MyBatis学习笔记
教学视频
源码下载
1.简介
MyBatis是什么
- MyBatis 是支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架。
- MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集。
- MyBatis 可以使用简单的XML或注解用于配置和原始映射,将接口和Java的POJO( Plain Old Java Objects,普通的Java对象)映射成数据库中的记录
MyBatis历史
- 原是Apache的一个开源项目iBatis, 2010年6月这个项目由Apache Software Foundation 迁移到了Google Code,随着开发团队转投Google Code旗下, iBatis3.x正式更名为MyBatis ,代码于2013年11月迁移到Github(下载地址见后)。
- iBatis一词来源于“internet”和“abatis”的组合,是一个基于Java的持久层框架。 iBatis提供的持久层框架包括SQL Maps和Data Access Objects(DAO)
为什么要使用MyBatis?
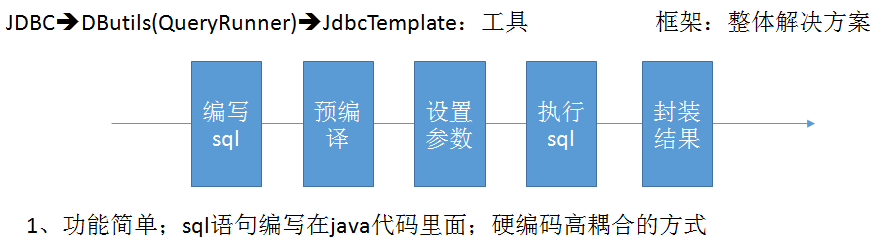
JDBC
- SQL夹在Java代码块里,耦合度高导致硬编码内伤
- 维护不易且实际开发需求中sql是有变化,频繁修改的情况多见
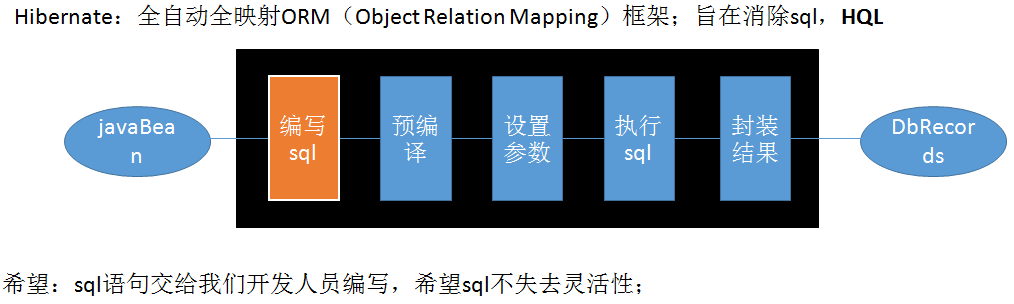
- Hibernate和JPA
– 长难复杂SQL,对于Hibernate而言处理也不容易
– 内部自动生产的SQL,不容易做特殊优化。
– 基于全映射的全自动框架,大量字段的POJO进行部分映射时比较困难,导致数据库性能下降。
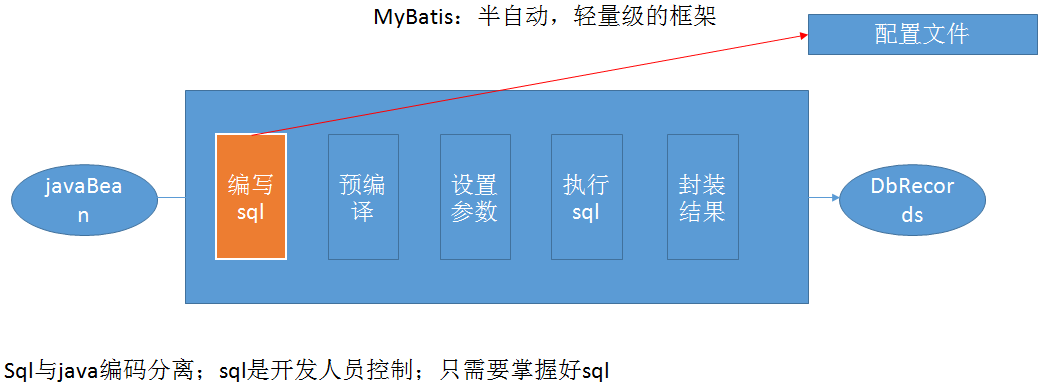
MyBatis是一个半自动化的持久化层框架。
- 对开发人员而言,核心sql还是需要自己优化
- sql和java编码分开,功能边界清晰,一个专注业务、一个专注数据。
2.下载
MyBatis下载
MyBatis官网
3.HelloWorld
在MySQL数据库创建一数据库实例
learnmybatis,在其创建一张表CREATE TABLE employee(
id INT(11) PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,last_name VARCHAR(255),gender CHAR(1),email VARCHAR(255)
);
再插进一条随意数据,用于测试
- 创建Maven工程,添加依赖
pom.xml
<dependency><groupId>org.mybatis</groupId><artifactId>mybatis</artifactId><version>3.4.1</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId><version>6.0.6</version></dependency>
- 创建对应的JavaBean
Employee.java
public class Employee {private Integer id;private String lastName;private String email;private String gender;//getter and setter and toString()}
创建mybatis配置文件,sql映射文件
- MyBatis 的全局配置文件包含了影响 MyBatis 行为甚深的设置( settings)和属性( properties)信息、如数据库连接池信息等。指导着MyBatis进行工作。我们可以参照官方文件的配置示例。
- 映射文件的作用就相当于是定义Dao接口的实现类如何工作。这也是我们使用MyBatis时编写的最多的文件。
mybatis全局配置文件
mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><configuration><environments default="development"><environment id="development"><transactionManager type="JDBC" /><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" /><property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/learnmybatis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=CTT" /><property name="username" value="root" /><property name="password" value="123" /></dataSource></environment></environments><!-- 将我们写好的sql映射文件(EmployeeMapper.xml)一定要注册到全局配置文件(mybatis-config.xml)中 --><mappers><mapper resource="c01/EmployeeMapper.xml" /></mappers></configuration>
sql映射文件
EmployeeMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="abc"><!-- namespace:名称空间;通常指定为接口的全类名 id:唯一标识 resultType:返回值类型 #{id}:从传递过来的参数中取出id值 public Employee getEmpById(Integer id); --><select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select id,last_name lastName,email,gender from employee where id = #{id}</select></mapper>
- 测试
HelloWorldTest.java
public class HelloWorldTest {public SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {String resource = "c01/mybatis-config.xml";InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);return new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);}/** * 1、根据xml配置文件(全局配置文件)创建一个SqlSessionFactory对象 有数据源一些运行环境信息 * 2、sql映射文件;配置了每一个sql,以及sql的封装规则等。 * 3、将sql映射文件注册在全局配置文件中 * 4、写代码: * 1)、根据全局配置文件得到SqlSessionFactory; * 2)、使用sqlSession工厂,获取到sqlSession对象使用他来执行增删改查 * 一个sqlSession就是代表和数据库的一次会话,用完关闭 * 3)、使用sql的唯一标志来告诉MyBatis执行哪个sql。sql都是保存在sql映射文件中的。 * * @throws IOException */@Testpublic void test() throws IOException {// 2、获取sqlSession实例,能直接执行已经映射的sql语句// sql的唯一标识:statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.// 执行sql要用的参数:parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory();SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();try {Employee employee = openSession.selectOne("abc.getEmpById", 1);System.out.println(employee);} finally {openSession.close();}}}
4.接口式编程
日后主要用接口式编程
HelloWorld-接口式编程
- 创建一个Dao接口
EmployeeMapper.java
import com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee;public interface EmployeeMapper {public Employee getEmpById(Integer id);}
- 修改Mapper文件(命名空间,id,returnType)
EmployeeMapper2.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c01.helloworld.dao.EmployeeMapper"><!-- namespace:名称空间;指定为接口的全类名 id:唯一标识 resultType:返回值类型 #{id}:从传递过来的参数中取出id值 public Employee getEmpById(Integer id); --><select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select id,last_name lastName,email,gender from employee where id = #{id}</select></mapper>
- 测试
HelloWorldTest.java
@Testpublic void test01() throws IOException {// 1、获取sqlSessionFactory对象SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory();// 2、获取sqlSession对象SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();try {// 3、获取接口的实现类对象//会为接口自动的创建一个代理对象,代理对象去执行增删改查方法EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);Employee employee = mapper.getEmpById(1);System.out.println(mapper.getClass());System.out.println(employee);} finally {openSession.close();}}
5.小结(1)
接口式编程
- 原生: Dao ====> DaoImpl
- mybatis: Mapper ====> xxMapper.xml
- SqlSession代表和数据库的一次会话;用完必须关闭;
- SqlSession和connection一样她都是非线程安全。每次使用都应该去获取新的对象。
- mapper接口没有实现类,但是mybatis会为这个接口生成一个代理对象。
(将接口和xml进行绑定)EmployeeMapper empMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class); 两个重要的配置文件:
- mybatis的全局配置文件:包含数据库连接池信息,事务管理器信息等…系统运行环境信息
- sql映射文件:保存了每一个sql语句的映射信息:将sql抽取出来。
6.全局配置文件-引入dtd约束
MyBatis-全局配置文件
MyBatis 的配置文件包含了影响 MyBatis 行为甚深的设置( settings)和属性( properties)信息。文档的顶层结构如下:
configuration 配置
- properties 属性
- settings 设置
- typeAliases 类型命名
- typeHandlers 类型处理器
- objectFactory 对象工厂
- plugins 插件
environments 环境
environment 环境变量
- transactionManager 事务管理器
- dataSource 数据源
- databaseIdProvider 数据库厂商标识
- mappers 映射器
引入dtd约束
有时Eclipse在编辑全局xml或映射xml时没有编辑提示,这时可手动导入dtd,导入后才有编辑提示
dtd文件在Mybatis的Jar包的org/apache/ibatis/builder/xml,导入前需Mybatis的Jar包中的dtd存放到本地目录
设置路径:Window -> Preferences -> XML -> XML Catalog -> Add Catalog Entry ->Set URL key and DTD local location
7.全局配置文件-properties-引入外部配置文件
官方文档
mybatis-config.xml
<configuration><!-- 1、mybatis可以使用properties来引入外部properties配置文件的内容; resource:引入类路径下的资源 url:引入网络路径或者磁盘路径下的资源 --><properties resource ="dbconfig.properties"></properties>
dbconfig.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverjdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/learnmybatis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=CTTjdbc.username=rootjdbc.password=123
如果属性在不只一个地方进行了配置,那么 MyBatis 将按照下面的顺序来加载:
- 在 properties 元素体内指定的属性首先被读取。
- 然后根据 properties 元素中的 resource 属性读取类路径下属性文件或根
据 url 属性指定的路径读取属性文件,并覆盖已读取的同名属性。 - 最后读取作为方法参数传递的属性,并覆盖已读取的同名属性。
8.全局配置文件-settings-运行时行为设置
这是 MyBatis 中极为重要的调整设置,它们会改变MyBatis 的运行时行为。
mybatis-config2.xml
<configuration>...<!-- 2、settings包含很多重要的设置项 setting:用来设置每一个设置项 name:设置项名 value:设置项取值 --><settings><setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/></settings>
| 设置参数 | 描述 | 有效值 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| cacheEnabled | 该配置影响的所有映射器中配置的缓存的全局开关。 | true/false | TRUE |
| lazyLoadingEnabled | 延迟加载的全局开关。当开启时。所有关联对象都会延迟加载。特定关联关系中可通过设置fetchType属性来覆盖该项的开关状态。 | true/false | FALSE |
| useColumnLabel | 使用列标签代替列名。不同的驱动在这方面会有不同的表现,具体可参考相关驱动文档或通过测试这两种不同的模式来观察所用驱动的结果。 | true/false | TRUE |
| defaultStatementTimeout | 设置超时时间,它决定驱动等待数据库响应的秒数。 | Any positive integer | Not Set (null) |
| mapUnderscoreToCamelCase | 是否开启自动驼峰命名规则( camel case )映射即从经典数据库列名A_ COLUMN到经典Java属性名aColumn的类似映射 | true/false | FALSE |
更多设置
9.全局配置文件-typeAliases-别名
类型别名可为 Java 类型设置一个缩写名字。 它仅用于 XML 配置,意在降低冗余的全限定类名书写。例如:
<configuration>...<typeAliases><typeAlias alias="Author" type="domain.blog.Author"/><typeAlias alias="Blog" type="domain.blog.Blog"/><typeAlias alias="Comment" type="domain.blog.Comment"/><typeAlias alias="Post" type="domain.blog.Post"/><typeAlias alias="Section" type="domain.blog.Section"/><typeAlias alias="Tag" type="domain.blog.Tag"/></typeAliases>
当这样配置时,Blog 可以用在任何使用 domain.blog.Blog 的地方。
也可以指定一个包名,MyBatis 会在包名下面搜索需要的 Java Bean,比如:
<configuration>...<typeAliases><package name="domain.blog"/></typeAliases>
每一个在包 domain.blog 中的 Java Bean,在没有注解的情况下,会使用 Bean 的首字母小写的非限定类名来作为它的别名。 比如 domain.blog.Author 的别名为 author;若有注解,则别名为其注解值。见下面的例子:
@Alias("author")public class Author {...}
值得注意的是, MyBatis已经为许多常见的 Java 类型内建
了相应的类型别名。它们都是大小写不敏感的,我们在起
别名的时候千万不要占用已有的别名。
| 别名 | 映射的类型 | 别名 | 映射的类型 | 别名 | 映射的类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| _byte | byte | string | String | date | Date |
| _long | long | byte | Byte | decimal | BigDecimal |
| _short | short | long | Long | bigdecimal | BigDecimal |
| _int | int | short | Short | object | Object |
| _integer | int | int | Integer | map | Map |
| _double | double | integer | Integer | hashmap | HashMap |
| _float | float | double | Double | list | List |
| _boolean | boolean | float | Float | arraylist | ArrayList |
| - | - | boolean | Boolean | collection | Collection |
| - | - | - | - | iterator | Iterator |
mybatis-config3.xml
10.全局配置文件-typeHandlers-类型处理器简介
官方文档
无论是 MyBatis 在预处理语句( PreparedStatement)中设置一个参数时,还是从结果集中取出一个值时,都会用类型处理器将获取的值以合适的方式转换成 Java 类型。
| 类型处理器 | Java 类型 | JDBC 类型 |
|---|---|---|
| BooleanTypeHandler | java.lang.Boolean, boolean | 数据库兼容的 BOOLEAN |
| ByteTypeHandler | java.lang.Byte, byte | 数据库兼容的 NUMERIC 或 BYTE |
| ShortTypeHandler | java.lang.Short, short | 数据库兼容的 NUMERIC 或 SHORT INTEGER |
| IntegerTypeHandler | java.lang.Integer, int | 数据库兼容的 NUMERIC 或 INTEGER |
| LongTypeHandler | java.lang.Long, long | 数据库兼容的 NUMERIC 或 LONG INTEGER |
| FloatTypeHandler | java.lang.Float, float | 数据库兼容的 NUMERIC 或 FLOAT |
| DoubleTypeHandler | java.lang.Double, double | 数据库兼容的 NUMERIC 或 DOUBLE |
| BigDecimalTypeHandler | java.math.BigDecimal | 数据库兼容的 NUMERIC 或 DECIMAL |
| StringTypeHandler | java.lang.String | CHAR, VARCHAR |
more
日期类型的处理
- 日期和时间的处理, JDK1.8以前一直是个头疼的问题。我们通常使用JSR310规范领导者Stephen Colebourne创建的Joda-Time来操作。 1.8已经实现全部的JSR310规范了。
- 日期时间处理上,我们可以使用MyBatis基于JSR310( Date and Time API)编写的各种日期时间类型处理器。
MyBatis3.4以前的版本需要我们手动注册这些处理器,以后的版本都是自动注册的
自定义类型处理器
自定义类型处理器示例
我们可以重写类型处理器或创建自己的类型处理器来处理不支持的或非标准的类型。
步骤:
- 实现
org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandler接口或者继承org.apache.ibatis.type.BaseTypeHandler - 指定其映射某个JDBC类型(可选操作)
- 在mybatis全局配置文件中注册
11.全局配置文件-plugins-插件简介
官方文档
插件是MyBatis提供的一个非常强大的机制,我们可以通过插件来修改MyBatis的一些核心行为。 插件通过动态代理机制,可以介入四大对象的任何一个方法的执行。
了解mybatis运行原理才能更好开发插件。
Executor (update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed)ParameterHandler (getParameterObject, setParameters)ResultSetHandler (handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters)StatementHandler (prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query)
12.全局配置文件-enviroments-运行环境
enviroments - 官方文档
- MyBatis可以配置多种环境,比如开发、测试和生产环境需要有不同的配置。
- 每种环境使用一个environment标签进行配置并指定唯一标识符
- 可以通过environments标签中的default属性指定一个环境的标识符来快速的切换环境
environment-指定具体环境
- id:指定当前环境的唯一标识
transactionManager、和dataSource都必须有
<environment id="dev_mysql"><transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}" /><property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" /><property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" /><property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /></dataSource></environment>...
