Android Ble蓝牙开发(客户端)
最近项目里面需要集成一个蓝牙的连接功能,作为一枚刚刚毕业不久的新生,大学几年又白过的。只好在几天内搜搜百度,脑补一下。文章部分内容摘至各大Blog,加上本dust的见解,写了一份Client端和Service端的小呆毛。
参考链接–Link //m.blog.csdn.net/article/details?id=50504406
//m.blog.csdn.net/article/details?id=50504406
————————————————————————-我是分割线————————————————————————-
先来叨叨下历史
蓝牙我们应该很早就听过,最常见的就是原来我们偶尔通过手机上的蓝牙来传输文件。貌似在低功耗蓝牙(Bluetooth Low Energy)出现之前,蓝牙我们使用的并不多,蓝牙的产品貌似也不是很多。2010年6月30号蓝牙技术联盟推出了低功耗蓝牙,经过几年的发展,市场上基于低功耗系列的硬件产品越来越多,开发硬件,软件的厂商,公司越来越多。
蓝牙发展至今经历了8个版本的更新。1.1、1.2、2.0、2.1、3.0、4.0、4.1、4.2。那么在1.x~3.0之间的我们称之为传统蓝牙,4.x开始的蓝牙我们称之为低功耗蓝牙也就是蓝牙ble,当然4.x版本的蓝牙也是向下兼容的。android手机必须系统版本4.3及以上才支持BLE API,具体看厂商吧。低功耗蓝牙较传统蓝牙,传输速度更快,覆盖范围更广,安全性更高,延迟更短,耗电极低等等优点。这也是为什么近年来智能穿戴的东西越来越多,越来越火。还有传统蓝牙与低功耗蓝牙通信方式也有所不同,传统的一般通过socket方式,而低功耗蓝牙是通过Gatt协议来实现。若是之前没做过传统蓝牙开发,也是可以直接上手低功耗蓝牙开发的。因为它们在通信协议上都有所改变,关联不大。当然有兴趣的可以去下载些传统蓝牙开发的demo看看,在看看低功耗蓝牙的demo。两者的不同之处自然容易看出来。好了,我们下面开始讲低功耗蓝牙开发吧。低功耗蓝牙也叫BLE,下面都称之为BLE。
**
一、Ble概念了解
**
区别于传统蓝牙,Ble是使用Gatt协议来实现。所以协议中的几个概念得先理清楚。
Generic Attribute Profile (GATT)
通过BLE连接,读写属性类小数据的Profile通用规范。现在所有的BLE应用Profile都是基于GATT的。
Profile可以理解为一种规范,一个标准的通信协议,其存在于手机中,蓝牙组织规定了一些标准的profile:HID OVER GATT ,防丢器等,每个profile中包含了多个service。
Attribute Protocol (ATT)
GATT是基于ATT Protocol的。ATT针对BLE设备做了专门的优化,具体就是在传输过程中使用尽量少的数据。每个属性都有一个唯一的UUID,属性将以characteristics and services的形式传输。
Service
可以理解为一个服务,这里要区分的是BluetoothServer,一个是服务,一个是服务器端。在BLE从机中有多个服务,电量信息,系统服务信息等,每一个service中包含了多个characteristic特征值,每一个具体的characteristic特征值才是BLE通信的主题。 Characteristic的集合。例如一个service叫做“Heart Rate Monitor”,它可能包含多个Characteristics,其中可能包含一个叫做“heart rate measurement”的Characteristic。
Characteristic
Characteristic可以理解为一个数据类型,它包括一个value和0至多个对次value的描述(Descriptor)。通过操作Characteristic可以实现Ble的数据传输。
Descriptor
对Characteristic的描述,例如范围、计量单位等。
UUID(统一标识码)
service和characteristic均需要这个唯一的UUID进行标识。UUID可以双方自定义,例如客户端访问服务器端的写characteristic,那么客户端就需要有服务器端定义的写characteristic UUID
这三部分都用UUID作为唯一标识符。UUID为这种格式:0000ffe1-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb。比如有3个Service,那么就有三个不同的UUID与Service对应。这些UUID都写在硬件里,我们通过BLE提供的API可以读取到,同时也可以自定义Application层的UUID。
他们关系可以总结如下:一个BLE终端可以包含多个Service, 一个Service可以包含多个Characteristic,一个Characteristic包含一个value和多个Descriptor,一个Descriptor包含一个Value。
Characteristic是比较重要的,是手机与BLE终端交换数据的关键,读取设置数据等操作都是操作Characteristic的相关属性。
**
二、角色和职责:
**
Android设备与BLE设备交互有两组角色:
中心设备和外围设备(Central vs. peripheral)和 GATT server vs. GATT client.
