springmvc源码解析
总结:
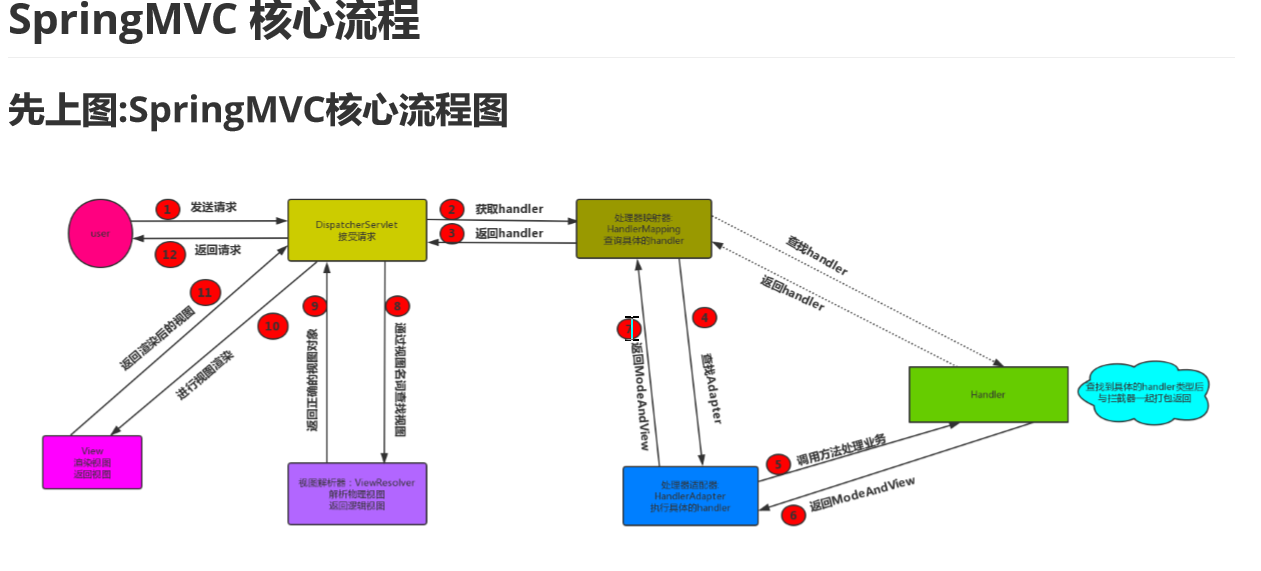
首先请求进入DispatcherServlet 由DispatcherServlet 从HandlerMappings中提取对应的Handler
此时只是获取到了对应的Handle,然后得去寻找对应的适配器,即:HandlerAdapter
拿到对应HandlerAdapter时,这时候开始调用对应的Handler处理业务逻辑了(这时候实际上已经执行完了我们 的Controller) 执行完成之后返回一个ModeAndView
这时候交给我们的ViewResolver通过视图名称查找出对应的视图然后返回
最后 渲染视图 返回渲染后的视图 —>响应请求
实例:
在pom.xml文件上添加spring-mvc的依赖
<dependencies><!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId><version>5.0.8.RELEASE</version></dependency><!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.servlet/javax.servlet-api --><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet</groupId><artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId><version>3.1.0</version><scope>provided</scope></dependency></dependencies>添加App类import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** @author wufei* @create 2018-12-24 9:37**/@ComponentScan("com.wf.spring.mvc")@Configurationpublic class App {}
添加DispatcherServlet类
/*** 添加DispatcherServlet* @author wufei* @create 2018-12-24 9:47**/public class MyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {@Overridepublic void onStartup(ServletContext servletCxt) {// Load Spring web application configurationAnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();ac.register(AppConfig.class);ac.refresh();// Create and register