LeetCode - Hard - 297. Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree
Topic
- Tree
- Design
Description
https://leetcode.com/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-binary-tree/
Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
Clarification: The input/output format is the same as how LeetCode serializes a binary tree. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
Example 1: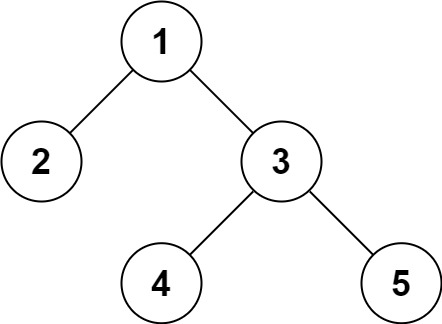
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]Output: [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
Example 2:
Input: root = []Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1]Output: [1]
Example 4:
Input: root = [1,2]Output: [1,2]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [ 0 , 1 0 4 ] [0, 10^4] [0,104].
- − 1000 < = N o d e . v a l < = 1000 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000 −1000<=Node.val<=1000
Analysis
方法一:自己写的,BFS
方法二:别人写的,前序遍历模式
方法三:别人写的,BFS
Submission
import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.Deque;import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.Queue;import com.lun.util.BinaryTree.TreeNode;public class SerializeAndDeserializeBinaryTree {//方法一:自己写的,BFSpublic static class Codec {// Encodes a tree to a single string.public String serialize(TreeNode root) {if(root == null) return "";StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();queue.offer(root);int maxDepth = maxDepth(root);int currentDepth = 0;while(!queue.isEmpty()) {currentDepth++;for(int size = queue.size(); size > 0; size--) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();sb.append(node != null ? node.val : "N");sb.append(',');if(node != null && currentDepth != maxDepth) {queue.offer(node.left);queue.offer(node.right);}}}return sb.substring(0, sb.length() - 1);}private int maxDepth(TreeNode node) {if(node == null) return 0;return 1 + Math.max(maxDepth(node.left), maxDepth(node.right));}// Decodes your encoded data to tree.public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {if(data == null || data.strip().isEmpty())return null;TreeNode root = null, parent = null;boolean pollFlag = true, sign = false;Integer value = null;LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();for(int i = 0; i <= data.length(); i++) {if(i == data.length() || data.charAt(i) == ',') {TreeNode node = null;if(value != null) {node = new TreeNode(value * (sign ? -1 : 1));if(root == null) {root = node;queue.offer(root);value = null;continue;}}if(pollFlag) {parent = queue.poll();if(value != null) {parent.left = node;queue.offer(node);}}else {if(value != null) {parent.right = node;queue.offer(node);}}pollFlag = !pollFlag;value = null;sign = false;}else {if(data.charAt(i) != 'N') {if(data.charAt(i) == '-') {sign = true;continue;}if(value == null) value = 0;value = value * 10 + data.charAt(i) - '0';}}}return root;}}//方法二:别人写的,前序遍历模式public static class Codec2 {private static final String spliter = ",";private static final String NN = "X";// Encodes a tree to a single string.public String serialize(TreeNode root) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();buildString(root, sb);return sb.toString();}private void buildString(TreeNode node, StringBuilder sb) {if (node == null) {sb.append(NN).append(spliter);} else {sb.append(node.val).append(spliter);buildString(node.left, sb);buildString(node.right,sb);}}// Decodes your encoded data to tree.public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {Deque<String> nodes = new LinkedList<>();nodes.addAll(Arrays.asList(data.split(spliter)));return buildTree(nodes);}private TreeNode buildTree(Deque<String> nodes) {String val = nodes.remove();if (val.equals(NN)) return null;else {TreeNode node = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(val));node.left = buildTree(nodes);node.right = buildTree(nodes);return node;}}}//方法三:别人写的,BFSpublic static class Codec3 {public String serialize(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return "";Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();q.add(root);while (!q.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = q.poll();if (node == null) {res.append("n ");continue;}res.append(node.val + " ");q.add(node.left);q.add(node.right);}return res.toString();}public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {if (data == "") return null;Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();String[] values = data.split(" ");TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(values[0]));q.add(root);for (int i = 1; i < values.length; i++) {TreeNode parent = q.poll();if (!values[i].equals("n")) {TreeNode left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(values[i]));parent.left = left;q.add(left);}if (!values[++i].equals("n")) {TreeNode right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(values[i]));parent.right = right;q.add(right);}}return root;}}}
