python实现pat 1071. Speech Patterns (25)
题目描述
People often have a preference among synonyms of the same word. For example, some may prefer “the police”, while others may prefer “the cops”. Analyzing such patterns can help to narrow down a speaker’s identity, which is useful when validating, for example, whether it’s still the same person behind an online avatar.
Now given a paragraph of text sampled from someone’s speech, can you find the person’s most commonly used word?
输入描述:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, there is one line of text no more than 1048576 characters in length, terminated by a carriage return ‘\n’. The input contains at least one alphanumerical character, i.e., one character from the set [0-9 A-Z a-z].
输出描述:
For each test case, print in one line the most commonly occurring word in the input text, followed by a space and the number of times it has occurred in the input. If there are more than one such words, print the lexicographically smallest one. The word should be printed in all lower case. Here a “word” is defined as a continuous sequence of alphanumerical characters separated by non-alphanumerical characters or the line beginning/end.
Note that words are case insensitive.
输入例子:
Can1: “Can a can can a can? It can!”
输出例子:
can 5
解答1
先提取单词,再排序,最后统计。运算超时了。
line=input()#Can1: "Can a can can a can? It can!"line=line.lower()words=[]bs = Falsebe=Falsefor i,c in enumerate(line):if (c>='a' and c<='z')or (c>='0' and c<='9'):if bs==False:s=ibs=Truebe=Falseelse:if be==False:e=ibe=Trueif bs==True and be==True:word=line[s:e]words.append(word)s=-1e=-1bs = Falseif s!= -1:word = line[s:]words.append(word)words.sort()word_max=Nonecount_max=1count=1for i,word in enumerate(words[:-1]):if word==words[i+1] :count+=1if word == words[-2]:if count > count_max:count_max = countcount = 1word_max = wordelif count>count_max :count_max=countcount=1word_max=wordelse:count = 1if count_max==1:word_max=words[0]print (word_max,count_max)
超时了。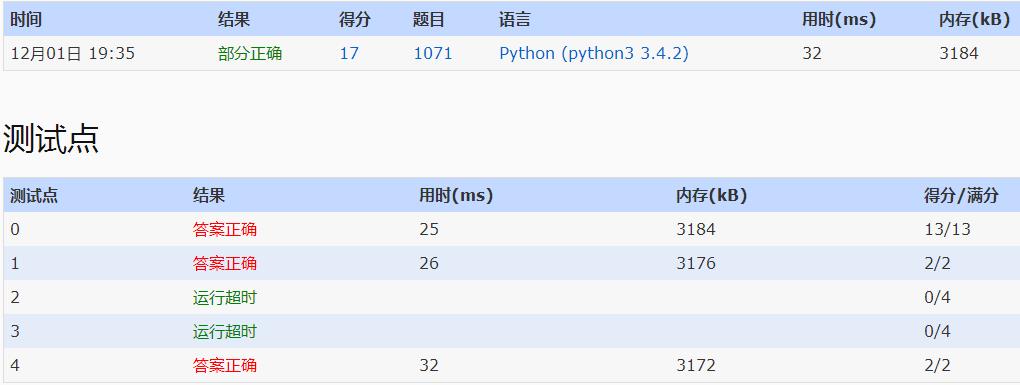
解答2
用了字典,在提取单词的同时统计频次。但还是超时了,并且估计超得更多了。
line=input()line=line.lower()#print (line)words={}bs = Falsebe=Falsefor i,c in enumerate(line):if (c>='a' and c<='z')or (c>='0' and c<='9'):if bs==False:s=ibs=Truebe=Falseelse:if be==False:e=ibe=Trueif bs==True and be==True:word=line[s:e]if word in words:words[word]+=1else:words[word]=1s=-1e=-1bs = Falseif s!= -1:word = line[s:]if word in words:words[word] += 1else:words[word] = 1count_max=0word_len=0word_max=Nonefor word in words:if words[word]>count_max or( words[word]==count_max and word <word_max):count_max=words[word]word_max=wordprint (word_max,count_max)






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...