人脸检测-基于模板匹配的实现
在人脸检测-基于肤色检测的实现一文中,我们以人脸具有肤色的特征作为实现的起点,通过在YCrCb色彩空间下肤色具有聚类性的特点,采用简单高斯模型对肤色进行数学建模,实现了肤色分割,最后用较为简单的方法对肤色区域进行判断,从而实现人脸的检测。但是这种方法检测率、误检率都不是很高,因此采用模板匹配的方法,对肤色分割后的肤色区域进行人脸匹配,匹配率较高的,认为是人脸。模板匹配的关键点在于得到标准的模板。
根据模板匹配的不同层次,可以将匹配分为以下三种:
①基于点的方法:它是通过划分图像的像素点为不同分类实现的,由于需要对所有的像素点进行处理,因而需要的计算量和计算时间相对较多,处理过程更加繁琐。由于是对点进行操作,所以细小的改变都会对处理结果造成影响,例如在不同的成像条件下图像中的相同点的像素值就会不一样,由此匹配结果就很有可能不一样。
②基于区域的方法:这种方法是通过对图片的区域的形状特征进行处理,通过对比区域特征,来实现匹配。相比于对整幅图像进行处理,区域识别的计算量和受细节的影响都要小得多。它的重点是区域的特征的提取,这种特征必须是易于识别以及不同于其他物体的普遍特征的。
③利用混合特征的方法:这类方法是基于点操作和区域操纵同时实现的,通过点操作过滤到部分干扰匹配的信息,最后通过区域特征实现最后的模板匹配。这种方法能够实现较高的匹配率。
这里介绍的的模板匹配是基于像素的方法实现的,这种方法简单,便于实现。设有大小m*m为的模板,大小为n*n待筛选区域,模板匹配的算法流程为:
① 计算出模板的均值,以及方差;
② 计算出当前待筛选区域的均值,以及方差;
③ 当模板匹配到待检测区域时,计算模板和区域的相关系数
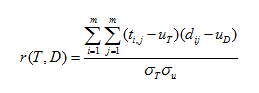
④ 得到相关系数后,与阈值比较,确定是否为人脸区域;
模板制作的方法:平均人脸模板的方法,具体制作方法如下:
①搜集人脸样本,筛选出具有显著特性的人脸样本,包括性别、年龄、种族等,转换为灰度图像;
②在筛选出的人脸样本中通过截图工具截取人脸区域,人的眼睛、鼻子、嘴巴必须包含在截取的样图中;
③对手工截图的人脸区域的尺寸大小规范化,保证人脸模板有相同的大小,同时满足人脸区域的长宽比、面积大小等要求,具体参照第二章内容;
④人脸模板的标准化。标准化的目的是为了消除光照对肤色的影响,相比于灰度均衡化,标准化可以减小人脸模板之间的区别,能制作出更标准的人脸模板。标准化的过程:首先需要计算出每个人脸模板的均值和方差,对每一个人脸模板,按照设定的灰度平均值和方差进行标准化,人脸模板中的像素值转为:
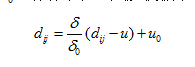
%Following function returns image regions which pass template matching testfunction [template_passed]=template_test(aspectBW,originalRGB,template)%convert original image into grayscaleimgray=rgb2gray(imread(originalRGB));imtemplate=imread(template);%label the binary image with regions[labels,num] = bwlabel(aspectBW,8);[m,n]=size(aspectBW);% %compute orientation angle for each regionorient = regionprops(labels,'Orientation');angles=cat(1,orient.Orientation);%compute centroid for each regionc = regionprops(labels,'Centroid');centroids=cat(1,c.Centroid);%image with regions which pass template matching testtemplate_passed=zeros(m,n);gray_matched=zeros(m,n);%resize,rotate and crop the template image according to region propertiesfor j=1:num,% Compute the coordinates for this region.[x,y] = find(labels == j);% Get an image that only has this region, the rest is blackbwsegment = bwselect(aspectBW,y,x,8);% Generate orignal gray scale with only one face regiononeface=immultiply(bwsegment,imgray);%centroid of the regioncx1=centroids(j,1);cy1=centroids(j,2);%width and height of the regionp=regionprops(bwlabel(bwsegment),'BoundingBox');boxdim=cat(1,p.BoundingBox);regw=boxdim(3);regh=boxdim(4);ratio=regh/regw;%if region is too long, set to resonable new height and shift centroid upif(ratio>1.6)regh=1.5*regw;cy1=cy1-(0.1*regh);end%resize the model with same scale as the regiongmodel_resize=imresize(imtemplate,[regh regw],'bilinear');%rotate the resized model