dubbo负载均衡算法源码解析
在集群负载均衡时,Dubbo提供了4种均衡策略,如:Random LoadBalance(随机均衡算法)、;RoundRobin LoadBalance(权重轮循均衡算法)、LeastAction LoadBalance(最少活跃调用数均衡算法)、ConsistentHash LoadBalance(一致性Hash均衡算法)。缺省时为Random随机调用。具体UML类图如下:
![Image 1][] 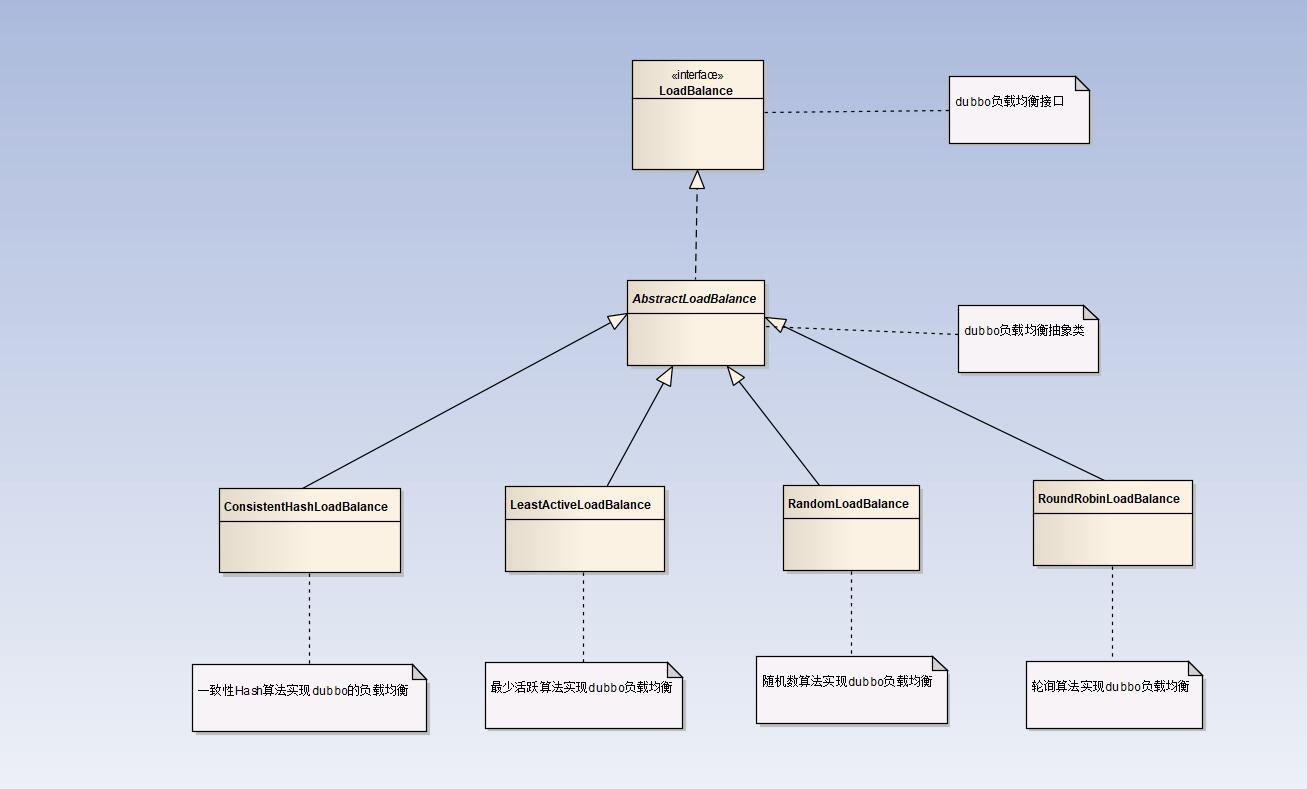
1、RandomLoadBalance(随机算法)
这个随机的策略是默认的策略,但是这个随机和我们理解上的随机还是不一样的,因为他还有个概念叫 weight(权重),这里说的权重就是用来控制这个随机的概率的,我们来看代码实现.protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {int length = invokers.size();// 总个数int totalWeight = 0;// 总权重boolean sameWeight = true;// 权重是否都一样int offset;int i;for(offset = 0; offset < length; ++offset) {i = this.getWeight((Invoker)invokers.get(offset), invocation);totalWeight += i;// 累计总权重if(sameWeight && offset > 0 && i != this.getWeight((Invoker)invokers.get(offset - 1), invocation)) {// 计算所有权重是否一样sameWeight = false;}}if(totalWeight > 0 && !sameWeight) {// 如果权重不相同且权重大于0则按总权重数随机offset = this.random.nextInt(totalWeight);// 并确定随机值落在哪个片断上for(i = 0; i < length; ++i) {offset -= this.getWeight((Invoker)invokers.get(i), invocation);if(offset < 0) {return (Invoker)invokers.get(i);}}}// 如果权重相同或权重为0则均等随机return (Invoker)invokers.get(this.random.nextInt(length));}
2、RoundRobinLoadBalance(轮询算法)
Round-Robin既是轮询算法,是按照公约后的权重设置轮询比率,即权重轮询算法(Weighted Round-Robin) ,它是基于轮询算法改进而来的。这里之所以写RoundRobin是为了跟Dubbo中的内容保持一致。
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {String key = ((Invoker)((List)invokers).get(0)).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();int length = ((List)invokers).size();// 总个数int maxWeight = 0;// 最大权重int minWeight = 2147483647;// 最小权重int currentWeight;for(int sequence = 0; sequence < length; ++sequence) {currentWeight = this.getWeight((Invoker)((List)invokers).get(sequence), invocation);maxWeight = Math.max(maxWeight, currentWeight);// 累计最大权重minWeight = Math.min(minWeight, currentWeight);// 累计最小权重}AtomicPositiveInteger var13;if(maxWeight > 0 && minWeight < maxWeight) { // 权重不一样var13 = (AtomicPositiveInteger)this.weightSequences.get(key);if(var13 == null) {this.weightSequences.putIfAbsent(key, new AtomicPositiveInteger());var13 = (AtomicPositiveInteger)this.weightSequences.get(key);}currentWeight = var13.getAndIncrement() % maxWeight;ArrayList weightInvokers = new ArrayList();Iterator weightLength = ((List)invokers).iterator();while(weightLength.hasNext()) {Invoker invoker = (Invoker)weightLength.next();if(this.getWeight(invoker, invocation) > currentWeight) { // 筛选权重大于当前权重基数的InvokerweightInvokers.add(invoker);}}int var14 = weightInvokers.size();if(var14 == 1) {return (Invoker)weightInvokers.get(0);}if(var14 > 1) {invokers = weightInvokers;length = weightInvokers.size();}}var13 = (AtomicPositiveInteger)this.sequences.get(key);if(var13 == null) {this.sequences.putIfAbsent(key, new AtomicPositiveInteger());var13 = (AtomicPositiveInteger)this.sequences.get(key);}// 取模轮循return (Invoker)((List)invokers).get(var13.getAndIncrement() % length);}
3、LeastActiveLoadBalance(最少活跃数)
1、最少活跃调用数,相同活跃数的随机,活跃数指调用前后计数差;
2、使慢的提供者收到更少请求,因为越慢的提供者的调用前后计数差会越大。
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {int length = invokers.size();//总活跃数int leastActive = -1;//初始化最小活跃数int leastCount = 0;//最少活跃数相同数量int[] leastIndexs = new int[length];//最少活跃数相同的数据int totalWeight = 0;//总权重int firstWeight = 0;//第一个权重方便对比boolean sameWeight = true;//是否所有权重相同int offsetWeight;int leastIndex;for(offsetWeight = 0; offsetWeight < length; ++offsetWeight) {Invoker i = (Invoker)invokers.get(offsetWeight);leastIndex = RpcStatus.getStatus(i.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName()).getActive();int weight = i.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), "weight", 100);// 权重if(leastActive != -1 && leastIndex >= leastActive) { // 发现更小的活跃数,重新开始if(leastIndex == leastActive) {leastIndexs[leastCount++] = offsetWeight;// 累计相同最小活跃数下标totalWeight += weight;// 累计总权重if(sameWeight && offsetWeight > 0 && weight != firstWeight) { // 判断所有权重是否一样sameWeight = false;}}} else {leastActive = leastIndex;// 