Redis之动态字符串 链表 跳跃表 整数集
分析结构体 + 重要API = 理清楚了架构。
Redis是键值,内存缓冲系统。Memcached内部仅仅支持字符串,直接用一个hash表管理。但是Redis支持数据类型更多,因此内部肯定使用了更过的数据结构。
内部数据结构是Redis高效的基础,这里主要详解内部最基本的数据结构以及操作其最基本的API。例如跳跃表,详解其创建、插入、删除、查找API,其他功能封装这些API不做详细解答。
柔性数组说明
柔性数据的好处在于,结构体里面既可以包含空间大小,也可以使用标记直接访问分配的内存,内存空间不足,直接使用realloc(空间重分配、复制原数据、释放原空间、返回新空间首地址)。memcached,Item内部的data域也使用了柔性数组。
陈皓-酷壳柔性数组
维基-柔性数组
动态字符串
1、介绍
C字符串叫做字符串字面量,对于不需要修改的字符串,使用这种默认表示则很简单。那作者为什么还需要造轮子,搞个SDS(Simple Dynamic String)?
封装字符串修改、扩容、缩容、拼接等可能都需要手动重新分配内存的细节,让客户端仅仅专注于上层使用。好处在下面几点。
- 因为使用了sdshrd结构,内部存储了字符串长度以及使用内存信息,可以快速定位字符串长度O(1),避免了strlen的O(N)的遍历。
- 扩展字符串长度,需要动态分配内存,全部右sdshrd的API自动完成,避免了手动重新分配内存,然后memcpy的繁琐。实际上sdshrd内部也是按照这个完成。
- 将一个字符串拼接到一个字符串后面,对于sds绝对不会缓冲区溢出,因为拼接之前会进行内层检测。
- sds具有内存预分配的作用,避免重复多次进行内存分配工作。
- 二进制安全,因为sds有字符串length信息,所以不需要以’/0’为结尾区分字符串,使得Redis内部不仅仅可以保存文本信息也可以存储图片,视频等二进制数据信息。但是为了兼容string内部函数功能,Redis的sds还是默认以’/0’结尾。
2、结构体部分
总共有3种结构体,完全是为了节约存储len和alloc的内存而设计。作者绝对是嵌入式出生,这么爱节约内存。可见作者的功力深厚。结构体的选择会依据字符串的长度动态选择。总之就是分配一块连续的内存块管理字符串。
typedef char *sds;//可代表sdshdr首地址,然后通过地址类型转换访问连续内存块//sds是为了兼容C字符串设计。/* Note: sdshdr5 is never used, we just access the flags byte directly. * However is here to document the layout of type 5 SDS strings. */struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */char buf[];};struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {uint8_t len; /* used */uint8_t alloc; /* 数据区域分配的全部内存,除去了head和'/0'。excluding the header and null terminator */unsigned char flags; /* 高3位代表结构体存储len的数据类型,有了整个参数就可以通过buf正确访问len和alloc了。宏定义就是这样做的。3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */char buf[];//柔性数组};struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {uint16_t len; /* used */uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */char buf[];};struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {uint32_t len; /* used */uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */char buf[];};struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {uint64_t len; /* used */uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */char buf[];};//强迫症,以上仅仅是为了节约存储len和alloc的内存而设计。#define SDS_TYPE_5 0#define SDS_TYPE_8 1#define SDS_TYPE_16 2#define SDS_TYPE_32 3#define SDS_TYPE_64 4#define SDS_TYPE_MASK 7#define SDS_TYPE_BITS 3#define SDS_HDR_VAR(T,s) struct sdshdr##T *sh = (void*)((s)-(sizeof(struct sdshdr##T)));//宏定义连接符##了解下,变量#define SDS_HDR(T,s) ((struct sdshdr##T *)((s)-(sizeof(struct sdshdr##T))))//找出sdshdr16的数据区域#define SDS_TYPE_5_LEN(f) ((f)>>SDS_TYPE_BITS)

直接返回地址buf即可,因为可以通过buf访问前面的len、alloc、flags字节。作者这种玩内存和指针的方法,真是出神入化了。sds[-1]就可以访问flag参数了。地址在堆中总是动态增加。所以可以通过指针的加或者减访问内存块。这就是玩内存的方法了,很聪明哦。
3、创建一个sds字符串
根据传入的C字符串,选择合适的sdshdr__,然后malloc+memcpy即可。整个大体过程就是这样。