transactionManager
type: JDBC | MANAGED | 自定义
- JDBC:使用了 JDBC 的提交和回滚设置,依赖于从数据源得到的连接来管理事务范围。JdbcTransactionFactory
- MANAGED:不提交或回滚一个连接、让容器来管理事务的整个生命周期(比如 JEE 应用服务器的上下文)。 ManagedTransactionFactory
- 自定义:实现TransactionFactory接口, type=全类名/别名
dataSource
type: UNPOOLED | POOLED | JNDI | 自定义
- UNPOOLED:不使用连接池,
UnpooledDataSourceFactory - POOLED:使用连接池, PooledDataSourceFactory
- JNDI: 在EJB 或应用服务器这类容器中查找指定的数据源
- 自定义:实现DataSourceFactory接口,定义数据源的获取方式。
- UNPOOLED:不使用连接池,
实际开发中我们使用Spring管理数据源,并进行事务控制的配置来覆盖上述配置。
13.全局配置文件-databaseIdProvider-多数据库支持
databaseIdProvider - 官方文档
MyBatis 可以根据不同的数据库厂商执行不同的语句。
Type: DB_VENDOR 使用MyBatis提供的VendorDatabaseIdProvider解析数据库厂商标识。也可以实现DatabaseIdProvider接口来自定义。
- Property-name:数据库厂商标识
- Property-value:为标识起一个别名,方便SQL语句使用databaseId属性引用
DB_VENDOR - 会通过 DatabaseMetaData#getDatabaseProductName() 返回的字符串进行设置。由于通常情况下这个字符串都非常长而且相同产品的不同版本会返回不同的值,所以最好通过设置属性别名来使其变短
databaseId属性在映射xml使用
通过
<environments default="mysql">切换数据库,便能切换SQL
MyBatis匹配规则如下:
- 如果没有配置databaseIdProvider标签,那么databaseId=null
- 如果配置了databaseIdProvider标签,使用标签配置的name去匹配数据库信息,匹配上设置databaseId=配置指定的值,否则依旧为null
- 如果databaseId不为null,他只会找到配置databaseId的sql语句
- MyBatis 会加载不带 databaseId 属性和带有匹配当前数据库 databaseId 属性的所有语句。如果同时找到带有 databaseId 和不带 databaseId 的相同语句, 则后者会被舍弃。
14.全局配置文件-mappers-sql映射注册
既然 MyBatis 的行为已经由上述元素配置完了,我们现在就要来定义 SQL 映射语句了。 但首先,我们需要告诉 MyBatis 到哪里去找到这些语句。 在自动查找资源方面,Java 并没有提供一个很好的解决方案,所以最好的办法是直接告诉 MyBatis 到哪里去找映射文件。 你可以使用相对于类路径的资源引用,或完全限定资源定位符(包括 file:/// 形式的 URL),或类名和包名等。例如:
<!-- 使用相对于类路径的资源引用 --><mappers><mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml"/><mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/BlogMapper.xml"/><mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/PostMapper.xml"/></mappers><!-- 使用完全限定资源定位符(URL) --><mappers><mapper url="file:///var/mappers/AuthorMapper.xml"/><mapper url="file:///var/mappers/BlogMapper.xml"/><mapper url="file:///var/mappers/PostMapper.xml"/></mappers><!-- 使用映射器接口实现类的完全限定类名 --><!-- 注册接口 class:引用(注册)接口, 1、有sql映射文件,映射文件名必须和接口同名,并且放在与接口同一目录下; 2、没有sql映射文件,所有的sql都是利用注解写在接口上; 推荐: 比较重要的,复杂的Dao接口我们来写sql映射文件 不重要,简单的Dao接口为了开发快速可以使用注解; --><mappers><mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.AuthorMapper"/><mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.BlogMapper"/><mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.PostMapper"/></mappers><!-- 将包内的映射器接口实现全部注册为映射器 --><mappers><package name="org.mybatis.builder"/></mappers>
这些配置会告诉 MyBatis 去哪里找映射文件
15.小结(2)
注意mybatis全局配置文件中的标签顺序,需要按以下顺序排列,否则抛异常
configuration 配置
- properties 属性
- settings 设置
- typeAliases 类型命名
- typeHandlers 类型处理器
- objectFactory 对象工厂
- plugins 插件
environments 环境
environment 环境变量
- transactionManager 事务管理器
- dataSource 数据源
- databaseIdProvider 数据库厂商标识
- mappers 映射器
16.映射文件-增删改查
映射文件指导着MyBatis如何进行数据库增删改查,有着非常重要的意义;
- cache –命名空间的二级缓存配置
- cache-ref – 其他命名空间缓存配置的引用。
- resultMap – 自定义结果集映射
- parameterMap – 已废弃!老式风格的参数映射
- sql –抽取可重用语句块。
- insert – 映射插入语句
- update – 映射更新语句
- delete – 映射删除语句
- select – 映射查询语句
CRUD初体验
EmployeeMapper.java
public interface EmployeeMapper {public Employee getEmpById(Integer id);public Long addEmp(Employee employee);public boolean updateEmp(Employee employee);public void deleteEmpById(Integer id);}
EmployeeMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper"><select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from employee where id = #{id}</select><!-- public void addEmp(Employee employee); --><insert id="addEmp" parameterType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id" >insert into employee(last_name,email,gender)values(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender})</insert><!-- public void updateEmp(Employee employee); --><update id="updateEmp">update employeeset last_name=#{lastName},email=#{email},gender=#{gender}where id=#{id}</update><!-- public void deleteEmpById(Integer id); --><delete id="deleteEmpById">delete from employee where id=#{id}</delete></mapper>
EmployeeMapperTest.java
public class MapperTest {@Testpublic void testCrud() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c03/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {EmployeeMapper mapper = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);Employee newEmployee = new Employee(null,"kuang","kuang@163.com","1");//增Long count = mapper.addEmp(newEmployee);//查System.out.println("After creating : " + mapper.getEmpById(newEmployee.getId()));//改newEmployee.setGender("0");mapper.updateEmp(newEmployee);//查System.out.println("After updating : " + mapper.getEmpById(newEmployee.getId()));//删mapper.deleteEmpById(newEmployee.getId());System.out.println("After deleting : " + mapper.getEmpById(newEmployee.getId()));session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}}
另外
mybatis允许增删改直接定义以下类型返回值
- Integer、Long、Boolean、void
我们需要手动提交数据
- sqlSessionFactory.openSession();===》手动提交
- sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);===》自动提交
17.映射文件-insert-获取自增主键的值
- parameterType:参数类型,可以省略,
获取自增主键的值:
- mysql支持自增主键,自增主键值的获取,mybatis也是利用statement.getGenreatedKeys();
- useGeneratedKeys=“true”;使用自增主键获取主键值策略
- keyProperty;指定对应的主键属性,也就是mybatis获取到主键值以后,将这个值封装给javaBean的哪个属性
EmployeeMapper.xml
<!-- public void addEmp(Employee employee); --><insert id="addEmp" parameterType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id" >insert into employee(last_name,email,gender)values(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender})</insert>
18.映射文件-insert-Oracle使用序列生成主键演示
- Oracle不支持自增;Oracle使用序列来模拟自增;
每次插入的数据的主键是从序列中拿到的值;如何获取到这个值;
从序列获取新主键值
select employee_seq.nextval from dual;
19.映射文件-insert-获取非自增主键的值-selectKey
<insert id="addEmp" databaseId="oracle"><!-- keyProperty:查出的主键值封装给javaBean的哪个属性 order="BEFORE":当前sql在插入sql之前运行 AFTER:当前sql在插入sql之后运行 resultType:查出的数据的返回值类型 BEFORE运行顺序: 先运行selectKey查询id的sql;查出id值封装给javaBean的id属性 在运行插入的sql;就可以取出id属性对应的值 AFTER运行顺序: 先运行插入的sql(从序列中取出新值作为id); 再运行selectKey查询id的sql; --><selectKey keyProperty="id" order="BEFORE" resultType="Integer"><!-- 编写查询主键的sql语句 --><!-- BEFORE-->select EMPLOYEES_SEQ.nextval from dual<!-- AFTER: select EMPLOYEES_SEQ.currval from dual --></selectKey><!-- 插入时的主键是从序列中拿到的 --><!-- BEFORE:-->insert into employees(EMPLOYEE_ID,LAST_NAME,EMAIL)values(#{id},#{lastName},#{email<!-- ,jdbcType=NULL -->})<!-- AFTER: insert into employees(EMPLOYEE_ID,LAST_NAME,EMAIL) values(employees_seq.nextval,#{lastName},#{email}) --></insert>
selectKey 元素的属性
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| keyProperty | selectKey 语句结果应该被设置到的目标属性。如果生成列不止一个,可以用逗号分隔多个属性名称。 |
| keyColumn | 返回结果集中生成列属性的列名。如果生成列不止一个,可以用逗号分隔多个属性名称。 |
| resultType | 结果的类型。通常 MyBatis 可以推断出来,但是为了更加准确,写上也不会有什么问题。MyBatis 允许将任何简单类型用作主键的类型,包括字符串。如果生成列不止一个,则可以使用包含期望属性的 Object 或 Map。 |
| order | 可以设置为 BEFORE 或 AFTER。如果设置为 BEFORE,那么它首先会生成主键,设置 keyProperty 再执行插入语句。如果设置为 AFTER,那么先执行插入语句,然后是 selectKey 中的语句 - 这和 Oracle 数据库的行为相似,在插入语句内部可能有嵌入索引调用。 |
| statementType | 和前面一样,MyBatis 支持 STATEMENT,PREPARED 和 CALLABLE 类型的映射语句,分别代表 Statement, PreparedStatement 和 CallableStatement 类型。 |
20.映射文件-参数处理-单个参数&多个参数&命名参数
单个参数:mybatis不会做特殊处理,
#{参数名/任意名}:取出参数值。
多个参数:mybatis会做特殊处理。
通常操作:
- 方法:public Employee getEmpByIdAndLastName(Integer id,String lastName);
- 取值:
#{id},#{lastName}
- 上述操作会抛出异常:
org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException: Parameter 'id' not found. Available parameters are [1, 0, param1, param2] 多个参数会被封装成 一个map,
- key:param1…paramN,或者参数的索引也可以
- value:传入的参数值
#{}就是从map中获取指定的key的值;
【命名参数】:明确指定封装参数时map的key;@Param(“id”)
多个参数会被封装成 一个map,
- key:使用@Param注解指定的值
- value:参数值
#{指定的key}取出对应的参数值
EmployeeMapperTest.java
@Testpublic void testParameters() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c03/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {EmployeeMapper mapper = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);//1.//单个参数:mybatis不会做特殊处理System.out.println(mapper.getEmpById2(1));//2.//多个参数,未作处理 ,mapper直用#{id},#{lastName}会抛异常try {System.out.println(mapper.getEmpByIdAndLastName(1, "jallen"));//org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.PersistenceException://### Error querying database. Cause: org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException: Parameter 'id' not found. Available parameters are [0, 1, param1, param2]//### Cause: org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException: Parameter 'id' not found. Available parameters are [0, 1, param1, param2]}catch(PersistenceException ex) {System.err.println(ex);}//多个参数会被封装成 一个map//key:param1...paramN,或者参数的索引0, 1..也可以(这种方法的可读性较差)//value:传入的参数值System.out.println(mapper.getEmpByIdAndLastName2(1, "jallen"));System.out.println(mapper.getEmpByIdAndLastName3(1, "jallen"));//3.//【命名参数】:明确指定封装参数时map的key;@Param("id")System.out.println(mapper.getEmpByIdAndLastName4(1, "jallen"));session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}
EmployeeMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper"><!-- 多个参数,不能直写id或lastName,否则抛出 org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException: Parameter 'id' not found. Available parameters are [1, 0, param1, param2]--><select id="getEmpByIdAndLastName" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from tbl_employee where id = #{id} and last_name=#{lastName}</select><select id="getEmpByIdAndLastName2" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from employee where id = #{0} and last_name=#{1}</select><select id="getEmpByIdAndLastName3" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from employee where id = #{param1} and last_name=#{param2}</select><select id="getEmpByIdAndLastName4" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from employee where id = #{id} and last_name=#{lastName}</select>...
