian Goetz and Tim Peierls*/public class M_LinkedQueue <E> {private static class Node <E> {final E item;final AtomicReference<Node<E>> next;public Node(E item, Node<E> next) {this.item = item;this.next = new AtomicReference<Node<E>>(next);}}private final Node<E> dummy = new Node<E>(null, null);private final AtomicReference<Node<E>> head= new AtomicReference<Node<E>>(dummy);private final AtomicReference<Node<E>> tail= new AtomicReference<Node<E>>(dummy);public boolean put(E item) {Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(item, null);while (true) {Node<E> curTail = tail.get();Node<E> tailNext = curTail.next.get();if (curTail == tail.get()) {//检测状态是否处于C-D之间if (tailNext != null) {// Queue in intermediate state, advance tail//队列处于中间状态,推进尾节点,处于状态C-D之间,curTail.next是有值得tail.compareAndSet(curTail, tailNext);} else {// In quiescent state, try inserting new node//处于稳定状态,尝试插入新节点到列表队尾if (curTail.next.compareAndSet(null, newNode)) {//状态C// Insertion succeeded, try advancing tail//插入操作成功,尝试推进尾节点,推入失败也没事,其他线程会帮忙推送tail.compareAndSet(curTail, newNode); //状态D//因为其他线程帮忙推送又或者自己推送成功,保证了幂等性,所以直接返回即可return true;}}}}}}



































还没有评论,来说两句吧...