/* Create a new sds string starting from a null terminated C string. *///通过c字符串,创建一个sds。将c字符串复制到sds中,并返回sdshrd中的buf。sds sdsnew(const char *init) {size_t initlen = (init == NULL) ? 0 : strlen(init);//需求长度return sdsnewlen(init, initlen);//分配sdshrd,并返回其中的buf数据区域地址。}/* Create a new sds string with the content specified by the 'init' pointer* and 'initlen'.* If NULL is used for 'init' the string is initialized with zero bytes.** The string is always null-termined (all the sds strings are, always) so* even if you create an sds string with:** mystring = sdsnewlen("abc",3);** You can print the string with printf() as there is an implicit \0 at the* end of the string. However the string is binary safe and can contain* \0 characters in the middle, as the length is stored in the sds header. */sds sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen) {//创建SDS字符串,直接返回char即可,需要访问SDS,通过指针回溯即可void *sh;sds s;char type = sdsReqType(initlen);//根据输入字符串长度,选择合适的sdshrd,完全为了节约内存。/* Empty strings are usually created in order to append. Use type 8* since type 5 is not good at this. */if (type == SDS_TYPE_5 && initlen == 0) type = SDS_TYPE_8;int hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type);//头结构体节点占用内存。unsigned char *fp; /* flags pointer. */sh = s_malloc(hdrlen+initlen+1);//分配=头结点+数据长度+结束符if (!init)memset(sh, 0, hdrlen+initlen+1);//将新分配的sh内存清空。因为malloc并不保证先前位置为空,所以必须设为0if (sh == NULL) return NULL;s = (char*)sh+hdrlen;//定位head中的数据区域fp = ((unsigned char*)s)-1;//sdshdr中的flags域switch(type) {case SDS_TYPE_5: {*fp = type | (initlen << SDS_TYPE_BITS);break;}case SDS_TYPE_8: {SDS_HDR_VAR(8,s);sh->len = initlen;sh->alloc = initlen;*fp = type;break;}case SDS_TYPE_16: {SDS_HDR_VAR(16,s);//通过数据域的地址,获取整个sdshrd的地址sh->len = initlen;//初始化sh->alloc = initlen;//初始化*fp = type;//结构体中类型break;'/0'}case SDS_TYPE_32: {SDS_HDR_VAR(32,s);sh->len = initlen;sh->alloc = initlen;*fp = type;break;}case SDS_TYPE_64: {SDS_HDR_VAR(64,s);sh->len = initlen;sh->alloc = initlen;*fp = type;break;}}if (initlen && init)memcpy(s, init, initlen);//将init数据全部拷贝到s数据区域s[initlen] = '\0';//结束符return s;//返回s}
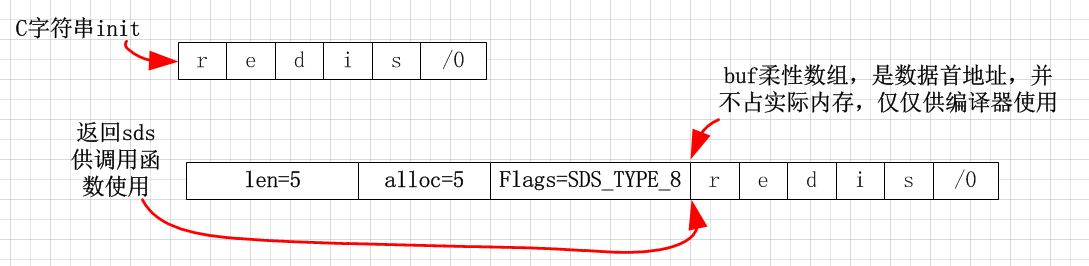
上述过程可以用简单的图表示,很容易理解,所以sds很简单,就不细说了。antirez
4、sdscat将一个字符串加到sds之后,不会内存溢出
整个过程很简单,绝对不会有内存溢出的问题。首先确定sds是否有足够的空间。假如空间足够则直接realloc+memcpy;假如空间不足,则依据总长度选择合适的类型,然后malloc(分配新内存)+free(释放旧内存)+memcpy(先拷贝旧字符串)+memcpy(再拷贝新字符串)即可。如果没有这个函数的封装,利用C字符串,也会是这样的一个过程。
/* Append the specified binary-safe string pointed by 't' of 'len' bytes to the* end of the specified sds string 's'.** After the call, the passed sds string is no longer valid and all the* references must be substituted with the new pointer returned by the call. */sds sdscatlen(sds s, const void *t, size_t len) {size_t curlen = sdslen(s);//获取s长度s = sdsMakeRoomFor(s,len);//扩容sds,若容量够,则直接拼接,防止溢出if (s == NULL) return NULL;memcpy(s+curlen, t, len);//将t直接拷贝到s+curlen位置处。