EmployeeMapper.java
public interface EmployeeMapper {public Employee getEmpByIdAndLastName(Integer id, String name);public Employee getEmpByIdAndLastName2(Integer id, String name);public Employee getEmpByIdAndLastName3(Integer id, String name);public Employee getEmpByIdAndLastName4(@Param("id")Integer id,//@Param("lastName")String name);...
21.映射文件-参数处理-POJO&Map&TO
POJO:如果多个参数正好是我们业务逻辑的数据模型,我们就可以直接传入pojo;
#{属性名}:取出传入的pojo的属性值
Map:如果多个参数不是业务模型中的数据,没有对应的pojo,不经常使用,为了方便,我们也可以传入map
#{key}:取出map中对应的值
TO:如果多个参数不是业务模型中的数据,但是经常要使用,推荐来编写一个TO(Transfer Object)数据传输对象,如:
Page{
int index;int size;
}
EmployeeMapperTest.java
@Testpublic void testParameters() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c03/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {EmployeeMapper mapper = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);...//4.//传入mapMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("id", 1);map.put("lastName", "jallen");System.out.println("4. " + mapper.getEmpByMap(map));session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}
EmployeeMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper"><!-- map 作参输入 --><select id="getEmpByMap" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from employee where id = #{id} and last_name=#{lastName}</select>...
EmployeeMapper.java
public interface EmployeeMapper {public Employee getEmpByMap(Map<String, Object> map);...
22.映射文件-参数处理-参数封装扩展思考
思考========
public Employee getEmp(@Param("id")Integer id,String lastName);- 取值:id==>#{id/param1} lastName==>#{param2}
public Employee getEmp(Integer id,@Param("e")Employee emp);- 取值:id==>#{param1} lastName===>#{param2.lastName/e.lastName}
特别注意:如果是Collection(List、Set)类型或者是数组,
- 也会特殊处理。也是把传入的list或者数组封装在map中。
- key:Collection(collection),如果是List还可以使用这个key(list)
public Employee getEmpById(List<Integer> ids);- 取值:取出第一个id的值: #{list[0]}
23.源码分析-参数处理-参数封装map的过程
结合源码,mybatis怎么处理参数
- (@Param(“id”)Integer id,@Param(“lastName”)String lastName);
- ParamNameResolver解析参数封装map的;
- names:{0=id, 1=lastName};构造器的时候就确定好了
确定流程:
1.获取每个标了param注解的参数的@Param的值:id,lastName; 赋值给name;
2.每次解析一个参数给map中保存信息:(key:参数索引,value:name的值)
name的值:
标注了param注解:注解的值
没有标注:
1.全局配置:useActualParamName(jdk1.8):name=参数名
2.name=map.size();相当于当前元素的索引
{0=id, 1=lastName,2=2}
args【1,“Tom”,‘hello’】:
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {final int paramCount = names.size();//1、参数为null直接返回if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {return null;//2、如果只有一个元素,并且没有Param注解;args[0]:单个参数直接返回} else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {return args[names.firstKey()];//3、多个元素或者有Param标注} else {final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<Object>();int i = 0;//4、遍历names集合;{0=id, 1=lastName,2=2}for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : names.entrySet()) {//names集合的value作为key; names集合的key又作为取值的参考args[0]:args【1,"Tom"】://eg:{id=args[0]:1,lastName=args[1]:Tom,2=args[2]}param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);// add generic param names (param1, param2, ...)param//额外的将每一个参数也保存到map中,使用新的key:param1...paramN//效果:有Param注解可以#{指定的key},或者#{param1}final String genericParamName = GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX + String.valueOf(i + 1);// ensure not to overwrite parameter named with @Paramif (!names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);}i++;}return param;}}}
总结:参数多时会封装map,为了不混乱,我们可以使用@Param来指定封装时使用的key;#{key}就可以取出map中的值;
24.映射文件-参数处理-#与$取值区别
#{}和${}都可以获取map中的值或者pojo对象属性的值;
select * from tbl_employee where id=${id} and last_name=#{lastName}#Preparing:select * from tbl_employee where id=2 and last_name=?
区别:
#{}: 是以预编译的形式,将参数设置到sql语句中;PreparedStatement;防止sql注入${}: 取出的值直接拼装在sql语句中;会有安全问题;
大多情况下,我们去参数的值都应该去使用#{}。
原生jdbc不支持占位符的地方我们就可以使用${}进行取值,比如分表、排序。。。;按照年份分表拆分
select * from ${year}_salary where xxx;select * from tbl_employee order by ${f_name} ${order}
25.映射文件-参数处理-#取值时指定参数相关规则
#{}:更丰富的用法:
规定参数的一些规则:
- javaType、
- jdbcType、
- mode(存储过程)、
- numericScale、
- resultMap、
- typeHandler、
- jdbcTypeName、
- expression(未来准备支持的功能);
例如:jdbcType
jdbcType通常需要在某种特定的条件下被设置:
- 在我们数据为null的时候,有些数据库可能不能识别mybatis对null的默认处理。比如Oracle DB(报错);
- JdbcType OTHER:无效的类型;因为mybatis对所有的null都映射的是原生Jdbc的OTHER类型,Oracle DB不能正确处理;
由于全局配置中:jdbcTypeForNull=OTHER,Oracle DB不支持,两种解决方法:
- 在mapper文件中写
#{email,jdbcType=NULL}; - 在全局配置文件
<setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="NULL"/>
26.映射文件-select-返回List
EmployeeMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper"><!-- public List<Employee> getEmpsByLastNameLike(String lastName); --><!--resultType:如果返回的是一个集合,要写集合中元素的类型 --><select id="getEmpsByLastNameLike" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from employee where last_name like #{lastName}</select>...
EmployeeMapper.java
public interface EmployeeMapper {return Collectionpublic List<Employee> getEmpsByLastNameLike(String str);...
EmployeeMapperTest.java
@Testpublic void testList() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c03/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {EmployeeMapper em = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);List<Employee> result = em.getEmpsByLastNameLike("%a%");System.out.println(result);session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}
27.映射文件-select-记录封装map
EmployeeMapper.java
public interface EmployeeMapper {//多条记录封装一个map:Map<Integer,Employee>:键是这条记录的主键,值是记录封装后的javaBean//@MapKey:告诉mybatis封装这个map的时候使用哪个属性作为map的key@MapKey("lastName")public Map<String, Employee> getEmpByLastNameLikeReturnMap(String lastName);//返回一条记录的map;key就是列名,值就是对应的值public Map<String, Object> getEmpByIdReturnMap(Integer id);...
EmployeeMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper"><!--public Map<Integer, Employee> getEmpByLastNameLikeReturnMap(String lastName); --><select id="getEmpByLastNameLikeReturnMap" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from employee where last_name like #{lastName}</select><!--public Map<String, Object> getEmpByIdReturnMap(Integer id); --><select id="getEmpByIdReturnMap" resultType="map">select * from employee where id=#{id}</select>...
MapperTest
@Testpublic void testMap() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c03/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {EmployeeMapper em = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);Map<String, Object> result = em.getEmpByIdReturnMap(1);System.out.println(result);System.out.println("---");Map<String, Employee> result2 = em.getEmpByLastNameLikeReturnMap("%a%");System.out.println(result2);session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}
28.映射文件-select-resultMap-自定义结果映射规则
EmployeeMapper.java
public interface EmployeeMapper {//自定义结果映射规则public Employee getEmpByIdWithResultMap(Integer id);...
EmployeeMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper"><!--自定义某个javaBean的封装规则 type:自定义规则的Java类型 id:唯一id方便引用 --><resultMap type="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee" id="MySimpleEmp"><!--指定主键列的封装规则 id定义主键会底层有优化; column:指定哪一列 property:指定对应的javaBean属性 --><id column="id" property="id"/><!-- 定义普通列封装规则 --><result column="last_name" property="lastName"/><!-- 其他不指定的列会自动封装:我们只要写resultMap就把全部的映射规则都写上。 --><result column="email" property="email"/><result column="gender" property="gender"/></resultMap><!-- resultMap:自定义结果集映射规则; --><!-- public Employee getEmpById(Integer id); --><select id="getEmpByIdWithResultMap" resultMap="MySimpleEmp">select * from employee where id=#{id}</select>
EmployeeMapperTest.java
@Testpublic void testResultMap() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c03/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {EmployeeMapper em = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);System.out.println(em.getEmpByIdWithResultMap(1));session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}
29.映射文件-select-resultMap-关联查询-环境搭建
新建类Department.java
public class Department {private Integer id;private String departmentName;private List<Employee> emps;//getter and setter and toString()
修改类Employee.java
public class Employee {...private Department department;...public Employee() { }//add department's getter and setter
创建数据库表
CREATE TABLE department(id int(11) primary key auto_increment,department_name varchar(255));ALTER TABLE employee ADD COLUMN department_id int(11);ALTER TABLE employee ADD CONSTRAINT fk_employee_departmentFOREIGN KEY(department_id) REFERENCES department(id);INSERT INTO department(department_name) values ('开发部');INSERT INTO department(department_name) values ('测试部');
30.映射文件-select-resultMap-关联查询-级联属性封装结果
EmployeeMapper.java
public interface EmployeeMapper {//联合查询:级联属性封装结果集public Employee getEmpAndDept(Integer id);...
EmployeeMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper"><!-- 联合查询:级联属性封装结果集 --><resultMap type="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee" id="MyDifEmp"><id column="id" property="id"/><result column="last_name" property="lastName"/><result column="gender" property="gender"/><result column="department_id" property="department.id"/><result column="department_name" property="department.departmentName"/></resultMap><!-- public Employee getEmpAndDept(Integer id);--><select id="getEmpAndDept" resultMap="MyDifEmp">SELECTe.id id,e.last_name last_name,e.gender gender,e.department_id department_id, d.department_name department_nameFROM employee e, department dWHERE e.department_id=d.id AND e.id=#{id}</select>...
EmployeeMapperTest.java
@Testpublic void testResultMapAssociation() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c03/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {EmployeeMapper em = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);System.out.println(em.getEmpAndDept(1));session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}
31.映射文件-select-resultMap-关联查询-association定义关联对象封装规则
EmployeeMapper.java
public interface EmployeeMapper {//联合查询:级联属性封装结果集public Employee getEmpAndDept2(Integer id);
EmployeeMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper"><!-- association可以指定联合的javaBean对象 --><resultMap type="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee" id="MyDifEmp2"><id column="id" property="id"/><result column="last_name" property="lastName"/><result column="gender" property="gender"/><!-- association可以指定联合的javaBean对象 property="dept":指定哪个属性是联合的对象 javaType:指定这个属性对象的类型[不能省略] --><association property="department" javaType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Department"><id column="department_id" property="id"/><result column="department_name" property="departmentName"/></association></resultMap><!-- public Employee getEmpAndDept2(Integer id);--><select id="getEmpAndDept2" resultMap="MyDifEmp2">SELECTe.id id,e.last_name last_name,e.gender gender,e.department_id department_id, d.department_name department_nameFROM employee e, department dWHERE e.department_id=d.id AND e.id=#{id}</select>
EmployeeMapperTest.java
@Testpublic void testResultMapAssociation2() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c03/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {EmployeeMapper em = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);System.out.println(em.getEmpAndDept2(1));System.out.println(em.getEmpAndDept2(1).getDepartment());session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}
32.映射文件-select-resultMap-关联查询-association分步查询
DepartmentMapper.java
public interface DepartmentMapper {public Department getDeptById(Integer id);}
DepartmentMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.DepartmentMapper"><!--public Department getDeptById(Integer id); --><select id="getDeptById" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Department">select id,department_name departmentName from department where id=#{id}</select></mapper>
mybatis-config.xml
...<mappers><mapper resource="c03/EmployeeMapper.xml" /><mapper resource="c03/DepartmentMapper.xml" /></mappers></configuration>
EmployeeMapper.java
public interface EmployeeMapper {//association分步查询public Employee getEmpByIdStep(Integer id);...
EmployeeMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper"><!-- association分步查询 --><!-- 使用association进行分步查询: 1、先按照员工id查询员工信息 2、根据查询员工信息中的department_id值去部门表查出部门信息 3、部门设置到员工中; --><!-- id last_name email gender d_id --><resultMap type="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee" id="MyEmpByStep"><id column="id" property="id"/><result column="last_name" property="lastName"/><result column="email" property="email"/><result column="gender" property="gender"/><!-- association定义关联对象的封装规则 select:表明当前属性是调用select指定的方法查出的结果 column:指定将哪一列的值传给这个方法 流程:使用select指定的方法(传入column指定的这列参数的值)查出对象,并封装给property指定的属性 --><association property="department" select="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.DepartmentMapper.getDeptById" column="department_id"></association></resultMap><!-- public Employee getEmpByIdStep(Integer id);--><select id="getEmpByIdStep" resultMap="MyEmpByStep">select * from employee where id=#{id}</select>
EmployeeMapperTest.java
@Testpublic void testResultMapAssociation3() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c03/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {EmployeeMapper em = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);System.out.println(em.getEmpByIdStep(1));System.out.println(em.getEmpByIdStep(1).getDepartment());session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}
33.映射文件-select-resultMap-关联查询-分步查询&延迟加载
我们每次查询Employee对象的时候,都将一起查询出来。部门信息在我们使用的时候再去查询;分段查询的基础之上加上两个配置:
在全局配置文件中配置,实现懒加载
mybatis-config.xml
<configuration>...<settings>...<!--显示的指定每个我们需要更改的配置的值,即使他是默认的。防止版本更新带来的问题 --><setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/><setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/></settings>
| Setting | Description | Valid Values | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| lazyLoadingEnabled | Globally enables or disables lazy loading. When enabled, all relations will be lazily loaded. This value can be superseded for an specific relation by using the fetchType attribute on it. | true/false | false |
| aggressiveLazyLoading | When enabled, an object with lazy loaded properties will be loaded entirely upon a call to any of the lazy properties. Otherwise, each property is loaded on demand. | true/false | true |
aggressive
英 [əˈɡresɪv] 美 [əˈɡresɪv]
adj.
