用Python在地图上模拟疫情扩散
用Python在地图上模拟疫情扩散
受杰森的《Almost Looks Like Work》启发,我来展示一些病毒传播模型。需要注意的是这个模型并不反映现实情况,因此不要误以为是西非可怕的传染病。相反,它更应该被看做是某种虚构的僵尸爆发现象。那么,让我们进入主题。
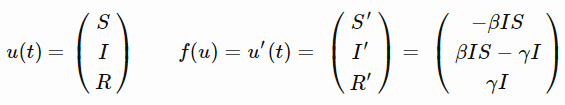
这就是SIR模型,其中字母S、I和R反映的是在僵尸疫情中,个体可能处于的不同状态。
- S 代表易感群体,即健康个体中潜在的可能转变的数量。
- I 代表染病群体,即僵尸数量。
- R 代表移除量,即因死亡而退出游戏的僵尸数量,或者感染后又转回人类的数量。但对与僵尸不存在治愈者,所以我们就不要自我愚弄了(如果要把SIR模型应用到流感传染中,还是有治愈者的)。
至于β(beta)和γ(gamma):
- β(beta)表示疾病的传染性程度,只要被咬就会感染。
- γ(gamma)表示从僵尸走向死亡的速率,取决于僵尸猎人的平均工作速率,当然,这不是一个完美的模型,请对我保持耐心。
S′=−βIS告诉我们健康者变成僵尸的速率,S′是对时间的导数。
I′=βIS−γI告诉我们感染者是如何增加的,以及行尸进入移除态速率(双关语)。
R′=γI只是加上(gamma I),这一项在前面的等式中是负的。
上面的模型没有考虑S/I/R的空间分布,下面来修正一下!
一种方法是把瑞典和北欧国家分割成网格,每个单元可以感染邻近单元,描述如下:
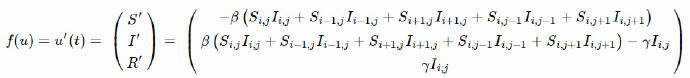
实验完整代码如下:
Main.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-import numpy as npimport mathimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom matplotlib import rcParamsimport matplotlib.image as mpimgfrom PIL import ImagercParams['font.family'] = 'serif'rcParams['font.size'] = 16rcParams['figure.figsize'] = 12, 8beta = 0.010gamma = 1def euler_step(u, f, dt):return u + dt * f(u)def f(u):S = u[0]I = u[1]R = u[2]new = np.array([-beta*(S[1:-1, 1:-1]*I[1:-1, 1:-1] + \S[0:-2, 1:-1]*I[0:-2, 1:-1] + \S[2:, 1:-1]*I[2:, 1:-1] + \S[1:-1, 0:-2]*I[1:-1, 0:-2] + \S[1:-1, 2:]*I[1:-1, 2:]),beta*(S[1:-1, 1:-1]*I[1:-1, 1:-1] + \S[0:-2, 1:-1]*I[0:-2, 1:-1] + \S[2:, 1:-1]*I[2:, 1:-1] + \S[1:-1, 0:-2]*I[1:-1, 0:-2] + \S[1:-1, 2:]*I[1:-1, 2:]) - gamma*I[1:-1, 1:-1],gamma*I[1:-1, 1:-1]])padding = np.zeros_like(u)padding[:,1:-1,1:-1] = newpadding[0][padding[0] < 0] = 0padding[0][padding[0] > 255] = 255padding[1][padding[1] < 0] = 0padding[1][padding[1] > 255] = 255padding[2][padding[2] < 0] = 0padding[2][padding[2] > 255] = 255return paddingimg = Image.open('popdens2.png')img = img.resize((img.size[0]/2,img.size[1]/2))img = 255 - np.asarray(img)imgplot = plt.imshow(img)imgplot.set_interpolation('nearest')S_0 = img[:,:,1]I_0 = np.zeros_like(S_0)I_0[309,170] = 1 # patient zeroR_0 = np.zeros_like(S_0)T = 900 # final timedt = 1 # time incrementN = int(T/dt) + 1 # number of time-stepst = np.linspace(0.0, T, N) # time discretization# initialize the array containing the solution for each time-stepu = np.empty((N, 3, S_0.shape[0], S_0.shape[1]))u[0][0] = S_0u[0][1] = I_0u[0][2] = R_0import matplotlib.cm as cmtheCM = cm.get_cmap("Reds")theCM._init()alphas = np.abs(np.linspace(0, 1, theCM.N))theCM._lut[:-3,-1] = alphasfor n in range(N-1):u[n+1] = euler_step(u[n], f, dt)from images2gif import writeGifkeyFrames = []frames = 60.0for i in range(0, N-1, int(N/frames)):imgplot = plt.imshow(img, vmin=0, vmax=255)imgplot.set_interpolation("nearest")imgplot = plt.imshow(u[i][1], vmin=0, cmap=theCM)imgplot.set_interpolation("nearest")filename = "outbreak" + str(i) + ".png"plt.savefig(filename)keyFrames.append(filename)images = [Image.open(fn) for fn in keyFrames]gifFilename = "outbreak.gif"writeGif(gifFilename, images, duration=0.3)plt.clf()
image2gif.py
""" MODULE images2gifProvides a function (writeGif) to write animated gif from a seriesof PIL images or numpy arrays.This code is provided as is, and is free to use for all.Almar Klein (June 2009)- based on gifmaker (in the scripts folder of the source distribution of PIL)- based on gif file structure as provided by wikipedia"""try:import PILfrom PIL import Image, ImageChopsfrom PIL.GifImagePlugin import getheader, getdataexcept ImportError:PIL = Nonetry:import numpy as npexcept ImportError:np = None# getheader gives a 87a header and a color palette (two elements in a list).# getdata()[0] gives the Image Descriptor up to (including) "LZW min code size".