很简单的memcpy。注意内存已分配,绝对不会造成重叠的问题。sdssetlen(s, curlen+len);//设置字符串长度s[curlen+len] = '\0';//末尾加上空return s;//返回s,s可能被修改,也可能没有被修改。}/* Enlarge the free space at the end of the sds string so that the caller* is sure that after calling this function can overwrite up to addlen* bytes after the end of the string, plus one more byte for nul term.** Note: this does not change the *length* of the sds string as returned* by sdslen(), but only the free buffer space we have. */sds sdsMakeRoomFor(sds s, size_t addlen) {void *sh, *newsh;size_t avail = sdsavail(s);//返回sds可用容量size_t len, newlen;char type, oldtype = s[-1] & SDS_TYPE_MASK;int hdrlen;/* Return ASAP if there is enough space left. */if (avail >= addlen) return s;//可用容量足够放下addlen长度字符串,直接返回/*不够则需要进行扩容加上搬移。*/len = sdslen(s);//原来字符串长度sh = (char*)s-sdsHdrSize(oldtype);//找到结构体头部newlen = (len+addlen);//需要分配新的长度if (newlen < SDS_MAX_PREALLOC)//新的长度小于1M,则直接重新分配2倍,为以后使用避免重新分配内存newlen *= 2;elsenewlen += SDS_MAX_PREALLOC;//大于1M,则直接多分配1Mtype = sdsReqType(newlen);//获取相应的sdshrd的类型表示。/* Don't use type 5: the user is appending to the string and type 5 is* not able to remember empty space, so sdsMakeRoomFor() must be called* at every appending operation. */if (type == SDS_TYPE_5) type = SDS_TYPE_8;hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type);//获取头类型字节数if (oldtype==type) {//类型一致,则当前sdshrd长度变量足够存储newlen,则realloc即可newsh = s_realloc(sh, hdrlen+newlen+1);//realloc并返回if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen;} else {//不一致,则malloc + memcpy + free/* Since the header size changes, need to move the string forward,* and can't use realloc */newsh = s_malloc(hdrlen+newlen+1);//分配新的的内存if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;memcpy((char*)newsh+hdrlen, s, len+1);//将数据拷贝到新的内存s_free(sh);//释放老的内存块s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen;//s重新指向新的数据块s[-1] = type;//赋值类型,这种操作很明白,一看就懂了,往回退1字节,不愧是搞嵌入式的人。sdssetlen(s, len);//设置字符串长度,并没有strcat,所以长度不变}sdssetalloc(s, newlen);//设置分配的内容return s;}
其余API都对应着类似的操作,整个我们已经可很清楚的看懂了。下面一幅图对应着
在sds.c中,几乎所有的函数所传的参数都是sds类型,而非表头sdshdr的地址,但是使用了通过sds指针运算从而求得表头的地址的技巧,因为sds是指向sdshdr结构buf成员,在堆中地址向上增长,所以可以通过指针的算术元算找到表头即可。
跳跃表
https://blog.csdn.net/ict2014/article/details/17394259
https://blog.csdn.net/men_wen/article/details/70040026
1、跳跃表(skiplist)介绍
跳跃表是一种有序数据结构,通过每个节点中维持多个指向其他节点的指针,从而达到快速访问节点的目的。其中节点中指针的数目是通过随机生成的,所以跳跃表是使用概率均衡技术而不是使用强制性均衡,因此,对于插入和删除结点比传统上的平衡树算法更为简洁高效。跳跃表支持平均O(LogN)、最坏O(N)复杂度的节点查找,还可以通过顺序性操作批处理节点,因此大部分情况下可以和平衡树媲美,其实现起来更为简单。
通过在每个节点中存放多个指向下一个不同节点的指针,实现跳跃的功能。类似于将一系列节点跳跃性的连接成多条有序链表,查找过程就是先从最高层开始,然后遍历所以层次,最后定位到节点。
上图是一个4层的跳跃表。将处在相同层次的节点联结起来,于是类似于含有4条跳跃的链表。每个节点中层是随机生成的。随机生成函数可以自己写,
2、随机数生成函数
在redis中,返回一个随机层数值,随机算法所使用的幂次定律。
- 含义是:如果某件事的发生频率和它的某个属性成幂关系,那么这个频率就可以称之为符合幂次定律。
表现是:少数几个事件的发生频率占了整个发生频率的大部分, 而其余的大多数事件只占整个发生频率的一个小部分。