好斗的;挑衅的;侵略的;富于攻击性的;气势汹汹的;声势浩大的;志在必得的
PS. 个人认为aggressiveLazyLoading 可防止懒加载对象链情况出现。TODO: 待验证
34.映射文件-select-resultMap-关联查询-collection定义关联集合封装规则
DepartmentMapper.java
public interface DepartmentMapper {public Department getDeptByIdPlus(Integer id);...
DepartmentMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.DepartmentMapper"><!-- public class Department { private Integer id; private String departmentName; private List<Employee> emps; did dept_name || eid last_name email gender --><!--嵌套结果集的方式,使用collection标签定义关联的集合类型的属性封装规则 --><resultMap type="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Department" id="MyDept"><id column="did" property="id"/><result column="department_name" property="departmentName"/><!-- collection定义关联集合类型的属性的封装规则 ofType:指定集合里面元素的类型 --><collection property="emps" ofType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee"><!-- 定义这个集合中元素的封装规则 --><id column="eid" property="id"/><result column="last_name" property="lastName"/><result column="email" property="email"/><result column="gender" property="gender"/></collection></resultMap><!-- public Department getDeptByIdPlus(Integer id); --><select id="getDeptByIdPlus" resultMap="MyDept">SELECT d.id did,d.department_name department_name,e.id eid,e.last_name last_name,e.email email,e.gender genderFROM department d LEFT JOIN employee e ON d.id=e.department_idWHERE d.id=#{id}</select>...
DepartmentMapperTest.java
public class DepartmentTest {@Testpublic void testGetDeptByIdPlus() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c03/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {DepartmentMapper dm = session.getMapper(DepartmentMapper.class);Department department = dm.getDeptByIdPlus(1);System.out.println(department);System.out.println(department.getEmps());session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}}
35.映射文件-select-resultMap-关联查询-collection分步查询&延迟加载
EmployeeMapper.java
public interface EmployeeMapper {public Employee getEmpsByDeptId(Integer id);...
EmployeeMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper"><!-- public Employee getEmpsByDeptId(Integer departmentId);--><select id="getEmpsByDeptId" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from employee where department_id=#{department_id}</select>
DepartmentMapper.java
public interface DepartmentMapper {public Department getDeptByIdStep(Integer id);...
DepartmentMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.DepartmentMapper"><!-- collection:分段查询 --><resultMap type="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Department" id="MyDeptStep"><id column="id" property="id"/><id column="department_name" property="departmentName"/><collection property="emps" select="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper.getEmpsByDeptId" column="id"></collection></resultMap><!-- public Department getDeptByIdStep(Integer id); --><select id="getDeptByIdStep" resultMap="MyDeptStep">select id,department_name from department where id=#{id}</select>
DepartmentMapperTest.java
public class DepartmentMapperTest {@Testpublic void testGetDeptByIdStep() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c03/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {DepartmentMapper dm = session.getMapper(DepartmentMapper.class);Department department = dm.getDeptByIdStep(1);System.out.println(department);System.out.println(department.getEmps());session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}...
36.映射文件-select-resultMap-分步查询传递多列值&fetchType
扩展:
多列的值传递过去:
- 将多列的值封装map传递;
column="{key1=column1,key2=column2}"
- 将多列的值封装map传递;
fetchType=“lazy”:表示使用延迟加载;
- lazy:延迟
- eager:立即
<id column="id" property="id"/><id column="department_name" property="departmentName"/><collection property="emps" select="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper.getEmpsByDeptId" column="{deptId=id}" fetchType="lazy"></collection>
37.映射文件-select-resultMap-discriminator鉴别器
EmployeeMapper.java
public interface EmployeeMapper {//带有鉴别器的public List<Employee> getEmpsWithDiscriminator();...
EmployeeMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper"><!-- =======================鉴别器============================ --><!-- <discriminator javaType=""></discriminator> 鉴别器:mybatis可以使用discriminator判断某列的值,然后根据某列的值改变封装行为 封装Employee: 如果查出的是女生:就把部门信息查询出来,否则不查询; 如果是男生,把last_name这一列的值赋值给email; --><resultMap type="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee" id="MyEmpDis"><id column="id" property="id"/><result column="last_name" property="lastName"/><result column="email" property="email"/><result column="gender" property="gender"/><!-- column:指定判定的列名 javaType:列值对应的java类型 --><discriminator javaType="string" column="gender"><!--女生 resultType:指定封装的结果类型;不能缺少。/resultMap--><case value="0" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee"><association property="department" select="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.DepartmentMapper.getDeptById" column="department_id" fetchType="eager" ></association></case><!--男生 ;如果是男生,把last_name这一列的值赋值给email; --><case value="1" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee"><id column="id" property="id"/><result column="last_name" property="lastName"/><result column="last_name" property="email"/><result column="gender" property="gender"/></case></discriminator></resultMap><!-- public Employee getEmpByIdStep(Integer id);--><select id="getEmpsWithDiscriminator" resultMap="MyEmpDis">select * from employee limit 10</select>
EmployeeMapperTest.java
@Testpublic void testGetEmpsWithDiscriminator() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c03/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {EmployeeMapper em = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);System.out.println(em.getEmpsWithDiscriminator());session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}
38.动态sql-简介&环境搭建
- 动态SQL是MyBatis强大特性之一。极大的简化我们拼装SQL的操作。
- 动态SQL元素和使用 JSTL 或其他类似基于 XML 的文本处理器相似。
MyBatis采用功能强大的基于 OGNL 的表达式来简化操作。
- if
- choose (when, otherwise)
- trim (where, set)
- foreach
39.动态sql-if-判断&OGNL
DynamicSQLMapper.java
public interface DynamicSQLMapper {//携带了哪个字段查询条件就带上这个字段的值public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionIf(Employee employee);}
DynamicSQLMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c04.dynamicsql.DynamicSQLMapper"><!-- 查询员工,要求,携带了哪个字段查询条件就带上这个字段的值 --><!-- public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionIf(Employee employee); --><select id="getEmpsByConditionIf" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from employee where<!-- test:判断表达式(OGNL) OGNL参照PPT或者官方文档。 c:if test 从参数中取值进行判断 遇见特殊符号应该去写转义字符: &&: --><if test="id!=null">id=#{id}</if><if test="lastName!=null && lastName!=""">and last_name like #{lastName}</if><if test="email!=null and email.trim()!=""">and email=#{email}</if><!-- ognl会进行字符串与数字的转换判断 "0"==0 --><if test="gender==0 or gender==1">and gender=#{gender}</if></select></mapper>
DynamicSQLMapperTest.java
public class DynamicSQLMapperTest {@Testpublic void testGetEmpsByConditionIf() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c04/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {DynamicSQLMapper dsm = session.getMapper(DynamicSQLMapper.class);Employee employee = new Employee(1, "jallen", null, null);System.out.println(dsm.getEmpsByConditionIf(employee));session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}}
OGNL
OGNL官方文档
OGNL( Object Graph Navigation Language )对象图导航语言, 这是一种强大的表达式语言,通过它可以非常方便的来操作对象属性。 类似于我们的EL, SpEL等。
- 访问对象属性: person.name
- 调用方法: person.getName()
- 调用静态属性/方法: @java.lang.Math@PI、@java.util.UUID@randomUUID()
- 调用构造方法: new com.lun.Person(‘admin’).name
- 运算符: +, -*, /, %
- 逻辑运算符: in, not in, >, >=, <, <=, ==, !=
注意: xml中特殊符号如”,>,<等这些都需要使用转义字符
访问集合伪属性:
| 类型 | 伪属性 | 伪属性对应的 Java 方法 |
|---|---|---|
| List、 Set、 Map | size、 isEmpty | List/Set/Map.size(),List/Set/Map.isEmpty() |
| List、 Set | iterator | List.iterator()、 Set.iterator() |
| Map | keys、 values | Map.keySet()、 Map.values() |
| Iterator | next、 hasNext | Iterator.next()、 Iterator.hasNext() |
40.动态sql-where-查询条件
查询的时候如果某些条件没带可能sql拼装会有问题
- 给where后面加上1=1,以后的条件都and xxx。
- mybatis使用where标签来将所有的查询条件包括在内。mybatis就会将where标签中拼装的sql,多出来的and或者or去掉(where只会去掉第一个多出来的and或者or,但最后一个多出来的and或者or则不会去掉)。
DynamicSQLMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c04.dynamicsql.DynamicSQLMapper"><select id="getEmpsByConditionIfWithWhere" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from employee<where><if test="id!=null">id=#{id}</if><if test="lastName!=null && lastName!=""">and last_name like #{lastName}</if><if test="email!=null and email.trim()!=""">and email=#{email}</if><!-- ognl会进行字符串与数字的转换判断 "0"==0 --><if test="gender==0 or gender==1">and gender=#{gender}</if></where></select></select>
DynamicSQLMapper.java
public interface DynamicSQLMapper {public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionIfWithWhere(Employee employee);
DynamicSQLMapperTest.java
public class DynamicSQLMapperTest {@Testpublic void testGetEmpsByConditionIfWithWhere() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c04/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {DynamicSQLMapper dsm = session.getMapper(DynamicSQLMapper.class);Employee employee = new Employee(null, "jallen", null, null);System.out.println(dsm.getEmpsByConditionIfWithWhere(employee));session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}...
41.动态sql-trim-自定义字符串截取
后面多出的and或者or where标签不能解决
prefix=””:前缀:trim标签体中是整个字符串拼串后的结果。
- prefix给拼串后的整个字符串加一个前缀
prefixOverrides=””:
- 前缀覆盖: 去掉整个字符串前面多余的字符
suffix=””:后缀
- suffix给拼串后的整个字符串加一个后缀
suffixOverrides=””
- 后缀覆盖:去掉整个字符串后面多余的字符
DynamicSQLMapper.java
public interface DynamicSQLMapper {public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionTrim(Employee employee);...
DynamicSQLMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c04.dynamicsql.DynamicSQLMapper"><!--public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionTrim(Employee employee); --><select id="getEmpsByConditionTrim" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from employee<!-- 自定义字符串的截取规则 --><trim prefix="where" suffixOverrides="and"><if test="id!=null">id=#{id} and</if><if test="lastName!=null && lastName!=""">last_name like #{lastName} and</if><if test="email!=null and email.trim()!=""">email=#{email} and</if><!-- ognl会进行字符串与数字的转换判断 "0"==0 --><if test="gender==0 or gender==1">gender=#{gender}</if></trim></select>...
DynamicSQLMapperTest.java
public class DynamicSQLMapperTest {@Testpublic void testGetEmpsByConditionTrim() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c04/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {DynamicSQLMapper dsm = session.getMapper(DynamicSQLMapper.class);Employee employee = new Employee(1, "jallen", null, null);System.out.println(dsm.getEmpsByConditionTrim(employee));session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}...
42.动态sql-choose-分支选择
DynamicSQLMapper.java
public interface DynamicSQLMapper {public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionChoose(Employee employee);...
DynamicSQLMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c04.dynamicsql.DynamicSQLMapper"><!-- public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionChoose(Employee employee); --><select id="getEmpsByConditionChoose" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from employee<where><!-- 如果带了id就用id查,如果带了lastName就用lastName查;只会进入其中一个 --><choose><when test="id!=null">id=#{id}</when><when test="lastName!=null">last_name like #{lastName}</when><when test="email!=null">email = #{email}</when><otherwise>gender = 0</otherwise></choose></where></select>
DynamicSQLMapperTest.java
public class DynamicSQLMapperTest {@Testpublic void testGetEmpsByConditionChoose() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c04/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {DynamicSQLMapper dsm = session.getMapper(DynamicSQLMapper.class);Employee employee = new Employee(1, "jallen", null, null);System.out.println(dsm.getEmpsByConditionChoose(employee));session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}
43.动态sql-set-与if结合的动态更新
DynamicSQLMapper.java
public interface DynamicSQLMapper {public void updateEmp(Employee employee);
DynamicSQLMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c04.dynamicsql.DynamicSQLMapper"><!--public void updateEmp(Employee employee); --><update id="updateEmp"><!-- Set标签的使用 -->update employee<set><if test="lastName!=null">last_name=#{lastName},</if><if test="email!=null">email=#{email},</if><if test="gender!=null">gender=#{gender}</if></set>where id=#{id}<!-- Trim:更新拼串 update tbl_employee <trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=","> <if test="lastName!=null"> last_name=#{lastName}, </if> <if test="email!=null"> email=#{email}, </if> <if test="gender!=null"> gender=#{gender} </if> </trim> where id=#{id} --></update>
DynamicSQLMapperTest.java
public class DynamicSQLMapperTest {@Testpublic void testUpdateEmp() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c04/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {DynamicSQLMapper dsm = session.getMapper(DynamicSQLMapper.class);Employee employee = new Employee(1, "jallen2", null, null);dsm.updateEmp(employee);session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}
44.动态sql-foreach-遍历集合
collection:指定要遍历的集合:
- list类型的参数会特殊处理封装在map中,map的key就叫list
- item:将当前遍历出的元素赋值给指定的变量
- separator:每个元素之间的分隔符
- open:遍历出所有结果拼接一个开始的字符
- close:遍历出所有结果拼接一个结束的字符
index:索引。遍历list的时候是index就是索引,item就是当前值
- 遍历map的时候index表示的就是map的key,item就是map的值
#{变量名}就能取出变量的值也就是当前遍历出的元素
DynamicSQLMapper.java
public interface DynamicSQLMapper {public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionForeach(@Param("ids")List<Integer> ids);
DynamicSQLMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c04.dynamicsql.DynamicSQLMapper"><!--public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionForeach(List<Integer> ids); --><select id="getEmpsByConditionForeach" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from employee<foreach collection="ids" item="item_id" separator=","open="where id in(" close=")">#{ item_id}</foreach></select>
DynamicSQLMapperTest.java
public class DynamicSQLMapperTest {@Testpublic void testGetEmpsByConditionForeach() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c04/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {DynamicSQLMapper dsm = session.getMapper(DynamicSQLMapper.class);System.out.println(dsm.getEmpsByConditionForeach(Arrays.asList(1,2,3)));session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}
45.动态sql-foreach-mysql下foreach批量插入的两种方式
DynamicSQLMapper.java
public interface DynamicSQLMapper {public void addEmps(@Param("emps")List<Employee> emps);public void addEmps2(@Param("emps")List<Employee> emps);
DynamicSQLMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c04.dynamicsql.DynamicSQLMapper"><!-- 批量保存 --><!--public void addEmps(@Param("emps")List<Employee> emps); --><!--MySQL下批量保存:可以foreach遍历 mysql支持values(),(),()语法--><insert id="addEmps">insert into employee(last_name,email,gender,department_id)values<foreach collection="emps" item="emp" separator=",">(#{emp.lastName},#{emp.email},#{emp.gender},#{emp.department.id})</foreach></insert><!-- --><!-- 这种方式需要数据库连接属性allowMultiQueries=true; 这种分号分隔多个sql可以用于其他的批量操作(删除,修改) --><insert id="addEmps2"><foreach collection="emps" item="emp" separator=";">insert into employee(last_name,email,gender,department_id)values(#{emp.lastName},#{emp.email},#{emp.gender},#{emp.department.id})</foreach></insert>
注意,MySQL数据库连接属性allowMultiQueries=true,才能批量删除,修改数据。(在连接MySQL的URL后添加参数)。
DynamicSQLMapperTest.java
public class DynamicSQLMapperTest {@Testpublic void testAddEmps2() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c04/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {DynamicSQLMapper dsm = session.getMapper(DynamicSQLMapper.class);dsm.addEmps2(Arrays.asList(new Employee(null, "abc", null, null),new Employee(null, "cba",null, null)));session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}@Testpublic void testAddEmps() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c04/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {DynamicSQLMapper dsm = session.getMapper(DynamicSQLMapper.class);dsm.addEmps(Arrays.asList(new Employee(null, "abc", null, null),new Employee(null, "cba",null, null)));session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}
46.动态sql-foreach-oracle下批量插入的两种方式
Oracle数据库批量保存:
- Oracle不支持values(),(),()
Oracle支持的批量方式:
- 多个insert放在begin - end里面
利用中间表
多个insert放在begin - end里面
begin
insert into employees(employee_id,last_name,email)values(employees_seq.nextval,'test_001','test_001@atguigu.com');insert into employees(employee_id,last_name,email)values(employees_seq.nextval,'test_002','test_002@atguigu.com');
end;
利用中间表
insert into employees(employee_id,last_name,email)
select employees_seq.nextval,lastName,email from(select 'test_a_01' lastName,'test_a_e01' email from dualunionselect 'test_a_02' lastName,'test_a_e02' email from dualunionselect 'test_a_03' lastName,'test_a_e03' email from dual
);
47.动态sql-foreach-oracle下foreach批量保存两种方式
<insert id="addEmps" databaseId="oracle"><!-- oracle第一种批量方式 --><!-- <foreach collection="emps" item="emp" open="begin" close="end;"> insert into employees(employee_id,last_name,email) values(employees_seq.nextval,#{emp.lastName},#{emp.email}); </foreach> --><!-- oracle第二种批量方式 -->insert into employees(employee_id,last_name,email)<foreach collection="emps" item="emp" separator="union" open="select employees_seq.nextval,lastName,email from(" close=")">select #{emp.lastName} lastName,#{emp.email} email from dual</foreach></insert>
48.动态sql-内置参数 _parameter & _databaseId
不只是方法传递过来的参数可以被用来判断,
mybatis默认还有两个内置参数:
_parameter:代表整个参数
- 单个参数:_parameter就是这个参数
- 多个参数:参数会被封装为一个map;_parameter就是代表这个map
_databaseId:如果配置了databaseIdProvider标签。
- _databaseId就是代表当前数据库的别名oracle
49.动态sql-bind-绑定
<!--public List<Employee> getEmpsTestInnerParameter(Employee employee); --><select id="getEmpsTestInnerParameter" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"><!-- bind:可以将OGNL表达式的值绑定到一个变量中,方便后来引用这个变量的值 --><bind name="lastName" value="'%'+lastName+'%'"/><if test="_databaseId=='mysql'">select * from tbl_employee<if test="_parameter!=null">where last_name like #{lastName}<!-- 这里使用到lastName --></if></if><if test="_databaseId=='oracle'">select * from employees<if test="_parameter!=null">where last_name like #{_parameter.lastName}</if></if></select>
50.动态sql-sql-抽取可重用的sql片段
抽取可重用的sql片段。方便后面引用:
- sql抽取:经常将要查询的列名,或者插入用的列名抽取出来方便引用
- include来引用已经抽取的sql:
include还可以自定义一些property,sql标签内部就能使用自定义的属性
- include-property:取值的正确方式${prop},
- 不能使用
#{},而使用${}
${alias}.id,${alias}.username,${alias}.password
employee_id,last_name,email
last_name,email,gender,d_id
…
insert into tbl_employee(
)
values
(#{emp.lastName},#{emp.email},#{emp.gender},#{emp.dept.id})
51.缓存-缓存介绍
MyBatis官方文档
MyBatis 包含一个非常强大的查询缓存特性,它可以非常方便地配置和定制。缓存可以极大的提升查询效率。
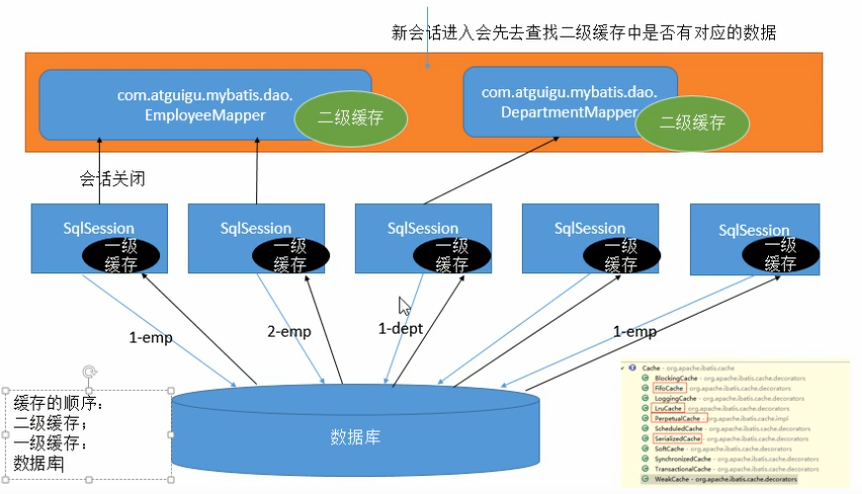
MyBatis系统中默认定义了两级缓存,一级缓存和二级缓存。
- 默认情况下,只有一级缓存( SqlSession级别的缓存,也称为本地缓存)开启。
- 二级缓存需要手动开启和配置,他是基于namespace级别的缓存。
- 为了提高扩展性。 MyBatis定义了缓存接口Cache。我们可以通过实现Cache接口来自定义二级缓存
52.缓存-一级缓存体验
一级缓存
- 一级缓存(local cache),即本地缓存,作用域默认为sqlSession。当 Session flush 或 close 后, 该Session 中的所有 Cache 将被清空。
- 本地缓存不能被关闭, 但可以调用 clearCache() 来清空本地缓存, 或者改变缓存的作用域.
- 在mybatis3.1之后, 可以配置本地缓存的作用域. 在 mybatis.xml 中配置
| - | - | - | - |
|---|---|---|---|
| localCacheScope | MyBatis uses local cache to prevent circular references and speed up repeated nested queries. By default (SESSION) all queries executed during a session are cached. If localCacheScope=STATEMENT local session will be used just for statement execution, no data will be shared between two different calls to the same SqlSession. | SESSION/STATEMENT | SESSION |
一级缓存体验
CacheTest.java
public class CacheTest {@Testpublic void testFirstCache() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c03/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();try {EmployeeMapper em = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);Employee e1 = em.getEmpById(1);System.out.println(e1);Employee e2 = em.getEmpById(1);System.out.println(e2);System.out.println("e1 == e2 : " + (e1 == e2));session.commit();} finally {session.close();}}}
输出结果:
DEBUG 08-02 22:50:35,092 ==> Preparing: select * from employee where id = ? (BaseJdbcLogger.java:145)DEBUG 08-02 22:50:35,192 ==> Parameters: 1(Integer) (BaseJdbcLogger.java:145)DEBUG 08-02 22:50:35,260 <== Total: 1 (BaseJdbcLogger.java:145)Employee [id=1, lastName=jallen2, email=jallen@good.com, gender=1, department=null]Employee [id=1, lastName=jallen2, email=jallen@good.com, gender=1, department=null]e1 == e2 : true <-------------e1和e2指向相同的对象
53.缓存-一级缓存失效的四种情况
同一次会话期间只要查询过的数据都会保存在当前SqlSession的一个Map中
- key = hashCode + 查询的SqlId + 编写的sql查询语句 + 参数
一级缓存失效的四种情况:
- 不同的SqlSession对应不同的一级缓存
- 同一个SqlSession但是查询条件不同
- 同一个SqlSession两次查询期间执行了任何一次增删改操作
- 同一个SqlSession两次查询期间手动清空了缓存
54.缓存-二级缓存介绍
- 二级缓存(second level cache),全局作用域缓存
- 二级缓存默认不开启,需要手动配置
- MyBatis提供二级缓存的接口以及实现,缓存实现要求 POJO实现Serializable接口
- 二级缓存在 SqlSession 关闭或提交之后才会生效
使用步骤
全局配置文件中开启二级缓存
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
需要使用二级缓存的映射文件处使用cache配置缓存
<cache />
- 注意: POJO需要实现Serializable接口
cache标签的属性:
eviction:缓存的回收策略:
- LRU – 最近最少使用的:移除最长时间不被使用的对象。
- FIFO – 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。
- SOFT – 软引用:移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。
- WEAK – 弱引用:更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。
- 默认的是 LRU。
flushInterval:缓存刷新间隔
- 缓存多长时间清空一次,默认不清空,设置一个毫秒值
readOnly:是否只读:
- true:只读;mybatis认为所有从缓存中获取数据的操作都是只读操作,不会修改数据。mybatis为了加快获取速度,直接就会将数据在缓存中的引用交给用户。不安全,速度快
- false:非只读:mybatis觉得获取的数据可能会被修改。mybatis会利用序列化&反序列的技术克隆一份新的数据给你。安全,速度慢
- size:缓存存放多少元素;
type=””:指定自定义缓存的全类名;
- 实现Cache接口即可;
55.缓存-二级缓存使用&细节
使用步骤:
全局配置文件中开启二级缓存
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
需要使用二级缓存的映射文件处使用cache配置缓存
<cache />
- 注意: POJO需要实现Serializable接口
mybatis-config.xml
<configuration><settings><setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
Employee.java
public class Employee implements Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = -7390587151857533202L;
EmployeeMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper"><cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000" readOnly="false" size="1024"></cache>
CacheTest.java
public class CacheTest {@Testpublic void testSecondCache() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c05/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();SqlSession session2 = ssf.openSession();try {EmployeeMapper em = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);Employee e1 = em.getEmpById(1);System.out.println(e1);session.close();EmployeeMapper em2 = session2.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);Employee e2 = em2.getEmpById(1);System.out.println(e2);System.out.println("e1 == e2 : " + (e1 == e2));} finally {session2.close();}}
输出结果:
DEBUG 08-03 01:13:02,575 Cache Hit Ratio [com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper]: 0.0 (LoggingCache.java:62)DEBUG 08-03 01:13:03,945 ==> Preparing: select * from employee where id = ? (BaseJdbcLogger.java:145)DEBUG 08-03 01:13:04,081 ==> Parameters: 1(Integer) (BaseJdbcLogger.java:145)DEBUG 08-03 01:13:04,186 <== Total: 1 (BaseJdbcLogger.java:145)Employee [id=1, lastName=jallen2, email=jallen@good.com, gender=1, department=null]DEBUG 08-03 01:13:04,218 Cache Hit Ratio [com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.EmployeeMapper]: 0.5 (LoggingCache.java:62)Employee [id=1, lastName=jallen2, email=jallen@good.com, gender=1, department=null]e1 == e2 : false
56.缓存-缓存有关的设置以及属性
- 全局setting的cacheEnable:
– 配置二级缓存的开关。一级缓存一直是打开的。 - select标签的useCache属性:
– 配置这个select是否使用二级缓存。一级缓存一直是使用的 - 每个增删改标签的flushCache属性:
– 增删改默认flushCache=true。sql执行以后,会同时清空一级和二级缓存。查询默认flushCache=false。 - sqlSession.clearCache():
– 只是用来清除一级缓存。 - 全局setting的localCacheScope:本地缓存作用域:(一级缓存SESSION),当前会话的所有数据保存在会话缓存中;STATEMENT:可以禁用一级缓存。
57.缓存-缓存原理图示
58.缓存-第三方缓存整合原理&ehcache适配包下载
- EhCache 是一个纯Java的进程内缓存框架,具有快速、精干等特点,是Hibernate中默认的CacheProvider。
MyBatis定义了Cache接口方便我们进行自定义扩展。
package org.apache.ibatis.cache;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock;
public interface Cache {
String getId();
void putObject(Object key, Object value);
Object getObject(Object key);
Object removeObject(Object key);
void clear();
int getSize();
ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock();
}
59.缓存-MyBatis整合ehcache&总结
步骤:
加入mybatis-ehcache依赖
org.mybatis.caches
mybatis-ehcache
1.2.1 编写ehcache.xml配置文件
<?xml version=”1.0” encoding=”UTF-8”?>
配置cache标签
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"></cache>
演示:
DepartmentMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c03.mapper.dao.DepartmentMapper"><cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
CacheTest.java
public class CacheTest {@Testpublic void testEhcache() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory ssf = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c05/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();SqlSession session2 = ssf.openSession();try {DepartmentMapper dm = session.getMapper(DepartmentMapper.class);Department dp = dm.getDeptById(1);System.out.println(dp);session.close();DepartmentMapper dm2 = session2.getMapper(DepartmentMapper.class);Department dp2 = dm2.getDeptById(1);System.out.println(dp2);} finally {session2.close();}}
另外:
参照缓存: 若想在命名空间中共享相同的缓存配置和实例。可以使用 cache-ref 元素来引用另外一个缓存。
<mapper namespace="com.lun.mybatis.dao.DepartmentMapper"><!-- 引用缓存:namespace:指定和哪个名称空间下的缓存一样 --><cache-ref namespace="com.lun.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper"/>
60.整合Spring-整合适配包下载
MyBatis-Spring 会帮助你将 MyBatis 代码无缝地整合到 Spring 中。它将允许 MyBatis 参与到 Spring 的事务管理之中,创建映射器 mapper 和 SqlSession 并注入到 bean 中,以及将 Mybatis 的异常转换为 Spring 的 DataAccessException。最终,可以做到应用代码不依赖于 MyBatis,Spring 或 MyBatis-Spring。
官方文档
源码仓库
官方整合示例
61.整合Spring-所有需要的jar包导入
pom.xml
<!-- DB连接池 --><dependency><groupId>com.mchange</groupId><artifactId>c3p0</artifactId><version>0.9.5.5</version></dependency><!-- JSP --><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet</groupId><artifactId>jstl</artifactId><version>1.2</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet</groupId><artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId><version>3.1.0</version><scope>provided</scope></dependency><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId><artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId><version>2.1</version><scope>provided</scope></dependency><!-- 用于整合Spring --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context</artifactId><version>${springframework.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId><version>${springframework.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId><version>${springframework.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId><version>${springframework.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId><version>${springframework.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId><version>${springframework.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId><version>${springframework.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-test</artifactId><version>${springframework.version}</version><scope>test</scope></dependency>
62.整合Spring-引入MyBatis之前的配置
mybatis-config.xml
<configuration><settings><setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/><!--显示的指定每个我们需要更改的配置的值,即使他是默认的。防止版本更新带来的问题 --><setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/><setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/><setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/></settings></configuration>
EmployeeMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lun.c06.spring.EmployeeMapper"><select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from employee where id = #{id}</select><select id="getEmps" resultType="com.lun.c01.helloworld.bean.Employee">select * from employee</select></mapper>
EmployeeMapper
public interface EmployeeMapper {public Employee getEmpById(Integer id);public List<Employee> getEmps();}
63.整合Spring-SpringMVC配置文件编写
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app ...><!--Spring配置: needed for ContextLoaderListener --><context-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value></context-param><!-- Bootstraps the root web application context before servlet initialization --><listener><listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class></listener><!-- SpringMVC配置 --><!-- The front controller of this Spring Web application, responsible for handling all application requests --><servlet><servlet-name>spring</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet><!-- Map all requests to the DispatcherServlet for handling --><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>spring</servlet-name><url-pattern>/</url-pattern></servlet-mapping></web-app>
spring-servlet.xml
<beans ..."><!--SpringMVC只是控制网站跳转逻辑 --><!-- 只扫描控制器 --><context:component-scan base-package="com.lun.c06" use-default-filters="false"><context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/></context:component-scan><!-- 视图解析器 --><bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"><property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/"></property><property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property></bean><mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven><mvc:default-servlet-handler/></beans>
64.整合Spring-Spring配置文件编写
applicationContext.xml
<beans ...><!-- Spring希望管理所有的业务逻辑组件,等。。。 --><context:component-scan base-package="com.lun.c06"><context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" /></context:component-scan><!-- 引入数据库的配置文件 --><context:property-placeholder location="classpath:c04/dbconfig.properties" /><!-- Spring用来控制业务逻辑。数据源、事务控制、aop --><bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"><property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"></property><property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property><property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"></property><property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property></bean><!-- spring事务管理 --><bean id="dataSourceTransactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"><property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property></bean><!-- 开启基于注解的事务 --><tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="dataSourceTransactionManager"/>...