# getdatas()[1:] is the image data itself in chuncks of 256 bytes (well# technically the first byte says how many bytes follow, after which that# amount (max 255) follows).def intToBin(i):""" Integer to two bytes """# devide in two parts (bytes)i1 = i % 256i2 = int( i/256)# make string (little endian)return chr(i1) + chr(i2)def getheaderAnim(im):""" Animation header. To replace the getheader()[0] """bb = "GIF89a"bb += intToBin(im.size[0])bb += intToBin(im.size[1])bb += "\x87\x00\x00"return bbdef getAppExt(loops=0):""" Application extention. Part that secifies amount of loops.if loops is 0, if goes on infinitely."""bb = "\x21\xFF\x0B" # application extensionbb += "NETSCAPE2.0"bb += "\x03\x01"if loops == 0:loops = 2**16-1bb += intToBin(loops)bb += '\x00' # endreturn bbdef getGraphicsControlExt(duration=0.1):""" Graphics Control Extension. A sort of header at the start ofeach image. Specifies transparancy and duration. """bb = '\x21\xF9\x04'bb += '\x08' # no transparancybb += intToBin( int(duration*100) ) # in 100th of secondsbb += '\x00' # no transparant colorbb += '\x00' # endreturn bbdef _writeGifToFile(fp, images, durations, loops):""" Given a set of images writes the bytes to the specified stream."""# initframes = 0previous = Nonefor im in images:if not previous:# first image# gather datapalette = getheader(im)[1]data = getdata(im)imdes, data = data[0], data[1:]header = getheaderAnim(im)appext = getAppExt(loops)graphext = getGraphicsControlExt(durations[0])# write global headerfp.write(header)fp.write(palette)fp.write(appext)# write imagefp.write(graphext)fp.write(imdes)for d in data:fp.write(d)else:# gather info (compress difference)data = getdata(im)imdes, data = data[0], data[1:]graphext = getGraphicsControlExt(durations[frames])# write imagefp.write(graphext)fp.write(imdes)for d in data:fp.write(d)# # delta frame - does not seem to work# delta = ImageChops.subtract_modulo(im, previous)# bbox = delta.getbbox()## if bbox:## # gather info (compress difference)# data = getdata(im.crop(bbox), offset = bbox[:2])# imdes, data = data[0], data[1:]# graphext = getGraphicsControlExt(durations[frames])## # write image# fp.write(graphext)# fp.write(imdes)# for d in data:# fp.write(d)## else:# # FIXME: what should we do in this case?# pass# prepare for next roundprevious = im.copy()frames = frames + 1fp.write(";") # end gifreturn framesdef writeGif(filename, images, duration=0.1, loops=0, dither=1):""" writeGif(filename, images, duration=0.1, loops=0, dither=1)Write an animated gif from the specified images.images should be a list of numpy arrays of PIL images.Numpy images of type float should have pixels between 0 and 1.Numpy images of other types are expected to have values between 0 and 255."""if PIL is None:raise RuntimeError("Need PIL to write animated gif files.")images2 = []# convert to PILfor im in images:if isinstance(im,Image.Image):images2.append( im.convert('P',dither=dither) )elif np and isinstance(im, np.ndarray):if im.dtype == np.uint8:passelif im.dtype in [np.float32, np.float64]:im = (im*255).astype(np.uint8)else:im = im.astype(np.uint8)# convertif len(im.shape)==3 and im.shape[2]==3:im = Image.fromarray(im,'RGB').convert('P',dither=dither)elif len(im.shape)==2:im = Image.fromarray(im,'L').convert('P',dither=dither)else:raise ValueError("Array has invalid shape to be an image.")images2.append(im)else:raise ValueError("Unknown image type.")# check durationif hasattr(duration, '__len__'):if len(duration) == len(images2):durations = [d for d in duration]else:raise ValueError("len(duration) doesn't match amount of images.")else:durations = [duration for im in images2]# open filefp = open(filename, 'wb')# writetry:n = _writeGifToFile(fp, images2, durations, loops)print n, 'frames written'finally:fp.close()if __name__ == '__main__':im = np.zeros((200,200), dtype=np.uint8)im[10:30,:] = 100im[:,80:120] = 255im[-50:-40,:] = 50images = [im*1.0, im*0.8, im*0.6, im*0.4, im*0]writeGif('lala3.gif',images, duration=0.5, dither=0)
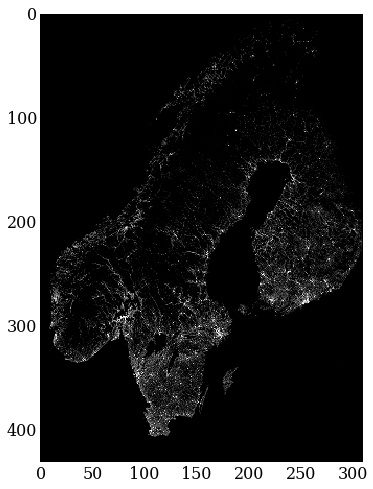
实验原始图像与实验后图像如下:






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...