int zslRandomLevel(void) { //返回一个随机层数值
int level = 1;//(random()&0xFFFF)只保留低两个字节的位值,其他高位全部清零,所以该值范围为0到0xFFFFwhile ((random()&0xFFFF) < (ZSKIPLIST_P * 0xFFFF)) //ZSKIPLIST_P(0.25)所以level+1的概率为0.25level += 1; //返回一个1到ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL(32)之间的值return (level<ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL) ? level : ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL;
}
define ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL 32 / Should be enough for 2^32 elements /
define ZSKIPLIST_P 0.25 / Skiplist P = 1/4 /
2、Redis跳跃表
typedef struct zskiplistNode {sds ele; //保存成员对象动态字符串double score; //分值struct zskiplistNode *backward; //后退指针,指向前一个节点,方便范围查找struct zskiplistLevel {struct zskiplistNode *forward; //前进指针,指向下一个节点unsigned int span; //跨度,此级跨越几个节点} level[]; //层级,是柔型数组,根据随机数动态分配} zskiplistNode;//跳跃表节点结构体typedef struct zskiplist {struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail;unsigned long length;int level;} zskiplist;//管理一个跳跃表,记录头部和尾部节点以及跳跃表长度。
通过ZADD操作之后,跳跃表的随机构成可能是下面结构,其中节点中层次是随机生成的。
127.0.0.1:6379> ZADD score 95.5 Mike 98 Li 96 Wang //socre是一个有序集合键(integer) 3127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGE score 0 -1 WITHSCORES//所有分数按从小到大排列,每一个成员都保存了一个分数1) "Mike"2) "95.5"3) "Wang"4) "96"5) "Li"6) "98"127.0.0.1:6379> ZSCORE score Mike //查询Mike的分值"95.5"
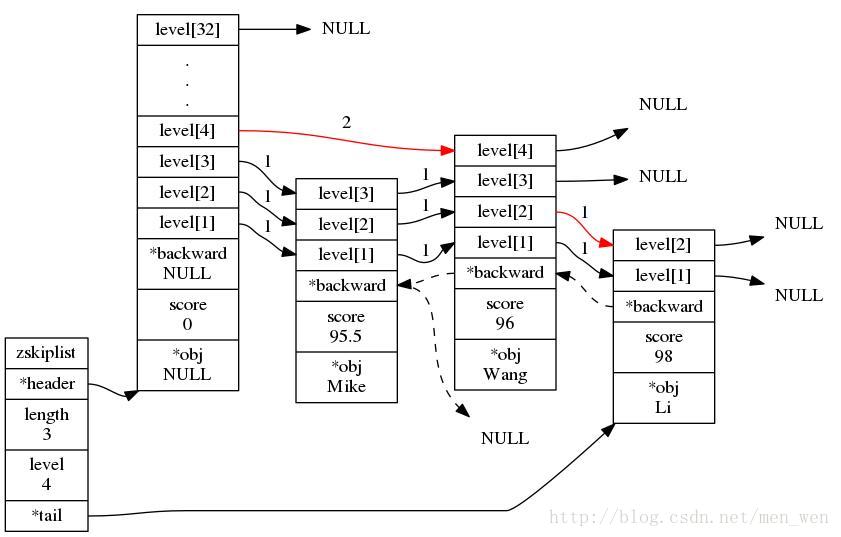
在level数组中,处于同一级的,就必须构造成链表,如上图。只要符合这一规则,那么就可以使用跳跃表了。根据上图,直接讲解Redis中跳跃表操作得API。
//创建一个新的跳跃表,管理跳跃表的结构体/* Create a new skiplist. */zskiplist *zslCreate(void) {int j;zskiplist *zsl;zsl = zmalloc(sizeof(*zsl));//分配内存zsl->level = 1;//层级初始化0zsl->length = 0;//元素个数初始化0zsl->header = zslCreateNode(ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL,0,NULL);//创建一个头结点,可见头结点最高是32层,分数是0,元素是空,这个用来管理链表for (j = 0; j < ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL; j++) {zsl->header->level[j].forward = NULL;zsl->header->level[j].span = 0;}//将header的下一个节点全部初始化为空且span为0zsl->header->backward = NULL;//前节点为空zsl->tail = NULL;//尾部为空return zsl;//返回链表首地址}//创建一个跳跃表节点,实现很简单。/* Create a skiplist node with the specified number of levels. * The SDS string 'ele' is referenced by the node after the call. */zskiplistNode *zslCreateNode(int level, double score, sds ele) {zskiplistNode *zn =zmalloc(sizeof(*zn)+level*sizeof(struct zskiplistLevel));//柔性数组,可以看到分配的内存是连续的,很方便。zn->score = score;//分数zn->ele = ele;//元素return zn;//返回节点地址。//Redis作者写的代码,真的很符合我的口味,写的没有那么绕口,不愧是搞嵌入式出生的人。}//释放一个节点/* Free the specified skiplist node. The referenced SDS string representation * of the element is freed too, unless node->ele is set to NULL before calling * this function. */void zslFreeNode(zskiplistNode *node) {sdsfree(node->ele);//先释放动态字符串内存。zfree(node);//然后释放当前节点占用内存。}//随机获取1到32之间的数字,作为节点中level层级。