65.整合Spring-Spring整合MyBatis关键配置
applicationContext.xml
...<!-- 整合mybatis 目的:1、spring管理所有组件。mapper的实现类。 service==>Dao @Autowired:自动注入mapper; 2、spring用来管理事务,spring声明式事务 --><!--创建出SqlSessionFactory对象 --><bean id="sqlSessionFactoryBean" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"><property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property><!-- configLocation指定全局配置文件的位置 --><property name="configLocation" value="classpath:c06/mybatis-config.xml"></property><!--mapperLocations: 指定mapper文件的位置--><property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:c06/*Mapper.xml"></property></bean><!--配置一个可以进行批量执行的sqlSession --><bean id="sqlSession" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate"><constructor-arg name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactoryBean"></constructor-arg><constructor-arg name="executorType" value="BATCH"></constructor-arg></bean><!-- 扫描所有的mapper接口的实现,让这些mapper能够自动注入; base-package:指定mapper接口的包名 --><mybatis-spring:scan base-package="com.lun.c06"/><!-- <bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"> <property name="basePackage" value="com.lun.dao"></property> </bean> --></beans>
66.整合Spring-整合测试
EmployeeController.java
@Controllerpublic class EmployeeController implements Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = -5415910268862124882L;@AutowiredEmployeeService employeeService;@RequestMapping("/getemps")public String emps(Map<String,Object> map){List<Employee> emps = employeeService.getEmps();map.put("allEmps", emps);return "list";}}
EmployeeService.java
@Servicepublic class EmployeeService {@Autowiredprivate EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;@Autowiredprivate SqlSession sqlSession;public List<Employee> getEmps(){////EmployeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);return employeeMapper.getEmps();}}
list.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"pageEncoding="UTF-8"%><%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><title>员工列表</title></head><body><table><tr><td>id</td><td>lastName</td><td>email</td><td>gender</td></tr><c:forEach items="${allEmps}" var="emp"><tr><td>${emp.id}</td><td>${emp.lastName}</td><td>${emp.email}</td><td>${emp.gender}</td></tr></c:forEach></table></body></html>
最后,在浏览器输入http://localhost:8080/LearnMybatis/getemps进行测试
MyBatis-代码生成器
MyBatis Generator:
简称MBG,是一个专门为MyBatis框架使用者定制的代码生成器,可以快速的根据表生成对应的映射文件,接口,以及bean类。支持基本的增删改查,以及QBC风格的条件查询。但是表连接、存储过程等这些复杂sql的定义需要我们手工编写
官方文档地址
官方工程地址
添加依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId><artifactId>mybatis-generator-core</artifactId><version>1.3.7</version></dependency>
使用说明
使用步骤:
编写MBG的配置文件(重要几处配置)
- jdbcConnection配置数据库连接信息
- javaModelGenerator配置javaBean的生成策略
- sqlMapGenerator 配置sql映射文件生成策略
- javaClientGenerator配置Mapper接口的生成策略
table 配置要逆向解析的数据表
- tableName:表名
- domainObjectName:对应的javaBean名
- 运行代码生成器生成代码
注意:
Context标签
- targetRuntime=“MyBatis3“可以生成带条件的增删改查
- targetRuntime=“MyBatis3Simple“可以生成基本的增删改查
- 如果再次生成,建议将之前生成的数据删除,避免xml向后追加内容出现的问题。
配置文件
mbg.xml
<generatorConfiguration><!-- targetRuntime="MyBatis3Simple":生成简单版的CRUD "MyBatis3":豪华版 --><properties resource="c04/dbconfig.properties"/><context id="DB2Tables" targetRuntime="MyBatis3"><!-- jdbcConnection:指定如何连接到目标数据库 --><jdbcConnection driverClass="${jdbc.driver}" connectionURL="${jdbc.url}" userId="${jdbc.username}" password="${jdbc.password}"></jdbcConnection><!-- --><javaTypeResolver ><property name="forceBigDecimals" value="false" /></javaTypeResolver><!-- javaModelGenerator:指定javaBean的生成策略 targetPackage="test.model":目标包名 targetProject="\MBGTestProject\src":目标工程 --><javaModelGenerator targetPackage="com.lun.bean" targetProject="C:\\src"><property name="enableSubPackages" value="true" /><property name="trimStrings" value="true" /></javaModelGenerator><!-- sqlMapGenerator:sql映射生成策略: --><sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="com.lun.dao" targetProject="C:\\src"><property name="enableSubPackages" value="true" /></sqlMapGenerator><!-- javaClientGenerator:指定mapper接口所在的位置 --><javaClientGenerator type="XMLMAPPER" targetPackage="com.lun.dao" targetProject="C:\\src"><property name="enableSubPackages" value="true" /></javaClientGenerator><!-- 指定要逆向分析哪些表:根据表要创建javaBean --><table tableName="department" domainObjectName="Department"></table><table tableName="employee" domainObjectName="Employee"></table></context></generatorConfiguration>
生成器代码
GenerateCode.java
