Netty之ByteBuf
一、功能原理
ByteBuf是一个byte存放的缓冲区。
ByteBuf通过两个位置的指针来协助缓冲区的读写操作,读操作使用readIndex,写操作使用writeIndex。
+-------------------+------------------+------------------+| discardable bytes | readable bytes | writable bytes || | (CONTENT) | |+-------------------+------------------+------------------+| | | |0 <= readerIndex <= writerIndex <= capacity
discardable bytes 丢弃的读空间
readable bytes 可读空间
writeable bytes 可写空间
比如:
[java] view plain copy print ?
- ByteBuf heapBuffer = Unpooled.buffer();
System.out.println(heapBuffer);
ByteBuf heapBuffer = Unpooled.buffer();
System.out.println(heapBuffer);
结果:
[java] view plain copy print ?
UnpooledHeapByteBuf(ridx: 0, widx: 0, cap: 256)
UnpooledHeapByteBuf(ridx: 0, widx: 0, cap: 256)
ridx是readerIndex读取数据索引,位置从0开始
widx是writeIndex写数据索引,位置从0开始
cap是capacity缓冲区初始化的容量,默认256,可以通过Unpooled.buffer(8)设置,初始化缓冲区容量是8。
如果写入内容超过cap,cap会自动增加容量,但不能超过缓冲区最大容量maxCapacity。
[java] view plain copy print ?
- ByteBuf heapBuffer = Unpooled.buffer(8);
- System.out.println(“初始化:”+heapBuffer);
- heapBuffer.writeBytes(“测试测试测试”);
System.out.println(“写入测试测试测试:”+heapBuffer);
ByteBuf heapBuffer = Unpooled.buffer(8);
System.out.println(“初始化:”+heapBuffer);
heapBuffer.writeBytes(“测试测试测试”);
System.out.println(“写入测试测试测试:”+heapBuffer);
结果:
[java] view plain copy print ?
- 初始化:UnpooledHeapByteBuf(ridx: 0, widx: 0, cap: 8)
写入测试测试测试:UnpooledHeapByteBuf(ridx: 0, widx: 18, cap: 64)
初始化:UnpooledHeapByteBuf(ridx: 0, widx: 0, cap: 8)
写入测试测试测试:UnpooledHeapByteBuf(ridx: 0, widx: 18, cap: 64)
cap初始化8,增加到64
缓冲内容复制到字节数组
[java] view plain copy print ?
- //1、创建缓冲区
- ByteBuf heapBuffer = Unpooled.buffer(8);
- //2、写入缓冲区内容
- heapBuffer.writeBytes(“测试测试测试”.getBytes());
- //3、创建字节数组
- byte[] b = new byte[heapBuffer.readableBytes()];
- System.out.println(b[11]);
- //4、复制内容到字节数组b
- heapBuffer.readBytes(b);
- System.out.println(b[11]);
- //5、字节数组转字符串
- String str = new String(b);
System.out.println(str);
//1、创建缓冲区
ByteBuf heapBuffer = Unpooled.buffer(8);//2、写入缓冲区内容
heapBuffer.writeBytes(“测试测试测试”.getBytes());//3、创建字节数组
byte[] b = new byte[heapBuffer.readableBytes()];System.out.println(b[11]);
//4、复制内容到字节数组b
heapBuffer.readBytes(b);System.out.println(b[11]);
//5、字节数组转字符串
String str = new String(b);System.out.println(str);
结果:
[java] view plain copy print ?
- 0
- -107
测试测试测试
0
-107
测试测试测试
ByteBuf转ByteBuffer
[java] view plain copy print ?
ByteBuffer bb = heapBuffer.nioBuffer();
ByteBuffer bb = heapBuffer.nioBuffer();
ByteBuf的主要类继承关系图
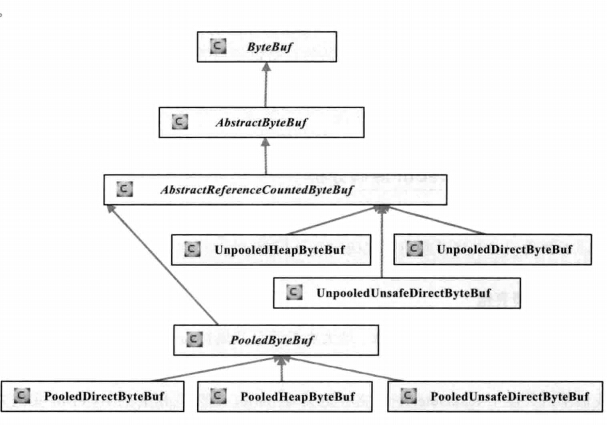
从内存分配的角度看,ByteBuf可以分为两类:
1、堆内存(HeapByteBuf)字节缓冲区:特点是内存的分配和回收速度快,可以被JVM自动回收;缺点就是如果进行Socket的IO读写,需要额外做一次内存复制,将堆内存对应的缓冲区复制到内核Channel中,性能会有一定程度的下降
2、直接内存(DirectByteBuf) 字节缓冲区:非堆内存,它在对外进行内存分配,相比于堆内存,它的分配和回收速度会慢一些,但是将它写入或者从Socket Channel中读取时,由于少一次内存复制,速度比堆内存快
Netty的最佳实践是在I/O通信线程的读写缓冲区使用DirectByteBuf,后端业务消息的编解码模块使用HeapByteBuf,这样组合可以达到性能最优。
ByteBuf的四种声明方式
[java] view plain copy print ?
- ByteBuf heapBuffer = Unpooled.buffer();
- System.out.println(heapBuffer);
- ByteBuf directBuffer = Unpooled.directBuffer();
- System.out.println(directBuffer);
- ByteBuf wrappedBuffer = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(new byte[128]);
- System.out.println(wrappedBuffer);
- ByteBuf copiedBuffer = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(new byte[128]);
System.out.println(copiedBuffer);
ByteBuf heapBuffer = Unpooled.buffer();
System.out.println(heapBuffer);ByteBuf directBuffer = Unpooled.directBuffer();
System.out.println(directBuffer);ByteBuf wrappedBuffer = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(new byte[128]);
System.out.println(wrappedBuffer);ByteBuf copiedBuffer = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(new byte[128]);
System.out.println(copiedBuffer);
结果:
[java] view plain copy print ?
- UnpooledHeapByteBuf(ridx: 0, widx: 0, cap: 256)
- SimpleLeakAwareByteBuf(UnpooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf(ridx: 0, widx: 0, cap: 256))
- UnpooledHeapByteBuf(ridx: 0, widx: 128, cap: 128/128)
- UnpooledHeapByteBuf(ridx: 0, widx: 128, cap: 128/128)



































还没有评论,来说两句吧...