/* Returns a random level for the new skiplist node we are going to create. * The return value of this function is between 1 and ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL * (both inclusive), with a powerlaw-alike distribution where higher * levels are less likely to be returned. */int zslRandomLevel(void) {int level = 1;while ((random()&0xFFFF) < (ZSKIPLIST_P * 0xFFFF))level += 1;return (level<ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL) ? level : ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL;}/* 向跳跃表中插入一个节点: 1、先通过score定位,ele应该所处的位置,并通过update记录每层中节点转向的指针。 2、新键一个节点,并用传入的值初始化。 3、通过前面的update记录的节点信息,将新节点插入对应层次的单向链表。 *//* Insert a new node in the skiplist. Assumes the element does not already * exist (up to the caller to enforce that). The skiplist takes ownership * of the passed SDS string 'ele'. */zskiplistNode *zslInsert(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele) {zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;unsigned int rank[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL];int i, level;serverAssert(!isnan(score));x = zsl->header;//相当于遍历level-1层链表,实现思路很容易for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {/* store rank that is crossed to reach the insert position */rank[i] = i == (zsl->level-1) ? 0 : rank[i+1];//更新rank[i]为i+1所跨越的节点数,但是最外一层为0while (x->level[i].forward &&(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0)))//后一个节点存在,且分数小于sore,则在当前链表中前进一步。{rank[i] += x->level[i].span;//记录该层一共跨越了多少节点 加上 上一层遍历所跨越的节点数x = x->level[i].forward;//更新并指向下一个节点}update[i] = x;//记录遍历过程中每条链表中跳转的节点,用于分析}/* we assume the element is not already inside, since we allow duplicated * scores, reinserting the same element should never happen since the * caller of zslInsert() should test in the hash table if the element is * already inside or not. */level = zslRandomLevel();//获得一个随机的层数if (level > zsl->level) {//如果大于当前所有节点最大的层数时for (i = zsl->level; i < level; i++) {rank[i] = 0; //将大于等于原来zsl->level层以上的rank[]设置为0update[i] = zsl->header;//将大于等于原来zsl->level层以上update[i]指向头结点update[i]->level[i].span = zsl->length;//update[i]已经指向头结点,将第i层的跨度设置为length}zsl->level = level;}//如果随机层数大于跳跃表层,则更新跳跃表zslx = zslCreateNode(level,score,ele);//创建一个节点for (i = 0; i < level; i++) {//遍历每一层,并更新每一层的链表x->level[i].forward = update[i]->level[i].forward;update[i]->level[i].forward = x;//将节点插入i层的链表,因为update记录了i层上一个节点信息,所以很容易实现。