public class GenerateCode {public static void main(String[] args) {try {List<String> warnings = new ArrayList<String>();boolean overwrite = true;File configFile = new File(GenerateCode.class.getClassLoader().getResource("c07/mbg.xml").getFile());ConfigurationParser cp = new ConfigurationParser(warnings);Configuration config = cp.parseConfiguration(configFile);DefaultShellCallback callback = new DefaultShellCallback(overwrite);MyBatisGenerator myBatisGenerator = new MyBatisGenerator(config, callback, warnings);myBatisGenerator.generate(null);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
QBC风格的带条件查询
生成器会QBC风格代码
QBC(Query By Criteria) API提供了检索对象的另一种方式,它主要由Criteria接口、Criterion接口和Expresson类组成,它支持在运行时动态生成查询语句。
From https://baike.baidu.com/item/QBC/1529451
QBC风格代码使用实例:
@Testpublic void test01(){SqlSession openSession = build.openSession();DeptMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(DeptMapper.class);DeptExample example = new DeptExample();//所有的条件都在example中封装Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();//select id, deptName, locAdd from tbl_dept WHERE//( deptName like ? and id > ? )criteria.andDeptnameLike("%部%");criteria.andIdGreaterThan(2);List<Dept> list = mapper.selectByExample(example);for (Dept dept : list) {System.out.println(dept);}}
MyBatis-工作原理
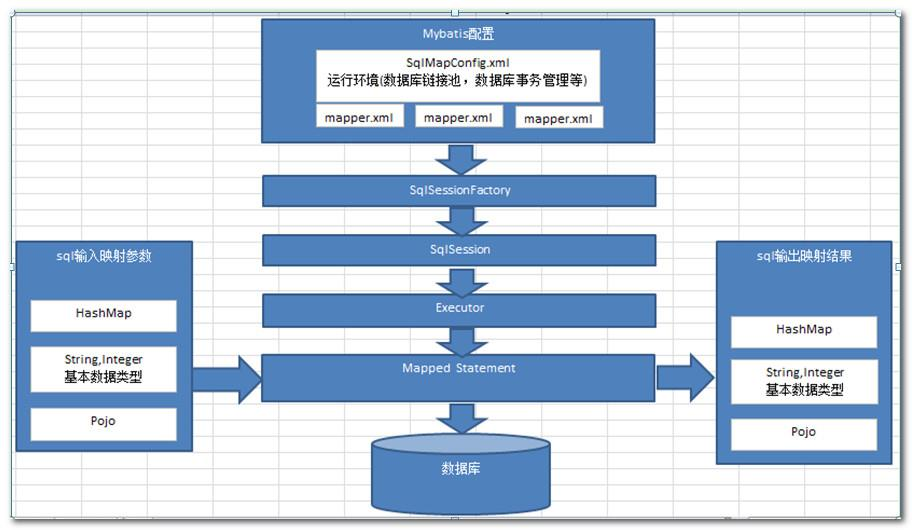

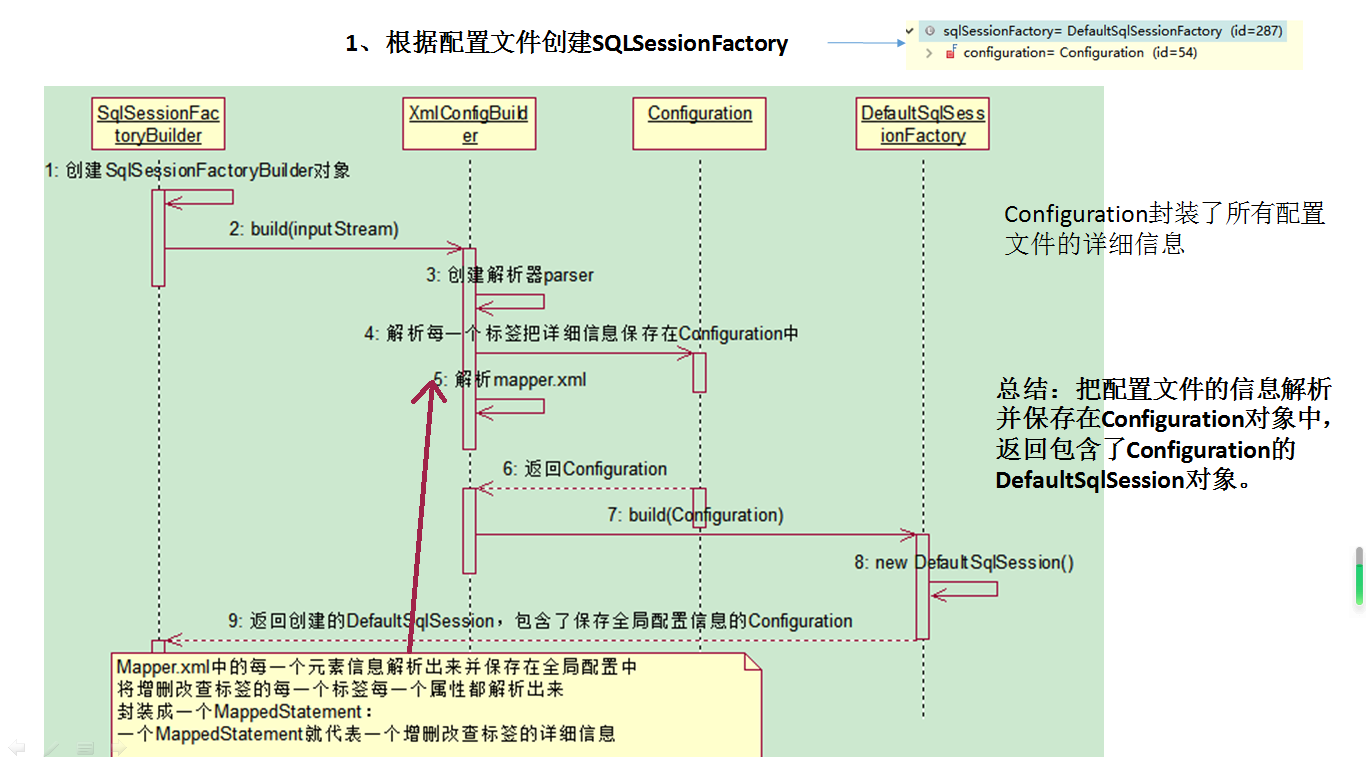
- Configuration封装了所有配置文件的详细信息
- 总结:把配置文件的信息解析并保存在Configuration对象中,返回包含了Configuration的DefaultSqlSession对象。
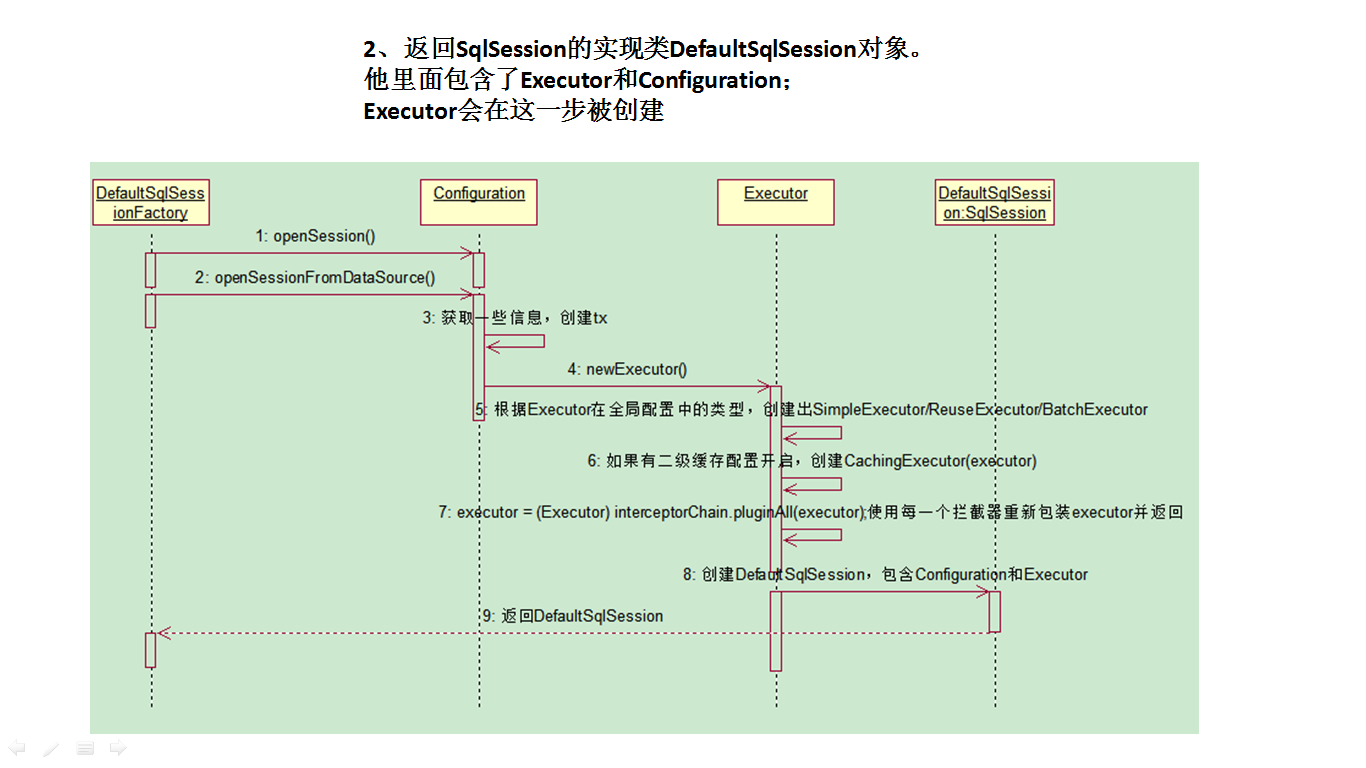
- 返回SqlSession的实现类DefaultSqlSession对象。他里面包含了Executor和Configuration
- Executor会在这一步被创建
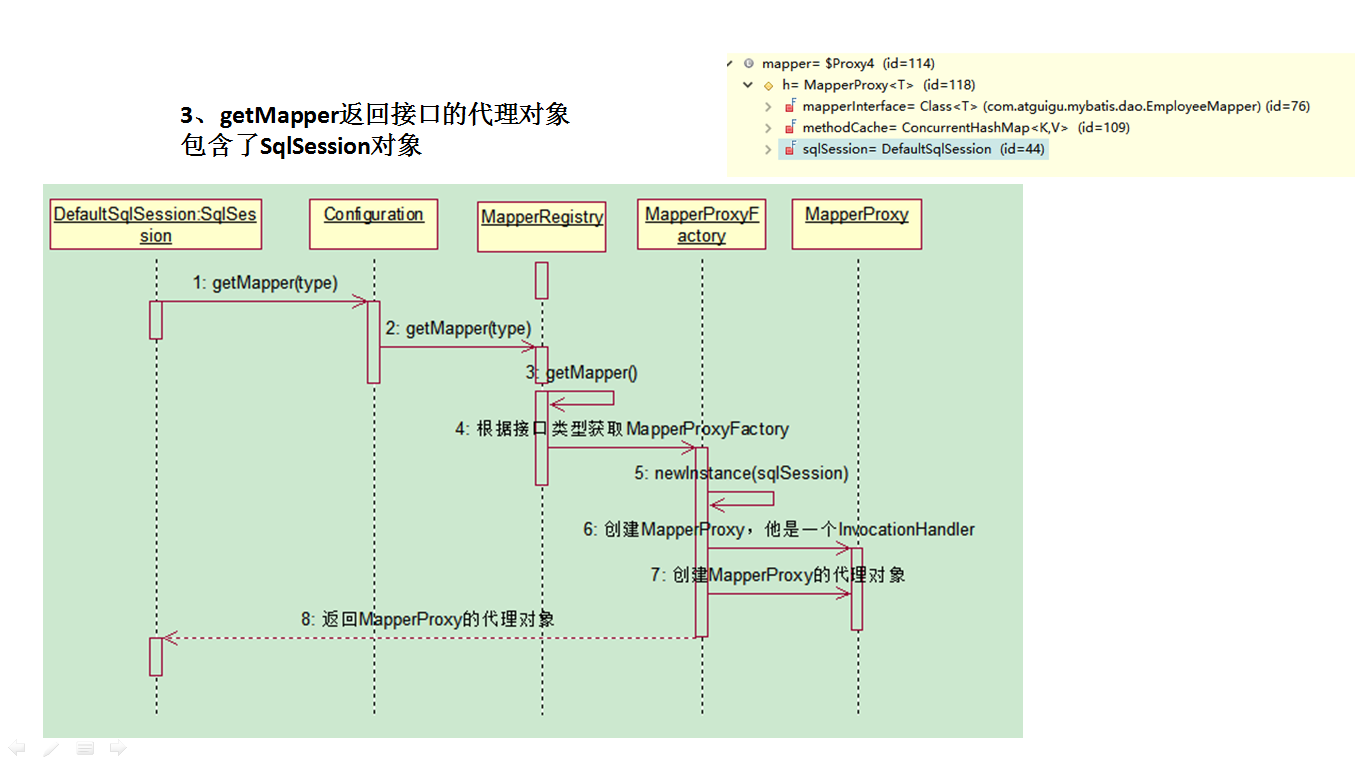
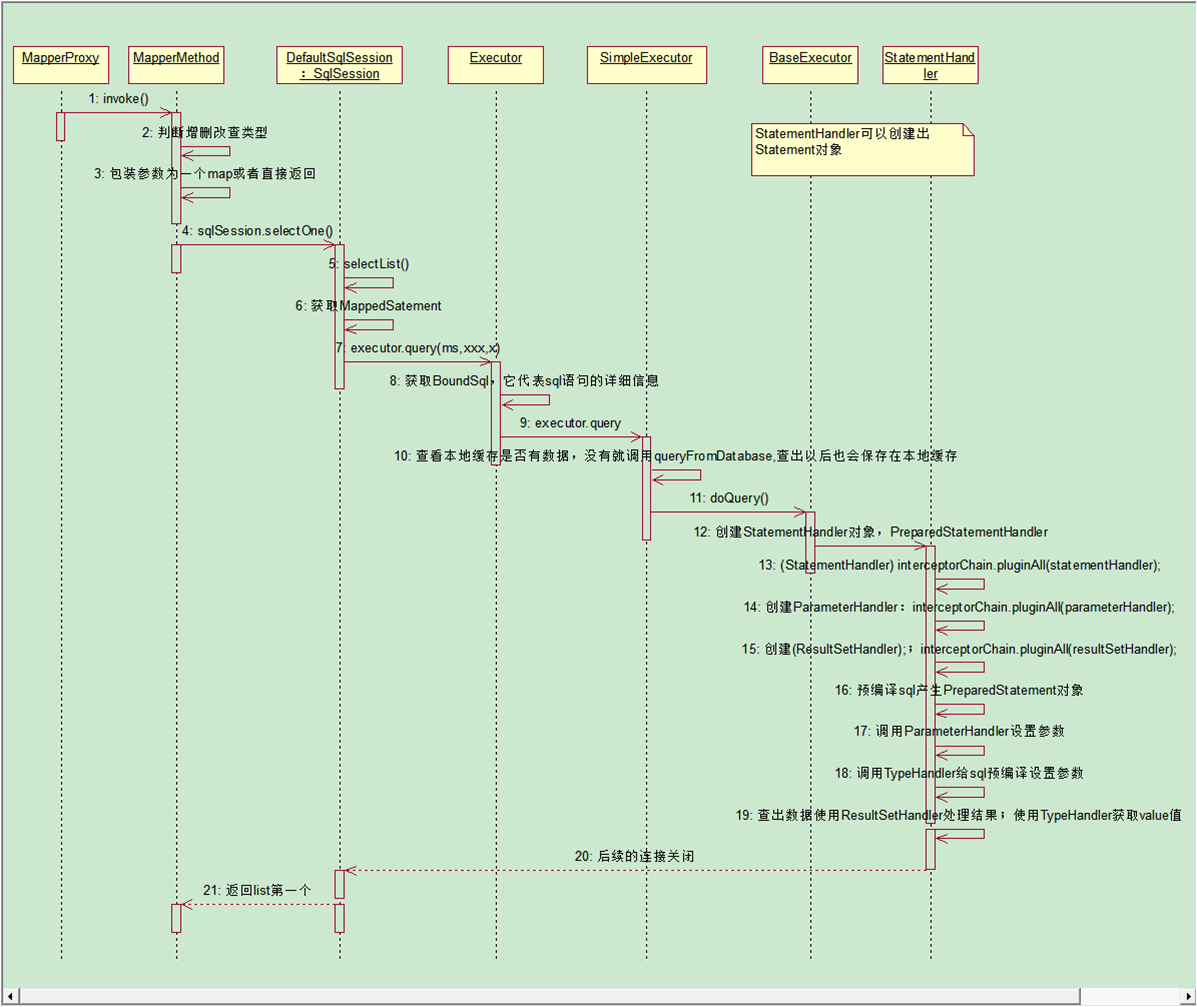
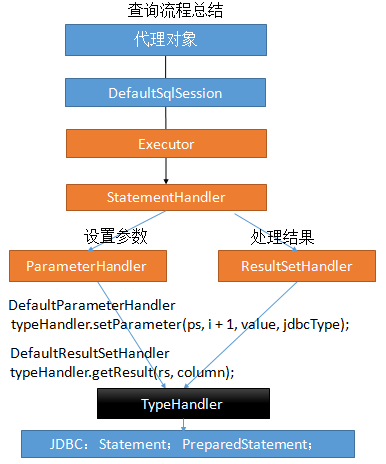
- StatementHandler:处理sql语句预编译,设置参数等相关工作;
- ParameterHandler:设置预编译参数用的
- ResultHandler:处理结果集
- TypeHandler:在整个过程中,进行数据库类型和javaBean类型的映射
小结
- 根据配置文件(全局,sql映射)初始化出Configuration对象
- 创建一个DefaultSqlSession对象,它里面包含Configuration以及Executor(根据全局配置文件中的defaultExecutorType创建出对应的Executor)
- DefaultSqlSession.getMapper():拿到Mapper接口对应的MapperProxy;
- MapperProxy里面有(DefaultSqlSession);
执行增删改查方法:
- 调用DefaultSqlSession的增删改查(Executor);
- 会创建一个StatementHandler对象。同时也会创建出ParameterHandler和ResultSetHandler)
- 调用StatementHandler预编译参数以及设置参数值,使用ParameterHandler来给sql设置参数
- 调用StatementHandler的增删改查方法;
- ResultSetHandler封装结果
注意:四大对象(Executor、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler)每个创建的时候都有一个interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
MyBatis-插件开发
在四大对象创建的时候
- 每个创建出来的对象不是直接返回的,而是interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
- 获取到所有的Interceptor(拦截器)(插件需要实现的接口);调用interceptor.plugin(target);返回target包装后的对象
插件机制,我们可以使用插件为目标对象创建一个代理对象;AOP(面向切面)我们的插件可以为四大对象创建出代理对象;代理对象就可以拦截到四大对象的每一个执行;
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {target = interceptor.plugin(target);}return target;
}
默认情况下,MyBatis 允许使用插件来拦截的方法调用包括:
- Executor (update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed)
- ParameterHandler (getParameterObject, setParameters)
- ResultSetHandler (handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters)
- StatementHandler (prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query)
插件开发
插件开发步骤:
- 编写插件实现Interceptor接口,并使用 @Intercepts注解完成插件签名
- 在全局配置文件中注册插件
MyFirstPlugin.java
//完成插件签名,用于拦截哪个对象的哪个方法@Intercepts({@Signature(type=StatementHandler.class,method="parameterize",args=java.sql.Statement.class)})public class MyFirstPlugin implements Interceptor {/** * intercept:拦截 * */@Overridepublic Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {// TODO Auto-generated method stubSystem.out.println("myfirstplugin...intercept:" + invocation.getMethod());Object target = invocation.getTarget();System.out.println("当前拦截到的对象:"+target);MetaObject metaObject = SystemMetaObject.forObject(target);Object value = metaObject.getValue("parameterHandler.parameterObject");System.out.println("sql语句中的参数是:"+value);metaObject.setValue("parameterHandler.parameterObject", 3);//执行目标方法Object proceed = invocation.proceed();//返回执行后的返回值return proceed;}//包装目标对象,为目标对象创建一个代理对象@Overridepublic Object plugin(Object target) {System.out.println("-->myfirstplugin...plugin,将要包装的对象:"+target);// TODO Auto-generated method stubObject wrap = Plugin.wrap(target, this);//返回为当前target创建的动态代理return wrap;}//将插件注册时的property属性设置进来@Overridepublic void setProperties(Properties properties) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubSystem.out.println("插件配置的信息:"+properties);}}
mybatis-config.xml
<configuration><plugins><plugin interceptor="com.lun.c08.interceptor.MyFirstPlugin"></plugin><!-- 可实现多个插件 --><plugin interceptor="com.lun.c08.interceptor.MySecondPlugin"></plugin></plugins>...