the DispatcherServletDispatcherServlet servlet = new DispatcherServlet(ac);ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletCxt.addServlet("app", servlet);registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);registration.addMapping("/app/*");}}/*** 第一种方式注册controller* 使用bean的形成注册controller* @author wufei* @create 2018-12-24 9:58**/@Component("/test")public class BeanController implements Controller{@Overridepublic ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) {System.out.println("test");return null;}}/*** 第二种方式注册controller* annotation形式注册controller* RequestMappingHandlerMapping* @author wufei* @create 2018-12-24 15:10**/@Controllerpublic class AnnotationController {@RequestMapping("/test1")public String test(){System.out.println("test1");return "test1";}}
源码分析:
首先我们看下DispatcherServlet继承关系图:
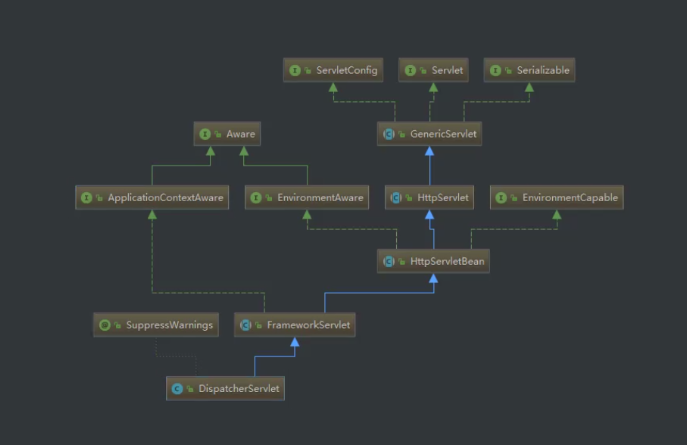
从图中可以看出DispatcherServlet最终继承的是个HttpServlet,即DispatcherServlet就是个Servlet。由此我们可以找到Servlet的doGet、doPost、service重要方法。在FrameworkServlet类中可以看到
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());if (httpMethod != HttpMethod.PATCH && httpMethod != null) {super.service(request, response);} else {this.processRequest(request, response);}}protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {this.processRequest(request, response);}protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {this.processRequest(request, response);}