/* update span covered by update[i] as x is inserted here */x->level[i].span = update[i]->level[i].span - (rank[0] - rank[i]);//更新插入节点的跨度值update[i]->level[i].span = (rank[0] - rank[i]) + 1;//更新插入节点前一个节点的跨度值}/* increment span for untouched levels */for (i = level; i < zsl->level; i++) {//如果插入节点的level小于原来的zsl->level才会执行update[i]->level[i].span++;//因为高度没有达到这些层,所以只需将查找时每层最后一个节点的值的跨度加1}//设置插入节点的后退指针,就是查找时最下层的最后一个节点,该节点的地址记录在update[0]中//如果插入在第二个节点,也就是头结点后的位置就将后退指针设置为NULLx->backward = (update[0] == zsl->header) ? NULL : update[0];if (x->level[0].forward)//如果x节点不是最尾部的节点x->level[0].forward->backward = x;//就将x节点后面的节点的后退节点设置成为x地址elsezsl->tail = x;//否则更新表头的tail指针,指向最尾部的节点xzsl->length++;//跳跃表节点计数器加1return x;//返回x地址}//根据传入的update指针数组,更新跳跃表中每条链表//被zslDelete, zslDeleteByScore and zslDeleteByRank使用的内部函数void zslDeleteNode(zskiplist *zsl, zskiplistNode *x, zskiplistNode **update) {int i;//设置前进指针和跨度for (i = 0; i < zsl->level; i++) { //遍历下标为0到跳跃表最大层数-1的层if (update[i]->level[i].forward == x) { //如果找到该节点update[i]->level[i].span += x->level[i].span - 1; //将前一个节点的跨度减1update[i]->level[i].forward = x->level[i].forward;//前一个节点的前进指针指向被删除的节点的后一个节点,跳过该节点} else {update[i]->level[i].span -= 1; //在第i层没找到,只将该层的最后一个节点的跨度减1}}//设置后退指针if (x->level[0].forward) { //如果被删除的前进节点不为空,后面还有节点x->level[0].forward->backward = x->backward; //就将后面节点的后退指针指向被删除节点x的回退指针} else {zsl->tail = x->backward; //否则直接将被删除的x节点的后退节点设置为表头的tail指针}//更新跳跃表最大层数while(zsl->level > 1 && zsl->header->level[zsl->level-1].forward == NULL)zsl->level--;zsl->length--; //节点计数器减1}//根据分数和元素删除元素/* Delete an element with matching score/element from the skiplist. * The function returns 1 if the node was found and deleted, otherwise * 0 is returned. * * If 'node' is NULL the deleted node is freed by zslFreeNode(), otherwise * it is not freed (but just unlinked) and *node is set to the node pointer, * so that it is possible for the caller to reuse the node (including the * referenced SDS string at node->ele). */int zslDelete(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele, zskiplistNode **node) {zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;int i;//查找位置x = zsl->header;for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {while (x->level[i].forward &&(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0))){x = x->level[i].forward;}update[i] = x;}/* We may have multiple elements with the same score, what we need * is to find the element with both the right score and object. */x = x->level[0].forward;//获取当前节点if (x && score == x->score && sdscmp(x->ele,ele) == 0) {//确实是这个元素zslDeleteNode(zsl, x, update);//更新删除节点之后的跳跃表。//zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL]是数组,类型是zskiplistNode *,所以应该传入其地址,为zskiplistNode * * 类似于int a[12],形参类型是int *。if (!node)zslFreeNode(x);//释放当前节点信息else*node = x;return 1;}return 0; /* not found */}
上述查找、插入、释放的过程。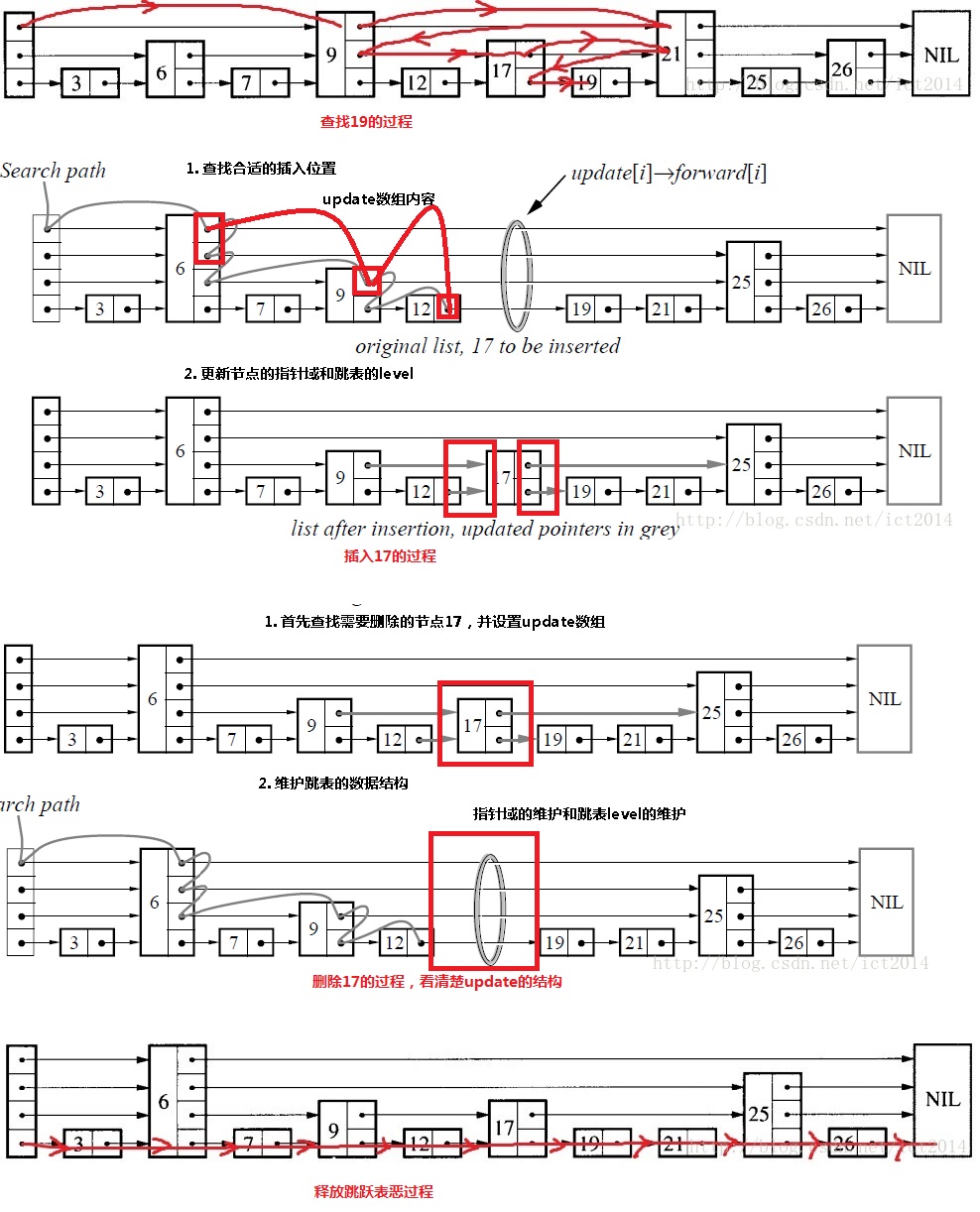
其他API暂时先放放。
整数集合
整数集合(intset)是集合键底层实现之一,以有序、无重复的方式保存集合原色。集合键另一实现是值为空的哈希表(hash table),虽然使用哈希表对集合的加入删除元素,判断元素是否存在等等操作时间复杂度为O(1),但是当存储的元素是整型且元素数目较少时,如果使用散列表存储,就会比较浪费内存,因此整数集合(intset)类型因为节约内存而存在,直接使用柔性数组存储即可。
将元素有序的放在柔性数组中,并且当数据超过当前编码,则会进行数据类型升级并合理迁移先前元素,防止存储溢出,这种实现方式在数据量比较少的时候,很有用。
