Map 基础知识整理
Map(接口):
与 Collection 并列存在。用于保存具有映射关系的数据:Key-Value。
Key 于 Value 可以是任何引用类型的数据。其中 K 不允许重复。Map 对象所对应的类,须重写 hashCode() 和 equals() 方法。key 和 value 之间总存在单向一对一关系,即通过指定的 key 总能找到唯一的,确定的值。因为 K 是唯一的,所以 keySet() 返回的是一个 Set.而 values() 返回的是一个 Collection。一个 K-V 对,是一个 Entry。 所有的 Entry 是用 Set 存放的,也是不可重复的。
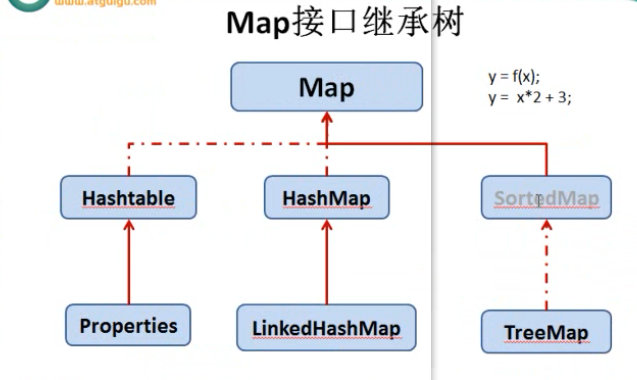
Map接口继承树:
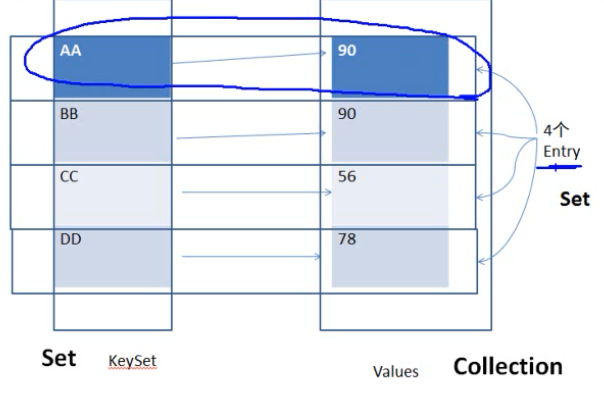
如果右侧 Value 全为 null,看起来不就是一个 HashSet。
下为 HashSet 构造方法
private transient HashMap
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap
}
说明 HashMap 与 HshSet 底层是有关系的。
Map常用方法

1、map.put( null,null );//可以传一个 null 键和多个 null 值。
2、HashMap 重写了 equals 方法,所以
map.put( new Person("SS"), 83);会被 map.put( new Person("SS"), 87); 覆盖。
实例练习:
1、@Test
public void map1(){
Random rand = new Random(47);
Map
for(int i=0;i<10000; i++){
int key = rand.nextInt(20);//生成一个[0,20)之间的随机数
Integer freq = m.get(key);
m.put(key, freq==null ? 1 : freq+1);//If the map 以前包含一个该键的映射关系, 则用指定值替换旧值;
//由此得出 每个 key 生成了多少次
}
System.out.println(m);
}
2、public class MapOfList{
public static Map<Person, List<? extends Pet>> petPeople= new HashMap<Person, List<? extends Pet>();static \{petPeople.put(new Person("Dawn"), Arrays.asList(new Cymric("Molly"), new Mutt("Spot")));petPeople.put(new Person("Dawn"), Arrays.asList(new Cymric("K"), new Mutt("S")));\}public static void main(String\[\] args)\{//第一种:获取 K-V 的方法(先竖着获取所有 K,再通过 K 单向映射到 V)for(Person person :petPeople.keySet() )\{System.out.printIn(person);for(Pet pet: petPeople.get(person))\{System.out.printIn(pet);\}//第二种:获取 K-V 的方法(先横着获取 K-V 对,再遍历每个 K-V 对的 K , V)for(Map.Entry<Person, List<? extends Pet>> m: petPeople.entrySet())\{String key=m.getKey();Object value=m.getValue();\}\}\}
Map 中的内部 接口
interface Entry
K getKey();
V getValue();
V setValue(V value);
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
}
被 HashMap 中的内部类继承
static class Entry
final K key;
V value;
Entry
int hash;
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) \{value = v;next = n;key = k;hash = h;\}public final K getKey() \{return key;\}public final V getValue() \{return value;\}public final V setValue(V newValue) \{V oldValue = value;value = newValue;return oldValue;\}public final boolean equals(Object o) \{if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))return false;Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;Object k1 = getKey();Object k2 = e.getKey();if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) \{Object v1 = getValue();Object v2 = e.getValue();if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))return true;\}return false;\}public final int hashCode() \{return Objects.hashCode(getKey()) ^ Objects.hashCode(getValue());\}public final String toString() \{return getKey() + "=" + getValue();\}void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) \{\}void recordRemoval(HashMap<K,V> m) \{\}\}
结论:可以看出其中的 hashCode() , equals(Object o), toString() 都被重写。
LinkedHashMap:
类比:LinkedHashSet使用链表维护添加进 Map 中的顺序。故遍历 Map 时按添加的顺序遍历。
TreeMap:
类比: TreeSet
按照添加进 Map 中的元素的 key 的指定属性进行排序。Key 必须是同一个类对象。
TreeMap 中的 V 全部为 null 时,相当于一个 TreeSet.
自然排序 和 定制排序。
自然排序,要求: Person implements Comparable
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o){
if(o instanceof Person){
Person p =(Person)o;
int i = this.age.compareTo(p.age);
if(i == 0){
return this.name.compare(p.name);
}else{
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
定制排序:
public void test1(){
//实现匿名内部类
Comparator com = new Comparator(){
public int compareTo(Object o1, Object o2){
if(o1 instanceof Customer && o2 instanceof Customer){
Customer c1 = (Customer) o1;
Customer c2 = (Customer) o2;
int i = c1.getId().compareTo(c2.getId());
if(i == 0){
return c1.getName().compareTo(c2.getName());
}
return i;
}
return 0;
}
};
TreeMap map = new TreeMap(com);map.put(new Customer("AA", 1001),87);map.put(new Customer("CC", 1001),87);map.put(new Customer("AA", 1002),87);map.put(new Customer("BB", 1001),87);
}
小结:
–自然排序:TreeMap 的所有的 Key 必须实现 Comparable 接口,而且所有的 Key 应该是同一个类的对象,否则将会抛出 ClasssCastException
–定制排序:创建 TreeMap 时,传入一个 Comparator 对象,该对象负责对 TreeMap 中的所有 key 进行排序。此时不需要 Map 的 Key 实现 Comparable 接口
HashMap & Hashtable
•HashMap 和 Hashtable 是 Map 接口的两个典型实现类
•区别:
–Hashtable 是一个古老的 Map 实现类,不建议使用
–Hashtable 是一个线程安全的 Map 实现,但 HashMap 是线程不安全的。
–Hashtable 不允许使用 null 作为 key 和 value,而 HashMap 可以
•与 HashSet 集合不能保证元素的顺序的顺序一样,Hashtable 、HashMap 也不能保证其中 key-value 对的顺序
•Hashtable 、HashMap 判断两个 Key 相等的标准是:两个 Key 通过 equals 方法返回 true,hashCode 值也相等。
•Hashtable 、HashMap 判断两个 Value相等的标准是:两个 Value 通过 equals 方法返回 true。
Prpperties:
Hashtable 的子类。
常用来处理属性文件,键值都为 String 类型的。



































还没有评论,来说两句吧...