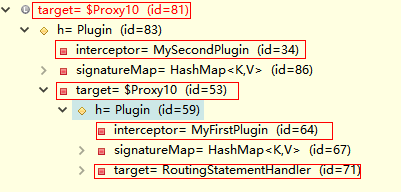
插件原理
- 按照插件注解声明,按照插件配置顺序调用插件plugin方法,生成被拦截对象的动态代理
- 多个插件依次生成目标对象的代理对象,层层包裹,先声明的先包裹;形成代理链
- 目标方法执行时依次从外到内执行插件的intercept方法。
- 多个插件情况下,我们往往需要在某个插件中分离出目标对象。可以借助MyBatis提供的SystemMetaObject类来进行获取最后一层的h以及target属性的值
Interceptor接口
- Intercept:拦截目标方法执行
- plugin:生成动态代理对象,可以使用MyBatis提供的Plugin类的wrap方法
- setProperties:注入插件配置时设置的属性
常用代码
从代理链中分离真实被代理对象
//1、分离代理对象。由于会形成多次代理,所以需要通过一个while 循环分离出最终被代理对象,从而方便提取信息MetaObject metaObject = SystemMetaObject.forObject(target);while (metaObject.hasGetter("h")) {Object h = metaObject.getValue("h");metaObject = SystemMetaObject.forObject(h);}//2、获取到代理对象中包含的被代理的真实对象Object obj = metaObject.getValue("target");//3、获取被代理对象的MetaObject方便进行信息提取MetaObject forObject = SystemMetaObject.forObject(obj);
扩展-MyBatis实用场景-PageHelper插件进行分页
PageHelper插件官网
pom.xml添加依赖
<!-- 分页插件 --><dependency><groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId><artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId><version>5.2.0</version></dependency>
MyBatis全局配置文件注册插件
<configuration><plugins><plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"></plugin></plugins>...
使用示例
public class PageHelperTest {@Testpublic void test() throws IOException {// 1、获取sqlSessionFactory对象SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c09/mybatis-config.xml");// 2、获取sqlSession对象SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();try {EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);Page<Object> page = PageHelper.startPage(5, 1);//<---------------------List<Employee> emps = mapper.getEmps();//传入要连续显示多少页PageInfo<Employee> info = new PageInfo<>(emps, 5);//<---------------------for (Employee employee : emps) {System.out.println(employee);}/*System.out.println("当前页码:"+page.getPageNum()); System.out.println("总记录数:"+page.getTotal()); System.out.println("每页的记录数:"+page.getPageSize()); System.out.println("总页码:"+page.getPages());*////xxxSystem.out.println("当前页码:"+info.getPageNum());System.out.println("总记录数:"+info.getTotal());System.out.println("每页的记录数:"+info.getPageSize());System.out.println("总页码:"+info.getPages());System.out.println("是否第一页:"+info.isIsFirstPage());System.out.println("连续显示的页码:");int[] nums = info.getNavigatepageNums();for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {System.out.println(nums[i]);}//xxxx} finally {openSession.close();}}}
扩展-MyBatis实用场景-批量操作
默认的 openSession() 方法没有参数,它会创建有如下特性的
- 会开启一个事务(也就是不自动提交)
- 连接对象会从由活动环境配置的数据源实例得到。
- 事务隔离级别将会使用驱动或数据源的默认设置。
- 预处理语句不会被复用,也不会批量处理更新。
openSession 方法的 ExecutorType 类型的参数,枚举类型:
- ExecutorType.SIMPLE: 这个执行器类型不做特殊的事情(这是默认装配的)。它为每个语句的执行创建一个新的预处理语句。
- ExecutorType.REUSE: 这个执行器类型会复用预处理语句。
- ExecutorType.BATCH: 这个执行器会批量执行所有更新语句

批量操作我们是使用MyBatis提供的BatchExecutor进行的,它的底层就是通过jdbc攒sql的方式进行的。我们可以让他攒够一定数量后发给数据库一次。
BatchTest.java
public class BatchTest {@Testpublic void test() throws IOException {SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c09/mybatis-config.xml");//可以执行批量操作的sqlSessionSqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH);long start = System.currentTimeMillis();try{EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {mapper.addEmp(new Employee(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 5), "b", "1"));}openSession.commit();long end = System.currentTimeMillis();//批量:(预编译sql一次==>设置参数===>10000次===>执行(1次))//Parameters: 616c1(String), b(String), 1(String)==>4598//非批量:(预编译sql=设置参数=执行)==》10000 10200System.out.println("执行时长:"+(end-start));}finally{openSession.close();}}}
与Spring整合中,我们推荐,额外的配置一个可以专门用来执行批量操作的SqlSession
<!--配置一个可以进行批量执行的sqlSession --><bean id="sqlSession" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate"><constructor-arg name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactoryBean"></constructor-arg><constructor-arg name="executorType" value="BATCH"></constructor-arg></bean>
需要用到批量操作的时候,我们可以注入配置的这个批量SqlSession。通过他获取到mapper映射器进行操作。
@Servicepublic class EmployeeService {@Autowiredprivate SqlSession sqlSession;...
注意:
- 批量操作是在session.commit()以后才发送sql语句给数据库进行执行的
- 如果我们想让其提前执行,以方便后续可能的查询操作获取数据,我们可以使用sqlSession.flushStatements()方法,让其直接冲刷到数据库进行执行。
扩展-MyBatis实用场景-存储过程
实际开发中,我们通常也会写一些存储过程,MyBatis也支持对存储过程的调用
一个最简单的存储过程:
delimiter $$create procedure test()beginselect 'hello';end $$delimiter ;
存储过程的调用:
- select标签中statementType=“CALLABLE”
- 标签体中调用语法:
{call procedure_name(#{param1_info},#{param2_info})}
MyBatis对存储过程的游标提供了一个JdbcType=CURSOR的支持,可以智能的把游标读取到的数据,映射到我们声明的结果集中
oracle存储过程
create or replace procedurehello_ test(p_start in int,p_end in int,p_count out int,p_emps out sys_refcursor)) asbeginselect count(*) into p_count from employees;open p_emps forselect * from (select rownum rn,e.* from employees e where rownum<=p_end )where rn>=p_start;end hello_test;
mapper.xml文件
<mapper namespace="com.lun.dao.EmployeeMapper"><!-- public void getPageByProcedure(); 1、使用select标签定义调用存储过程 2、statementType="CALLABLE":表示要调用存储过程 3、{call procedure_name(params)} --><select id="getPageByProcedure" statementType="CALLABLE" databaseId="oracle">{call hello_test(#{start,mode=IN,jdbcType=INTEGER},#{end,mode=IN,jdbcType=INTEGER},#{count,mode=OUT,jdbcType=INTEGER},#{emps,mode=OUT,jdbcType=CURSOR,javaType=ResultSet,resultMap=PageEmp})}</select><resultMap type="com.lun.bean.Employee" id="PageEmp"><id column="EMPLOYEE_ID" property="id"/><result column="LAST_NAME" property="email"/><result column="EMAIL" property="email"/></resultMap>
全局配置文件
<databaseIdProvider type="DB_VENDOR"><property name="MySQL" value="mysql"/><property name="Oracle" value="oracle"/></databaseIdProvider>
测试
/** * oracle分页: * 借助rownum:行号;子查询; * 存储过程包装分页逻辑 * @throws IOException */@Testpublic void testProcedure() throws IOException{SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory();SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();try{EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);OraclePage page = new OraclePage();page.setStart(1);page.setEnd(5);mapper.getPageByProcedure(page);System.out.println("总记录数:"+page.getCount());System.out.println("查出的数据:"+page.getEmps().size());System.out.println("查出的数据:"+page.getEmps());}finally{openSession.close();}}public class OraclePage {private int start;private int end;private int count;private List<Employee> emps;//setter and getter
扩展-MyBatis实用场景-typeHandler处理枚举
热身
新建一个枚举类
public enum EmpStatus {LOGIN,LOGOUT,REMOVE}
枚举的相关属性
@Testpublic void testEnumUse(){EmpStatus login = EmpStatus.LOGIN;System.out.println("枚举的索引:" + login.ordinal());System.out.println("枚举的名字:" + login.name());}
输出结果:
枚举的索引:0枚举的名字:LOGIN
若存入枚举属性到数据库,数据库表会呈现怎样的值?
Employee类添加一个枚举属性
public class Employee implements Serializable{private Integer id;private String lastName;private String email;private String gender;private EmpStatus empStatus = EmpStatus.LOGOUT;...
修改表结构
ALTER TABLE employee ADD COLUMN EmpStatus VARCHAR(255);
EmployeeMapper.java
public interface EmployeeMapper {public void addEmp2(com.lun.c09.other.bean.Employee em);public com.lun.c09.other.bean.Employee getEmpById2(Integer id);}
EmployeeMapper.xml
...<insert id="addEmp2" parameterType="com.lun.c09.other.bean.Employee" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id" >insert into employee(last_name,email,gender,empStatus)values(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender},#{empStatus})</insert><select id="getEmpById2" resultType="com.lun.c09.other.bean.Employee">select id,last_name lastName,email,gender,empStatus from employee where id = #{id}</select></mapper>
测试方法
/** * 默认mybatis在处理枚举对象的时候保存的是枚举的名字:EnumTypeHandler * 改变使用:EnumOrdinalTypeHandler: * @throws IOException */@Testpublic void testEnum() throws IOException{SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = Tools.getSqlSessionFactory("c09/mybatis-config.xml");SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();try{EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);Employee employee = new Employee("test_enum", "enum@abc.com","1");mapper.addEmp2(employee);//System.out.println("保存成功"+employee.getId());//openSession.commit();Employee empById = mapper.getEmpById2(employee.getId());System.out.println(empById.getEmpStatus());}finally{openSession.close();}}
结果是存入LOGOUT到数据库表。
因此,默认mybatis在处理枚举对象的时候保存的是枚举的名字:EnumTypeHandler
将想存数值到数据库表,改用EnumOrdinalTypeHandler
在MyBatis存储文件注册
<configuration><typeHandlers><typeHandler handler="org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumOrdinalTypeHandler" javaType="com.lun.c09.other.bean.EmpStatus"/></typeHandlers>...
自定义TypeHandler
我们可以通过自定义TypeHandler的形式来在设置参数或者取出结果集的时候自定义参数封装策略。
步骤:
- 实现TypeHandler接口或者继承BaseTypeHandler
- 使用@MappedTypes定义处理的java类型,使用@MappedJdbcTypes定义jdbcType类型
- 在自定义结果集标签或者参数处理的时候声明使用自定义TypeHandler进行处理或者在全局配置TypeHandler要处理的javaType。
示例:希望数据库保存的是100,200这些状态码,而不是默认0,1或者枚举的名字
EmpStatus.java
public enum EmpStatus {LOGIN(100,"用户登录"),LOGOUT(200,"用户登出"),REMOVE(300,"用户不存在");private Integer code;private String msg;private EmpStatus(Integer code,String msg){this.code = code;this.msg = msg;}//按照状态码返回枚举对象public static EmpStatus getEmpStatusByCode(Integer code){switch (code) {case 100:return LOGIN;case 200:return LOGOUT;case 300:return REMOVE;default:return LOGOUT;}}...
自定义Handler
public class MyEnumEmpStatusTypeHandler implements TypeHandler<EmpStatus> {/** * 定义当前数据如何保存到数据库中 */@Overridepublic void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, EmpStatus parameter,JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {// TODO Auto-generated method stubSystem.out.println("要保存的状态码:"+parameter.getCode());ps.setString(i, parameter.getCode().toString());}@Overridepublic EmpStatus getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName)throws SQLException {// TODO Auto-generated method stub//需要根据从数据库中拿到的枚举的状态码返回一个枚举对象int code = rs.getInt(columnName);System.out.println("从数据库中获取的状态码:"+code);EmpStatus status = EmpStatus.getEmpStatusByCode(code);return status;}@Overridepublic EmpStatus getResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex)throws SQLException {// TODO Auto-generated method stubint code = rs.getInt(columnIndex);System.out.println("从数据库中获取的状态码:"+code);EmpStatus status = EmpStatus.getEmpStatusByCode(code);return status;}@Overridepublic EmpStatus getResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex)throws SQLException {// TODO Auto-generated method stubint code = cs.getInt(columnIndex);System.out.println("从数据库中获取的状态码:"+code);EmpStatus status = EmpStatus.getEmpStatusByCode(code);return status;}}
注册自定义TypeHandler:
1.MyBatis全局配置文件中注册
<configuration><typeHandlers><typeHandler handler="com.lun.c09.other.typehandler.MyEnumEmpStatusTypeHandler" javaType="com.lun.c09.other.bean.EmpStatus"/></typeHandlers>...
也可以在处理某个字段的时候告诉MyBatis用什么类型处理器
- 保存:
#{empStatus,typeHandler=xxxx} - 查询:
- 保存:
注意:如果在参数位置修改TypeHandler,应该保证保存数据和查询数据用的TypeHandler是一样的。


























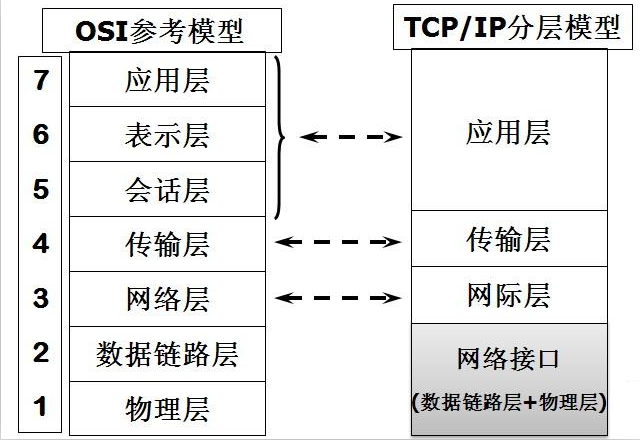



还没有评论,来说两句吧...