Central vs. peripheral:中心设备和外围设备的概念针对的是BLE连接本身。
Central角色负责scan advertisement。而peripheral角色负责make advertisement。
GATT server vs. GATT client:这两种角色取决于BLE连接成功后,两个设备间通信的方式。
在我个人开发经历知道,不是所有Android设备都支持peripheral模式的
举例说明:
现有一个活动追踪的BLE设备和一个支持BLE的Android设备。
Android设备支持Central角色,而BLE设备支持peripheral角色。
创建一个BLE连接需要这两个角色都存在,都仅支持Central角色或者都仅支持peripheral角色则无法建立连接。
当连接建立后,它们之间就需要传输GATT数据。
谁做server,谁做client,则取决于具体数据传输的情况。
例如,如果活动追踪的BLE设备需要向Android设备传输sensor数据,则活动追踪器自然成为了server端;
而如果活动追踪器需要从Android设备获取更新信息,则Android设备作为server端可能更合适。
这里就先普及Central角色的开发资料,后面一个篇章将谈论Android设备实现Peripheral角色。
**
三、API分析:
**
当前使用到的类包括:
BluetoothManager
BluetoothAdapter
BluetoothGatt
BluetoothDevice
BluetoothGattService
BluetoothGattCharacteristic
BluetoothManage
这个不多说了,系统的蓝牙服务。可以通过Context.getSystemService( Context.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE )获取到BluetoothManager实例,BluetoothManager也可以通过getAdapter() 方法获取到BluetoothAdapter
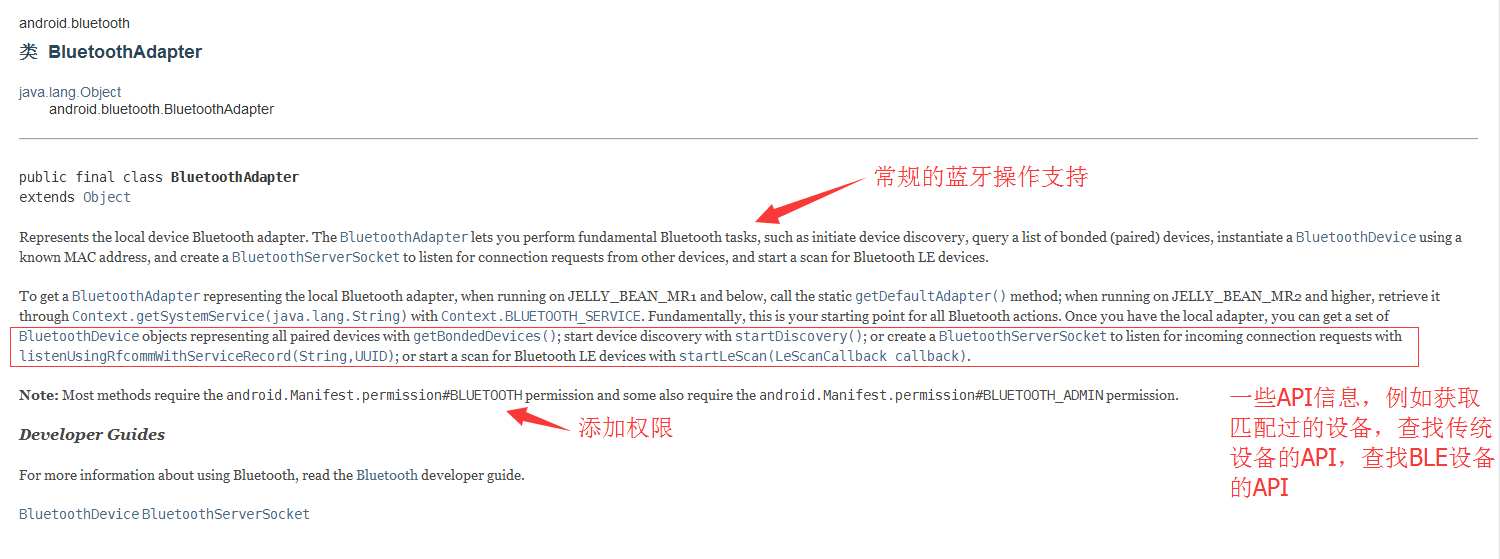
BluetoothAdapter
文档的解释大概是这样的:允许我们的Application通过此对象去读取蓝牙设备信息和操作蓝牙设备。
同时文档中也说明了,BluetoothAdapter支持传统蓝牙和Ble蓝牙,然后还有一些常用方法的说明。
BluetoothGatt
上面说过Ble的连接是通过Gatt协议的。API中的BluetoothGatt相当于连接设备的桥梁,提供api给我们操作characteristic和descriptor,可以BluetoothDevice.connectGatt连接到远程设备。
BluetoothDevice
这个也不说太多了,蓝牙设备
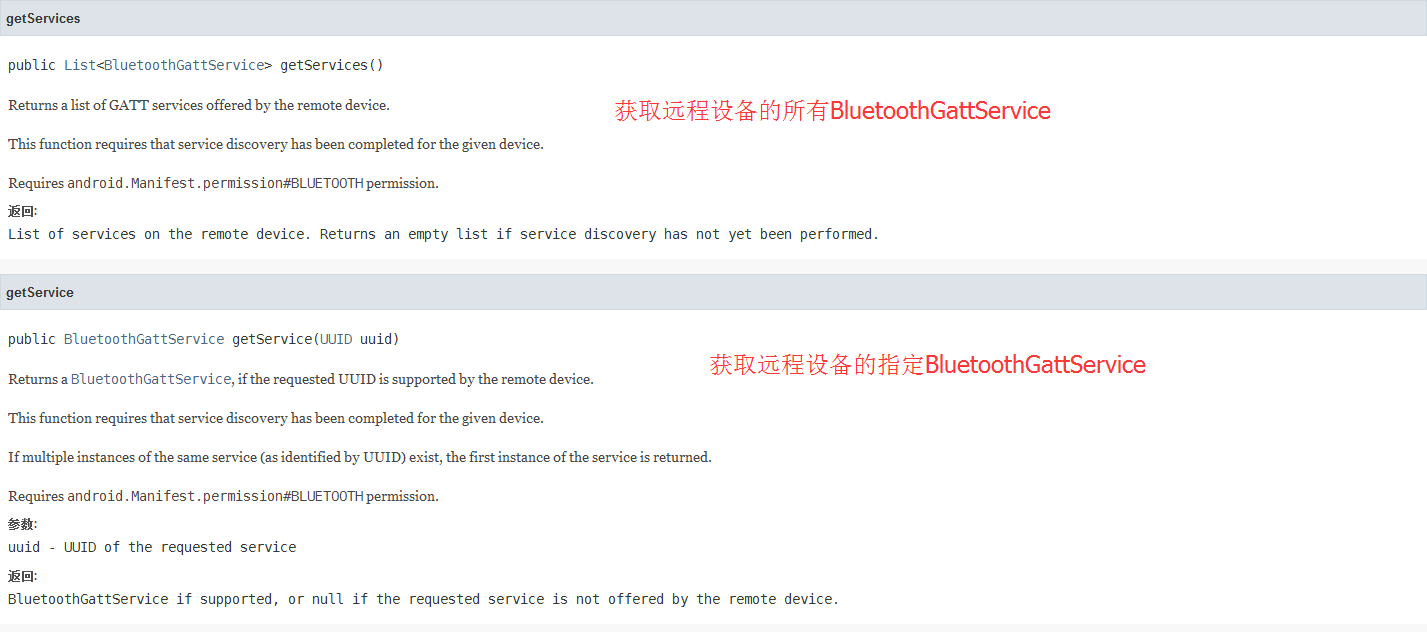
BluetoothGattService
Gatt协议服务,Server端可以配置Service,例如Service的UUID,Service的characteristic等等。
BluetoothGattCharacteristic
这个描述也和上面说的一致,不仅还有一个Value,还有descriptor。API用得比较多的也就是setValue和getValue了。
**
四、代码实现:
**
使用蓝牙必须先获取到相应的权限,因为需要使用BLE,所以Manifest中需要加入以下权限及说明,在6.0上面需要使用BLE蓝牙,我们还需要加上LOCATION权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN" /><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" /><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" /><uses-featureandroid:name="android.hardware.bluetooth_le"android:required="true" />
权限声明完毕之后,先做一些简单的蓝牙支持和开启判断。其中需要用到的就是BluetoothAdapter这个类(BluetoothManager),
这里加个括号是表示,BluetoothAdapter有两种获取方法。
方法一:
通过BluetoothManager.getAdapter获取;
final BluetoothManager bluetoothManager =(BluetoothManager) getSystemService(Context.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE);BluetoothAdapter mBluetoothAdapter = bluetoothManager.getAdapter();