类型升级的特点
- 提升灵活性:因为C语言是静态类型的语言,通常在在数组中只是用一种类型保存数据,例如,要么只用
int16_t类型,要么只用int32_t类型。通过自动升级底层数组来适应不同类型的新元素,不必担心类型的错误。 - 节约内存:整数集合既可以让集合保存三种不同类型的值,又可以确保升级操作只在有需要的时候进行,这样就节省了内存。
不支持降级:一旦对数组进行升级,编码就会一直保存升级后的状态。
typedef struct intset {
uint32_t encoding;//编码方式uint32_t length;//集合中元素数量int8_t contents[];//柔性数组,扩容通过realloc//从小到大存放元素,且不包含重复项
} intset;
//encoding可选范围define INTSET_ENC_INT16 (sizeof(int16_t)) //16位,2个字节,表示范围-32,768~32,767
define INTSET_ENC_INT32 (sizeof(int32_t)) //32位,4个字节,表示范围-2,147,483,648~2,147,483,647
define INTSET_ENC_INT64 (sizeof(int64_t)) //64位,8个字节,表示范围-9,223,372,036,854,775,808~9,223,372,036,854,775,807
/* Create an empty intset. */intset *intsetNew(void) {intset *is = zmalloc(sizeof(intset));is->encoding = intrev32ifbe(INTSET_ENC_INT16);is->length = 0;return is;}//创建空的intset集,默认是int16
1、往整数集中pos位置插入元素。
/* Set the value at pos, using the configured encoding. *///根据集合is设置的编码方式,设置下标为pos的值为value,用指针操作很容易,直接强制转换,然后赋值。//根据主机字节序用来做内存大小端的转换,主机字节序是大端,如果模板机器的小端,那么需要转换。static void _intsetSet(intset *is, int pos, int64_t value) {uint32_t encoding = intrev32ifbe(is->encoding);if (encoding == INTSET_ENC_INT64) {((int64_t*)is->contents)[pos] = value;//直接将地址转换成编码类型,然后通过指针智能设定。memrev64ifbe(((int64_t*)is->contents)+pos);//小端转大端存储。} else if (encoding == INTSET_ENC_INT32) {((int32_t*)is->contents)[pos] = value;memrev32ifbe(((int32_t*)is->contents)+pos);//如果模板机器是小端,则需要小转大端存储。} else {((int16_t*)is->contents)[pos] = value;memrev16ifbe(((int16_t*)is->contents)+pos);//如果模板机器是小端,则需要小转大端存储。}}
2、类型升级操作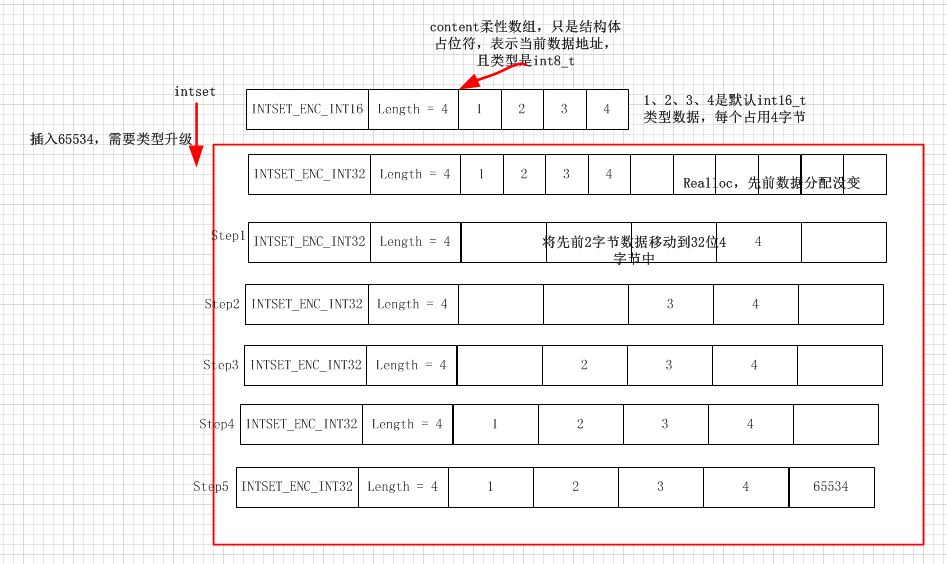
上图是需要升级的过程,如果不需要升级,则先扩容将元素通过有序二分查找找到合适的位置,然后在移动后面的元素,插入新的元素。
这种缺陷在于,每次插入元素都需要realloc,并且类型不匹配还需要升级和realloc。
复杂度很垃圾的。优点就在于可以节约内存,不知道为什么作者要使用这种骚东西,搞不明白。一个hash又浪费了多少空间了。
//当需要升级,或者不升级插入新元素,都需要扩容。注意使用的ralloc,这个在很多源代码使用很多。//https://blog.csdn.net/u010710458/article/details/77274704#t2//重置数组大小,依据新类型分配空间static intset *intsetResize(intset *is, uint32_t len) {uint32_t size = len*intrev32ifbe(is->encoding);is = zrealloc(is,sizeof(intset)+size);//注意柔性数组通过ralloc重新分配。return is;}//往intset中加入元素.//如果当前类型足够存储value,则不用升级,直接扩容//不够存储,则直接升级-->移动元素-->存储/* Insert an integer in the intset */intset *intsetAdd(intset *is, int64_t value, uint8_t *success) {uint8_t valenc = _intsetValueEncoding(value);uint32_t pos;if (success) *success = 1;/* Upgrade encoding if necessary. If we need to upgrade, we know that * this value should be either appended (if > 0) or prepended (if < 0), * because it lies outside the range of existing values. */if (valenc > intrev32ifbe(is->encoding)) {//编码大,则升级插入/* This always succeeds, so we don't need to curry *success. */return intsetUpgradeAndAdd(is,value);} else {//否则找到合适位置,再移动插入。