by the angle of orientation of the regionif(angles(j)>0)gmodel_rotate=imrotate(gmodel_resize,angles(j)-90,'bilinear','loose');elsegmodel_rotate=imrotate(gmodel_resize,90+angles(j),'bilinear','loose');end%computing the centroid and size of the modelbwmodel=im2bw(gmodel_rotate,0);%size of the model before crop[g,h]=size(bwmodel);%ensure that the bw model region has only one regionbwmorphed = bwmorph(bwmodel,'clean');[L,no]=bwlabel(bwmorphed,8);if(no==1)bwsingle=bwmorphed;elsear=regionprops(bwlabel(bwmorphed),'Area');areas=cat(1,ar.Area);[C,I]=max(areas);% Compute the coordinates for this region.[x1,y1] = find(bwlabel(bwmorphed)== I);% Get an image that only has this region, the rest is blackbwsingle = bwselect(bwmorphed,y1,x1,8);end%fill the model and crop - this option of region props crops automaticallyfilledmodel=regionprops(bwlabel(bwsingle),'FilledImage');bwcrop=filledmodel.FilledImage;%size of the scaled and rotated model after crop[modh,modw]=size(bwcrop);%crop the grayscale model to same size as that of bwlabel modelgmodel_crop=imresize(gmodel_rotate,[modh modw],'bilinear');%centroid of scaled,rotated and cropped modelcenmod=regionprops(bwlabel(bwcrop),'Centroid');central=cat(1,cenmod.Centroid);cx2=central(1,1);cy2=central(1,2);mfit = zeros(size(oneface));mfitbw = zeros(size(oneface));[limy, limx] = size(mfit);% Compute the coordinates of where the face model is going to be in% the main imagestartx = cx1-cx2;starty = cy1-cy2;endx = startx + modw-1;endy = starty + modh-1;% Check for boundaries of the imagestartx = checklimit(startx,limx);starty = checklimit(starty,limy);endx = checklimit(endx,limx);endy = checklimit(endy,limy);% The following is to generate a new image having the same% size as the original one, but with the face of the model on it% rotated accordingly.for i=starty:endy,for j=startx:endx,mfit(round(i),round(j)) = gmodel_crop(round(i-starty+1),round(j-startx+1));end;end;% subplot(3,3,9);% imshow(mfit,[0 255])%% Get the cross-correlation value between model and regiongray_matched=gray_matched+mfit;crosscorr =corr2(mfit,oneface);%if cross-correlation value higher than threshold, add the regionif(crosscorr>=0.6)template_passed=template_passed+bwsegment;end;subplot(4,3,11);imshow(gray_matched,[0 255])title('Template Matching')% subplot(4,3,12);% imshow(template_passed)end;
这只是模板匹配的代码,模板实现之前还有关于肤色建模以及肤色分割的核心代码。完整代码可以在去载:http://download.csdn.net/detail/mao19931004/9190143
最后实现的的效果是:

当然误检和漏检的情况还是有,主要是模板匹配的计算结果以及阈值的选取的影响问题,当然人脸的部分遮挡以及人脸的选装都会影响到最后的人脸检测结果,由于是基于肤色的人脸检测以及模板匹配,模板的标准性以及图片中的有效干扰都会对检测结果造成不可忽略的影响。






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...