方法二:
通过BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter获取;
BluetoothAdapter mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();//如果mBluetoothAdapter == null,说明设备不支持蓝牙
然后我们要做的就是判断设备是否支持蓝牙设备和开启设备,假若蓝牙没开启的情况下,我们还需要请求开启蓝牙。
if (mBlueToothAdapter != null) {if (getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_BLUETOOTH_LE)) {if (mBlueToothAdapter.isEnabled()) {intent.putExtra("Order", Const.SCAN_START);startService(intent);} else {Intent enableBtIntent = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE);startActivityForResult(enableBtIntent, REQUEST_ENABLE_BT);}} else {ShowToast("该设备不支持BLE蓝牙");}} else {ShowToast("该设备不支持蓝牙");}
在onActivityResult回调中
@Overrideprotected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {switch (requestCode) {case REQUEST_ENABLE_BT:if (resultCode == -1) {//允许ShowToast("蓝牙已启用");intent.putExtra("Order", Const.SCAN_START);startService(intent);} else {ShowToast("蓝牙未启用");}break;}}
具体的扫描,连接设备,发送数据的函数都写到一个Service里面,BluetoothService
扫描函数
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR2)public void scanStart(final boolean isEnable) {if (isEnable) {handler.postDelayed(runnable, SCAN_TIME_LIMIT);Log.i(TAG, "开始搜索");mScanning = true;//BluetoothAdapter.startLeScan()具体有两个方法,可以根据指定的UUID找到对应的UUID设备。// mBlueToothAdapter.startLeScan(uuidList, mCallBack); //使用startLeScan只能扫描出指定UUID的BLE设备,mBlueToothAdapter.startLeScan(mCallBack);} else {stopScan();}}
扫描函数做了判断,防止扫描时间过长而消耗设备的电池
扫描停止函数
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR2)public void stopScan() {Log.i(TAG, "停止搜索");mScanning = false;handler.removeCallbacks(runnable);mBlueToothAdapter.stopLeScan(mCallBack);}
扫描函数回调
/*** BLE蓝牙搜索回调*/@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR2)public class BluetoothScanCallBack implements BluetoothAdapter.LeScanCallback {@Overridepublic void onLeScan(BluetoothDevice device, int rssi, byte[] scanRecord) {if (!devices.contains(device)) {handler.obtainMessage(SCANNING, device).sendToTarget();devices.add(device);}}}
handler中接收搜索出来的设备