/* Abort if the value is already present in the set. * This call will populate "pos" with the right position to insert * the value when it cannot be found. */if (intsetSearch(is,value,&pos)) {//二分查找定位,如果value已经存在,intsetSearch返回1,如果不存在,pos保存value可以插入的位置if (success) *success = 0;//value存在,success设置为0,并返回return is;}//不存在,pos保存可插入位置。is = intsetResize(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);//重新分配足够的空间if (pos < intrev32ifbe(is->length)) intsetMoveTail(is,pos,pos+1);//不在末尾,则移动pos后面的元素}_intsetSet(is,pos,value);//新值插入posis->length = intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);//返回长度return is;}//升级操作,下面用一副图片说明,扩容,然后升级//首先,需要升级,则必然是当前类型容不下,//要么太大,要么太小,所以必然存储在扩容之后的前或者尾部。/* Upgrades the intset to a larger encoding and inserts the given integer. *///根据value的编码方式,对整数集合is的编码格式升级static intset *intsetUpgradeAndAdd(intset *is, int64_t value) {uint8_t curenc = intrev32ifbe(is->encoding);//先前encodeduint8_t newenc = _intsetValueEncoding(value);//当前encodedint length = intrev32ifbe(is->length);int prepend = value < 0 ? 1 : 0;//小于0,则肯定最小,大于0则肯定最大,必定放在头部或者尾部。/* First set new encoding and resize */is->encoding = intrev32ifbe(newenc);is = intsetResize(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);//根据新的编码方式重新设置内存空间大小/* Upgrade back-to-front so we don't overwrite values. * Note that the "prepend" variable is used to make sure we have an empty * space at either the beginning or the end of the intset. */while(length--)//_intsetGetEncoded(is,length,curenc)根据先前编码获取先前位置值,这个很容易,通过指针获取即可。_intsetSet(is,length+prepend,_intsetGetEncoded(is,length,curenc));//将先前元素插入新位置。//先放先前最大的,然后第二大的,最后最小的。/* Set the value at the beginning or the end. */if (prepend)//如果插入最小,则将值插入最前面_intsetSet(is,0,value);else_intsetSet(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length),value);//最大,插入后面is->length = intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);//长度+1return is;}//注意这里作者使用memmove,免去了没存重叠的叨扰,牛逼得很咯。static void intsetMoveTail(intset *is, uint32_t from, uint32_t to) {void *src, *dst;uint32_t bytes = intrev32ifbe(is->length)-from;//从from到元素的个数uint32_t encoding = intrev32ifbe(is->encoding);if (encoding == INTSET_ENC_INT64) {src = (int64_t*)is->contents+from;dst = (int64_t*)is->contents+to;bytes *= sizeof(int64_t);} else if (encoding == INTSET_ENC_INT32) {src = (int32_t*)is->contents+from;//首地址dst = (int32_t*)is->contents+to;//目的地址bytes *= sizeof(int32_t);//个数*sizeof等于需要移动的全部字节} else {src = (int16_t*)is->contents+from;dst = (int16_t*)is->contents+to;bytes *= sizeof(int16_t);}//memmove可以保证在重叠的时候,将src指定地方复制到des。//https://blog.csdn.net/u010710458/article/details/78887755#t11 讲解了重叠问题memmove(dst,src,bytes);//将src开始地址的bytes字节,移动到des开始,des比大于src,所以不会发生覆盖问题。}
其他API暂时不许解释,这些API已经将这个数据结构讲清楚了。
作者在inset.c里面也写了许多测试代码,哈哈,看来都是需要测试的,作者估计写了好久也测试了好久,才确认这个写得没有问题。主要在于玩指针,玩内存。































还没有评论,来说两句吧...