LeetCode - Medium - 538. Convert BST to Greater Tree
Topic
- Tree
- Depth-first Search
- Binary Search Tree
- Recursion
Description
https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-bst-to-greater-tree/
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree (BST), convert it to a Greater Tree such that every key of the original BST is changed to the original key plus sum of all keys greater than the original key in BST.
As a reminder, a binary search tree is a tree that satisfies these constraints:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node’s key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Note: This question is the same as 1038: https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-search-tree-to-greater-sum-tree/
Example 1:
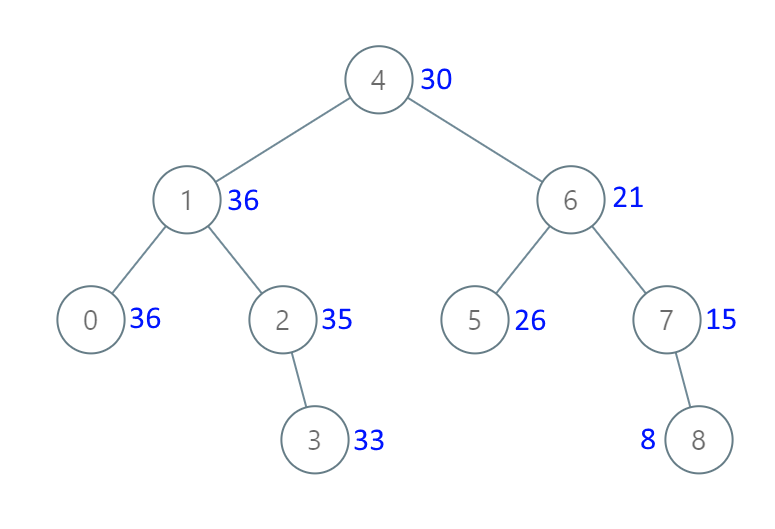
Input: root = [4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8]Output: [30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
Example 2:
Input: root = [0,null,1]Output: [1,null,1]
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,0,2]Output: [3,3,2]
Example 4:
Input: root = [3,2,4,1]Output: [7,9,4,10]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [ 0 , 1 0 4 ] [0, 10^4] [0,104].
- − 1 0 4 < = N o d e . v a l < = 1 0 4 -10^4 <= Node.val <= 10^4 −104<=Node.val<=104
- All the values in the tree are unique.
rootis guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.
Analysis
方法一:中序遍历模式的递归版
方法二:中序遍历模式的迭代版
Submission
import java.util.LinkedList;import com.lun.util.BinaryTree.TreeNode;public class ConvertBSTToGreaterTree {//方法一:中序遍历模式的递归版public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {dfs(root, new int[] { 0});return root;}private void dfs(TreeNode node, int[] sum) {if(node == null)return;dfs(node.right, sum);sum[0] = node.val += sum[0];dfs(node.left, sum);}//方法二:中序遍历模式的迭代版public TreeNode convertBST2(TreeNode root) {TreeNode p = root;LinkedList<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();int sum = 0;while(!stack.isEmpty() || p != null) {if(p != null) {stack.push(p);p = p.right;}else {TreeNode node = stack.pop();sum = node.val += sum;p = node.left;}}return root;}}
Test
import static org.junit.Assert.*;import org.junit.Test;import com.lun.util.BinaryTree;import com.lun.util.BinaryTree.TreeNode;public class ConvertBSTToGreaterTreeTest {@Testpublic void test() {ConvertBSTToGreaterTree obj = new ConvertBSTToGreaterTree();TreeNode root1 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8);TreeNode expected1 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(obj.convertBST(root1), expected1));TreeNode root2 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(0,null,1);TreeNode expected2 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(1,null,1);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(obj.convertBST(root2), expected2));TreeNode root3 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(1,0,2);TreeNode expected3 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(3,3,2);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(obj.convertBST(root3), expected3));TreeNode root4 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(3,2,4,1);TreeNode expected4 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(7,9,4,10);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(obj.convertBST(root4), expected4));}@Testpublic void test2() {ConvertBSTToGreaterTree obj = new ConvertBSTToGreaterTree();TreeNode root1 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8);TreeNode expected1 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(obj.convertBST2(root1), expected1));TreeNode root2 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(0,null,1);TreeNode expected2 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(1,null,1);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(obj.convertBST2(root2), expected2));TreeNode root3 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(1,0,2);TreeNode expected3 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(3,3,2);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(obj.convertBST2(root3), expected3));TreeNode root4 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(3,2,4,1);TreeNode expected4 = BinaryTree.integers2BinaryTree(7,9,4,10);assertTrue(BinaryTree.equals(obj.convertBST2(root4), expected4));}}































还没有评论,来说两句吧...