handler = new Handler() {@Overridepublic void handleMessage(Message msg) {switch (msg.what) {case SCANNING:Log.i(TAG, "输出设备:" + msg.obj.toString());break;case SCAN_FINISHED:Log.i(TAG, "列表大小:" + devices.size());Log.i(TAG, "输出列表:\n");if (devices.size() == 0) {scanStart(true);} else {/*这里是后台给我传输的数据,我遍历数据,获取到合适的deviceID*/Set set = mBluetoothData.keySet();for (BluetoothDevice target : devices) {for (Iterator iterator = set.iterator(); iterator.hasNext(); ) {bt_id = (String) iterator.next();bt_password = mBluetoothData.get(bt_id);Log.i(TAG, "BT_id:" + bt_id);Log.i(TAG, "BT_password:" + bt_password);Log.i(TAG, "target地址:" + target.getAddress() + "\nname:" + target.getName());/*获取的UUID貌似会空的,这里也不作解释了*/ParcelUuid[] uuids = target.getUuids();if (uuids != null)for (int i = 0; i < uuids.length; i++) {Log.i(TAG, "\ntargetUUID_" + i + ":" + uuids[i].toString());}/*因为各个用户实现的逻辑可能不统一,实际上这里就是判断扫描完的设备列表是否含有我们的指定目标设备,假若存在则连接该设备*/if (target.getName().equals(bt_id)) {mDevice = target;connectDevice(target.getAddress());} else {Log.i(TAG, "设备BT_id不一致");scanStart(true);}}}}break;case BLE_CONNECT_SUCCESS:break;case BLE_CONNECT_FAIL:connectDevice(mDevice.getAddress());break;}}};
设备连接函数
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR2)public boolean connectDevice(String address) {stopScan();Log.i(TAG, "连接设备:" + address);if (mBlueToothAdapter == null || address == null) {Log.w(TAG, "蓝牙设备不可用或连接的设备Address为null");return false;}//先前连接的设备。 尝试重新连接,减少蓝牙负荷if (mBluetoothAddress != null && address.equals(mBluetoothAddress) && mBluetoothGatt != null) {Log.d(TAG, "Trying to use an existing mBluetoothGatt for connection.");if (mBluetoothGatt.connect()) {return true;} else {return false;}}//通过Mac地址获取到远程设备BluetoothDevice bluetoothDevice = mBlueToothAdapter.getRemoteDevice(address);if (bluetoothDevice == null) {Log.w(TAG, "Device not found. Unable to connect.");return false;}//Gatt服务回调mGattCallback = new BluetoothConnectCallBack();//该函数才是真正的去进行连接mBluetoothGatt = bluetoothDevice.connectGatt(this, false, mGattCallback);Log.d(TAG, "Trying to create a new connection.BLE");//传统蓝牙是通过Socket连接的,呆毛可以无视/*BluetoothSocket socket = null;try {socket = bluetoothDevice.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(UUID.fromString(MY_UUID));socket.connect();Log.d(TAG, "Trying to create a new connection.EDR");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}*/return true;}