Test
import static org.junit.Assert.*;import org.junit.Test;import com.lun.hard.SerializeAndDeserializeBinaryTree.Codec;import com.lun.hard.SerializeAndDeserializeBinaryTree.Codec2;import com.lun.hard.SerializeAndDeserializeBinaryTree.Codec3;import com.lun.util.BinaryTree;import com.lun.util.BinaryTree.TreeNode;public class SerializeAndDeserializeBinaryTreeTest {@Testpublic void test() {Codec ser = new Codec();Codec deser = new Codec();TreeNode node1 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(1,2,3,null,null,4,5);String str1 = ser.serialize(node1);assertEquals("1,2,3,N,N,4,5", str1);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(node1, deser.deserialize(str1)));String str2 = ser.serialize(null);assertEquals("", str2);assertNull(deser.deserialize(str2));TreeNode node3 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(1);String str3 = ser.serialize(node3);assertEquals("1", str3);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(node3, deser.deserialize(str3)));TreeNode node4 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(1,2);String str4 = ser.serialize(node4);assertEquals("1,2,N", str4);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(node4, deser.deserialize(str4)));TreeNode node5 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(4,-7,-3,null,null,-9,-3,9,-7,-4,null,6,null,-6,-6,null,null,0,6,5,null,9,null,null,-1,-4,null,null,null,-2);String str5 = ser.serialize(node5);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(node5, deser.deserialize(str5)));TreeNode node6 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(-1,0,1);String str6 = ser.serialize(node6);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(node6, deser.deserialize(str6)));}@Testpublic void test2() {Codec2 ser = new Codec2();Codec2 deser = new Codec2();TreeNode node1 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(1,2,3,null,null,4,5);String str1 = ser.serialize(node1);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(node1, deser.deserialize(str1)));String str2 = ser.serialize(null);assertNull(deser.deserialize(str2));TreeNode node3 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(1);String str3 = ser.serialize(node3);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(node3, deser.deserialize(str3)));TreeNode node4 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(1,2);String str4 = ser.serialize(node4);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(node4, deser.deserialize(str4)));TreeNode node5 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(4,-7,-3,null,null,-9,-3,9,-7,-4,null,6,null,-6,-6,null,null,0,6,5,null,9,null,null,-1,-4,null,null,null,-2);String str5 = ser.serialize(node5);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(node5, deser.deserialize(str5)));TreeNode node6 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(-1,0,1);String str6 = ser.serialize(node6);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(node6, deser.deserialize(str6)));}@Testpublic void test3() {Codec3 ser = new Codec3();Codec3 deser = new Codec3();TreeNode node1 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(1,2,3,null,null,4,5);String str1 = ser.serialize(node1);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(node1, deser.deserialize(str1)));String str2 = ser.serialize(null);assertNull(deser.deserialize(str2));TreeNode node3 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(1);String str3 = ser.serialize(node3);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(node3, deser.deserialize(str3)));TreeNode node4 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(1,2);String str4 = ser.serialize(node4);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(node4, deser.deserialize(str4)));TreeNode node5 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(4,-7,-3,null,null,-9,-3,9,-7,-4,null,6,null,-6,-6,null,null,0,6,5,null,9,null,null,-1,-4,null,null,null,-2);String str5 = ser.serialize(node5);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(node5, deser.deserialize(str5)));TreeNode node6 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(-1,0,1);String str6 = ser.serialize(node6);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(node6, deser.deserialize(str6)));}}






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...