记录最小活跃数leastCount = 1;// 重新统计相同最小活跃数的个数leastIndexs[0] = offsetWeight;// 重新记录最小活跃数下标totalWeight = weight;// 重新累计总权重firstWeight = weight;// 记录第一个权重sameWeight = true;// 还原权重相同标识}}if(leastCount == 1) { // 如果只有一个最小则直接返回return (Invoker)invokers.get(leastIndexs[0]);} else {if(!sameWeight && totalWeight > 0) {// 如果权重不相同且权重大于0则按总权重数随机offsetWeight = this.random.nextInt(totalWeight);// 并确定随机值落在哪个片断上for(int var15 = 0; var15 < leastCount; ++var15) {leastIndex = leastIndexs[var15];offsetWeight -= this.getWeight((Invoker)invokers.get(leastIndex), invocation);if(offsetWeight <= 0) {return (Invoker)invokers.get(leastIndex);}}}// 如果权重相同或权重为0则均等随机return (Invoker)invokers.get(leastIndexs[this.random.nextInt(leastCount)]);}}
4、ConsistentHashLoadBalance(一致性hash算法)
一致性Hash,相同参数的请求总是发到同一个提供者。一:一致性Hash算法可以解决服务提供者的增加、移除及挂掉时的情况,能尽可能小的改变已存在 key 映射关系,尽可能的满足单调性的要求。二:一致性Hash通过构建虚拟节点,能尽可能避免分配失衡,具有很好的平衡性。
简单讲就是,假设我们有个时钟,各服务器节点映射放在钟表的时刻上,把key也映射到钟表的某个时刻上,然后key顺时针走,碰到的第一个节点则为我们需要找的服务器节点
还是假如我们有a,b,c,d四个节点(感觉整篇文章都在做这个假如….),把他们通过 某种规则转成整数,分别为0,3,6,9.所以按照时钟分布如下图
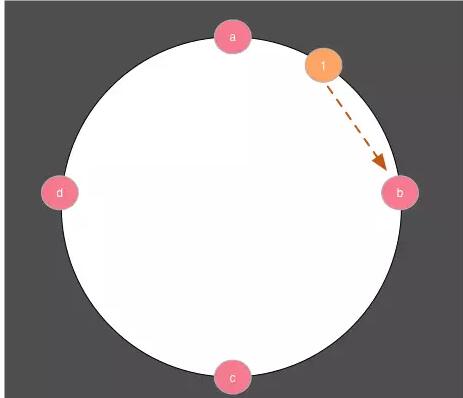
假设这个key通过 某种规则转化成1,那么他顺时针碰到的第一个节点就是b,也就是b是我们要找的节点
那么我们可能就有疑问了,这个 某种规则究竟是什么规则?
这个规则你可以自己设计,但是要注意的是,不同的节点名,转换为相同的整数的概率就是衡量这个规则的好坏,如果你能做到不同的节点名唯一对应一个整数,那就是棒棒哒.当然java里面的 CRC32这个类你可以了解一下.
说到这里可能又会有另个疑问,时钟点数有限,万一装不下怎么办
其实这个时钟只是方便大家理解做的比喻而已,在实际中,我们可以在圆环上分布 [0,2^32-1]的数字,这量级全世界的服务器都可以装得下.
down机影响
通过上图我们可以看出,当b节点挂了之后,根据顺时针的规则,那么目标节点就是c,也就是说,只影响了一个节点,其他节点不受影响.
如果是轮询的取模算法,假设从N台服务器变成了N-1台,那么命中率就变成 1/(N-1),因此服务器越多,影响也就越大.
虚拟节点
为什么要有虚拟节点的概念呢?我们还是回到第一个假设,我们还是有a,b,c,d四个节点,他们通过某个规则转化成0,3,6,9这种自然是均匀的.但是万一是0,1,2,3这样,那就是非常不均匀了.事实上, 一般的 Hash函数对于节点在圆环上的映射,并不均匀.所以我们需要引入虚拟节点,那么什么是虚拟节点呢?
假如有N个真实节点,把每个真实节点映射成M个虚拟节点,再把 M*N 个虚拟节点, 散列在圆环上. 各真实节点对应的虚拟节点相互交错分布这样,某真实节点down后,则把其影响平均分担到其他所有节点上.
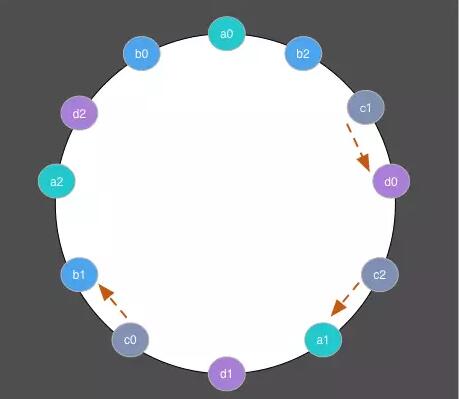
也就是a,b,c,d的虚拟节点 a0,a1,a2, b0,b1,b2, c0,c1,c2, d0,d1,d2散落在圆环上,假设C号节点down,则 c0,c1,c2的压力分别传给 d0,a1,b1,如下图
[Image 1]:






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...