设备连接接口回调
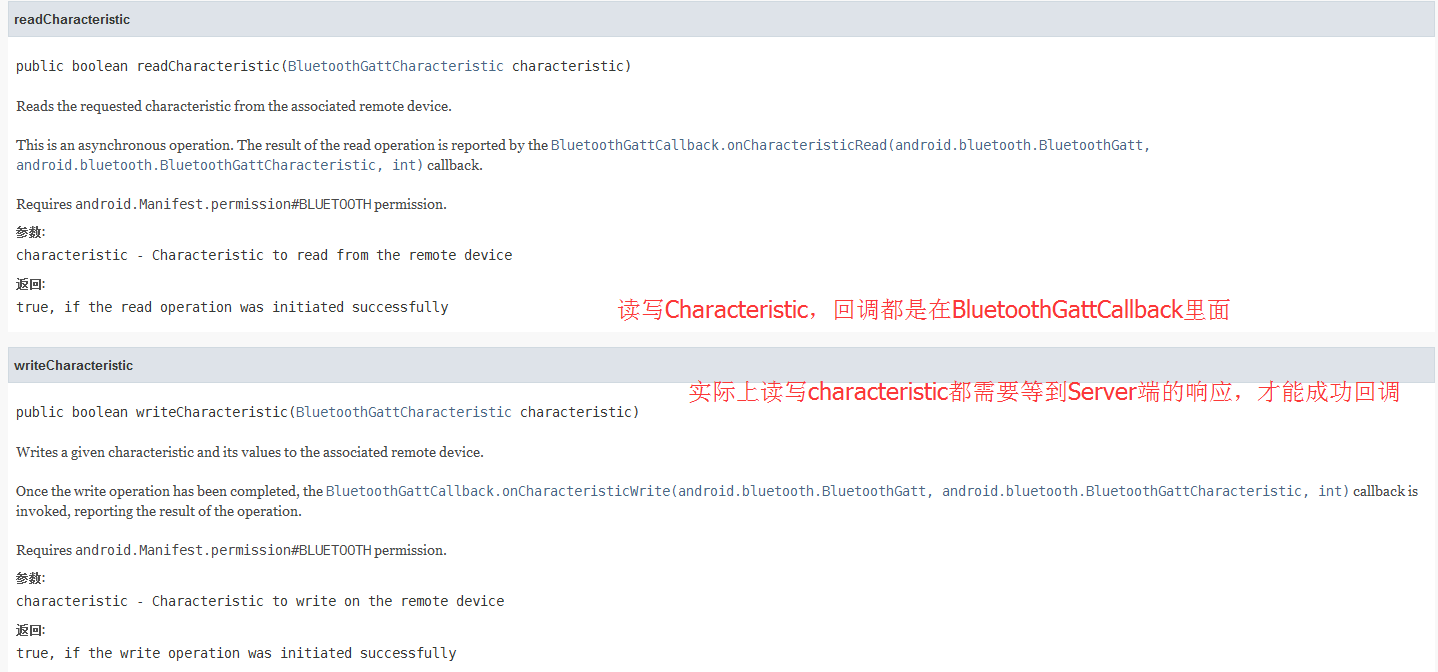
实际上BluetoothGattCallback中的回调不止有Device连接之后的回调,还有GattService的搜索回调,Charactistic的读写回调
/*** BLE蓝牙连接回调*/@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR2)public class BluetoothConnectCallBack extends BluetoothGattCallback {@Override //当连接上设备或者失去连接的时候会回调public void onConnectionStateChange(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status, int newState) {if (newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_CONNECTED) {Log.i(TAG, "连接设备成功!");handler.sendEmptyMessage(BLE_CONNECT_SUCCESS);gatt.discoverServices(); //连接成功后就去找出该设备中的服务Log.i(TAG, "查找设备服务");} else if (newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_DISCONNECTED) {Log.i(TAG, "连接设备失败!");handler.sendEmptyMessage(BLE_CONNECT_FAIL);}}@Override //当搜索到服务的时候回调public void onServicesDiscovered(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status) {if (status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS) {if (gatt == null) {return;}//找到Server端的服务,也许有多个,也许只有一个,看项目需求定制Log.i(TAG, "找到了GATT服务");mServices = getSupportServices(gatt);for (int i = 0; i < mServices.size(); i++) {Log.e(TAG, "GATT服务列表:" + mServices.get(i).toString());if (mServices.get(i).getUuid().equals(serviceUUID)) {Log.e(TAG, "找到了匹配的UUID服务:" + mServices.get(i).toString());mService = mServices.get(i);}}if (mService != null) {displayGattServices(mService, bt_password);}} else {Log.w(TAG, "onServicesDiscovered receiver:" + status);}}@Override //读取设备Charateristic的时候回调public void onCharacteristicRead(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, int status) {Log.i(TAG, "读取设备Charateristic回调成功");}@Override //当向设备的写入Charateristic的时候调用public void onCharacteristicWrite(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, int status) {Log.i(TAG, "当向设备的写入Charateristic回调成功");if (mBlueToothAdapter.isEnabled()) {mBlueToothAdapter.disable();Toast.makeText(BlueToothService.this, "写入信息成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();//MoreFragment.handler.sendEmptyMessage(1);stopSelf(); //关闭服务}}@Override 设备发出通知时会调用到该接口public void onCharacteristicChanged(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic) {Log.i(TAG, "设备发出通知时回调成功");}@Override //当向设备Descriptor中读取数据时,会回调该函数public void onDescriptorRead(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor, int status) {Log.i(TAG, "当向设备Descriptor中读取数据回调成功");}@Override //当向设备Descriptor中写数据时,会回调该函数public void onDescriptorWrite(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor, int status) {Log.i(TAG, "当向设备Descriptor中写数据回调成功");}}
displayGattServices函数
用于查找当前Service中的所有characteristic特征
/*** 遍历出指定GattServices中的所有Charateristic* 以供程序的写入和读取数据** @param gattService 指定Gatt服务* @param value 具体写入数据*/@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR2)private void displayGattServices(BluetoothGattService gattService, final String value) {if (gattService == null)return;//获取全部characteristic特征列表//List<BluetoothGattCharacteristic> gattCharacteristics = gattService.getCharacteristics();//根据UUID,获取指定characteristic特征列表BluetoothGattCharacteristic gattCharacteristics = gattService.getCharacteristic(characteristicUUID);Log.e(TAG, "-->service type:" + "");Log.e(TAG, "-->includedServices size:" + gattService.getIncludedServices().size());Log.e(TAG, "-->service uuid:" + gattService.getUuid());Log.e(TAG, "---->char uuid:" + gattCharacteristics.getUuid());int permission = gattCharacteristics.getPermissions();Log.e(TAG, "---->char permission:" + permission);int property = gattCharacteristics.getProperties();Log.e(TAG, "---->char property:" + property);byte[] data = gattCharacteristics.getValue();if (data != null && data.length > 0) {Log.e(TAG, "---->char value:" + new String(data));}//接受Characteristic被写的通知,收到蓝牙模块的数据后会触发mOnDataAvailable.onCharacteristicWrite()mBluetoothGatt.setCharacteristicNotification(gattCharacteristics, true);byte[] bytes = value.getBytes();gattCharacteristics.setValue(bytes); //具体写入的数据//往蓝牙模块写入数据boolean result = mBluetoothGatt.writeCharacteristic(gattCharacteristics);Log.i(TAG, "写入数据为:" + value);Log.i(TAG, result ? "写入characteristic数据成功" : "写入数据失败");/*for (final BluetoothGattCharacteristic gattCharacteristic : gattCharacteristics) { // 遍历每条服务里的所有CharacteristicLog.i(TAG, "遍历BluetoothGattCharacteristic特性");Log.e(TAG, "---->char uuid:" + gattCharacteristic.getUuid());int permission = gattCharacteristic.getPermissions();Log.e(TAG, "---->char permission:" + permission);int property = gattCharacteristic.getProperties();Log.e(TAG, "---->char property:" + property);byte[] data = gattCharacteristic.getValue();if (data != null && data.length > 0) {Log.e(TAG, "---->char value:" + new String(data));}if (gattCharacteristic.getUuid().toString().equals(characteristicUUID.toString())) { //需要通信的UUID// 有哪些UUID,每个UUID有什么属性及作用,一般硬件工程师都会给相应的文档。我们程序也可以读取其属性判断其属性。// 此处可以可根据UUID的类型对设备进行读操作,写操作,设置notification等操作// BluetoothGattCharacteristic gattNoticCharacteristic 假设是可设置通知的Characteristic// BluetoothGattCharacteristic gattWriteCharacteristic 假设是可写的Characteristic// BluetoothGattCharacteristic gattReadCharacteristic 假设是可读的Characteristic//接受Characteristic被写的通知,收到蓝牙模块的数据后会触发mOnDataAvailable.onCharacteristicWrite()mBluetoothGatt.setCharacteristicNotification(gattCharacteristic, true);byte[] bytes = value.getBytes();gattCharacteristic.setValue(bytes); //具体写入的数据//往蓝牙模块写入数据boolean result = mBluetoothGatt.writeCharacteristic(gattCharacteristic);Log.i(TAG, "写入数据为:" + value);Log.i(TAG, result ? "写入characteristic数据成功" : "写入数据失败");} else {Log.i(TAG, "写入的UUID不匹配");}//-----Descriptors的字段信息-----//List<BluetoothGattDescriptor> gattDescriptors = gattCharacteristic.getDescriptors();for (BluetoothGattDescriptor gattDescriptor : gattDescriptors) {Log.e(TAG, "-------->desc uuid:" + gattDescriptor.getUuid());int descPermission = gattDescriptor.getPermissions();//Log.e(TAG, "-------->desc permission:" + Utils.getDescPermission(descPermission));byte[] desData = gattDescriptor.getValue();if (desData != null && desData.length > 0) {Log.e(TAG, "-------->desc value:" + new String(desData));}}}*/}
最后补上6.0版本以上的权限请求问题
private void checkBlueToothPermission() {if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 23) {Log.i(TAG, "系统版本为6.0");boolean hasLocationPermission =ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED;Log.i(TAG, "当前有Location权限吗?" + hasLocationPermission);if (!hasLocationPermission) {ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, new String[]{Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION}, REQUEST_ENABLE_LOCATION);} else {if (isLocationEnable(this)) {connectDevice();} else {ShowToast("由于系统问题,请开启定位服务");Intent locationIntent = new Intent(Settings.ACTION_LOCATION_SOURCE_SETTINGS);this.startActivityForResult(locationIntent, REQUEST_CODE_LOCATION_SETTINGS);}}} else {connectDevice();}}
动态请求权限回调—-onRequestPermissionsResult
@Overridepublic void onRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode, String[] permissions,int[] grantResults) {super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults);if (requestCode == REQUEST_ENABLE_LOCATION) {if (grantResults.length > 0 && grantResults[0] == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {Log.i(TAG, "定位权限已经开启");if (isLocationEnable(this)) {connectDevice();} else {ShowToast("由于系统问题,请开启定位服务");Intent locationIntent = new Intent(Settings.ACTION_LOCATION_SOURCE_SETTINGS);this.startActivityForResult(locationIntent, REQUEST_CODE_LOCATION_SETTINGS);}} else {ShowToast("请开启权限,否则无法使用开门功能");}}}
connectDevice函数
private void connectDevice() {intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, BlueToothService.class);if (mBlueToothAdapter != null) {if (getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_BLUETOOTH_LE)) {if (mBlueToothAdapter.isEnabled()) {intent.putExtra("Order", Const.SCAN_START);startService(intent);} else {Intent enableBtIntent = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE);startActivityForResult(enableBtIntent, REQUEST_ENABLE_BT);}} else {ShowToast("该设备不支持BLE蓝牙");}} else {ShowToast("该设备不支持蓝牙");}}
以上就是呆毛里面的部分代码,这只是上面描述的两个角色中的Central (Client)。具体的Peripheral(Service)在下篇带上来。
可能项目结构上面有点乱,迟点我上传个demo的代码,也算是比较简单的实现
源码下载





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...