从三个方法上可以看出,都是调用了processRequest(request, response);方法,然后我们继续跟踪processRequest方法上
我们可以看到doService方法
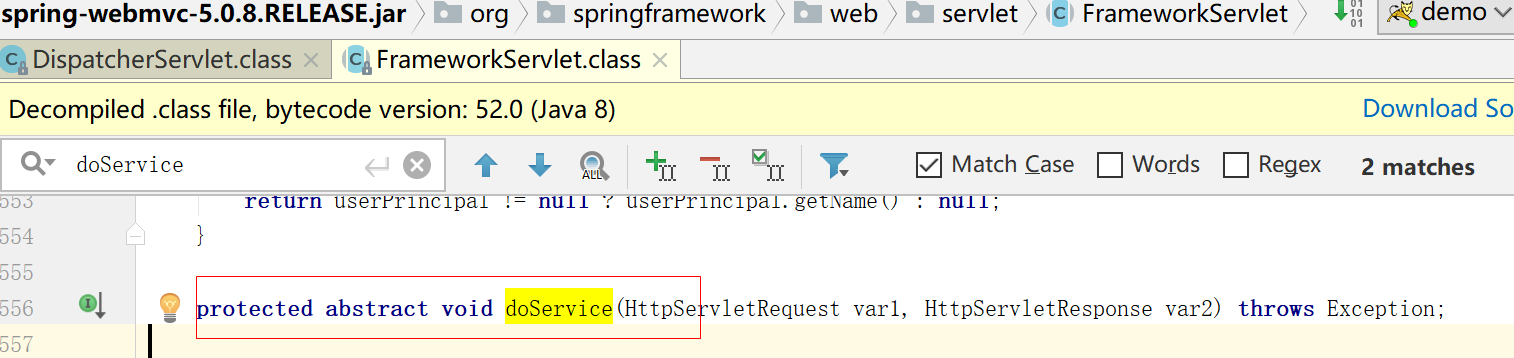
该方法是个抽象方法,由DispatcherServlet类实现该方法的具体逻辑。发现有个重要的关键代码方法this.doDispatch(request, response);
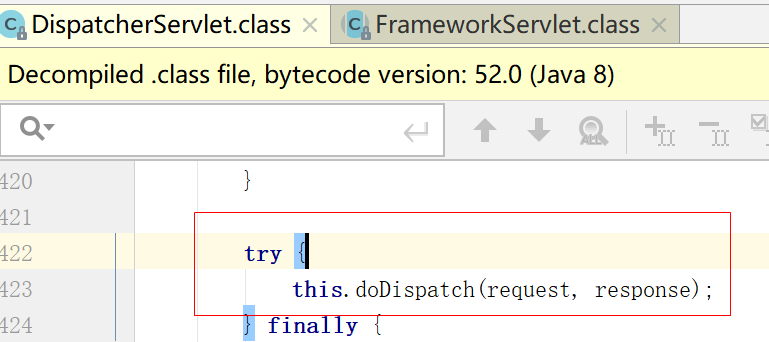
进入doDispatch方法里面
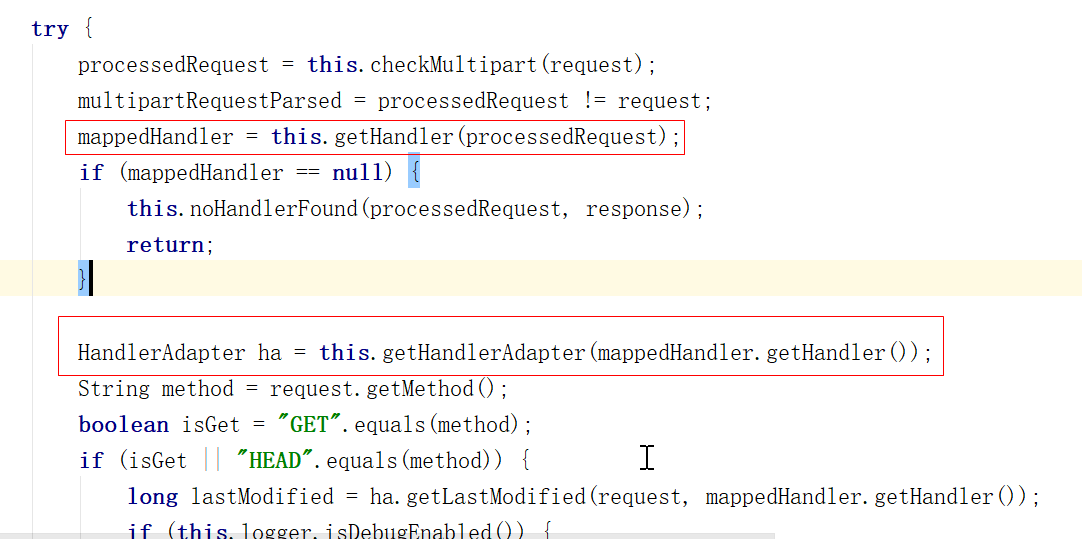
看到两个最重要的方法,getHandler(处理器)和getHandlerAdapter(适配器)
问题1 handler从哪来的呢
我们先查看getHandler方法里面的代码
@Nullableprotected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {if (this.handlerMappings != null) {Iterator var2 = this.handlerMappings.iterator();while(var2.hasNext()) {HandlerMapping hm = (HandlerMapping)var2.next();if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {this.logger.trace("Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + this.getServletName() + "'");}HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);if (handler != null) {return handler;}}}return null;}是在迭代handlerMappings,而handlerMappings是个List集合@Nullableprivate List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings;
handlerMapping存放两个值,一个是org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,一个是org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping
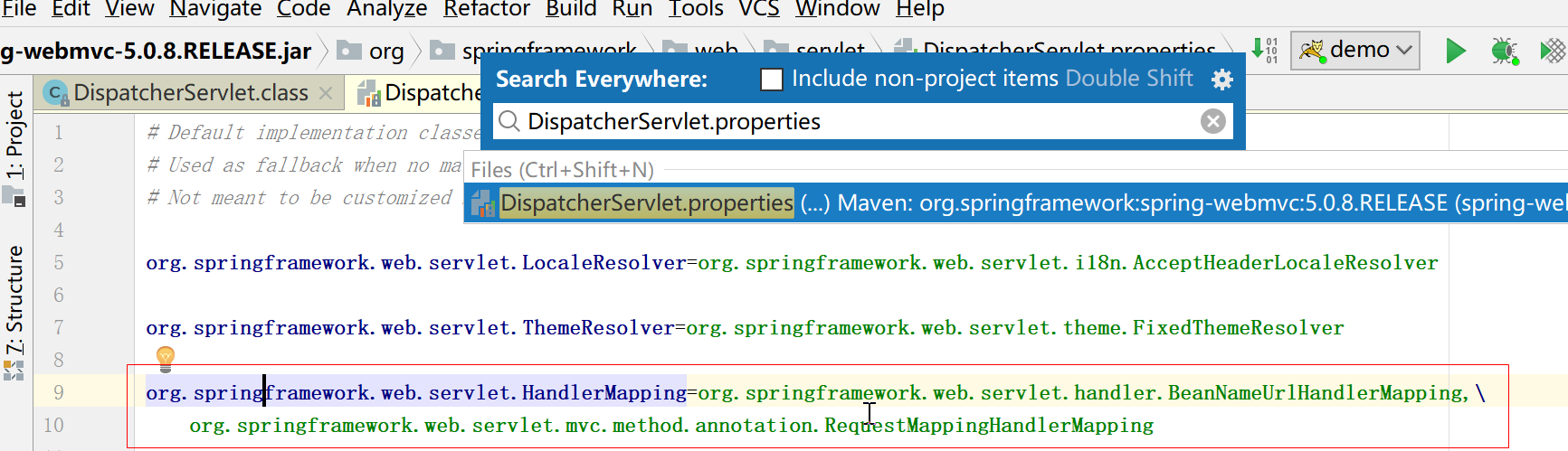
问题2 handlerMapping是什么?
我们端个点,查看下具体是什么
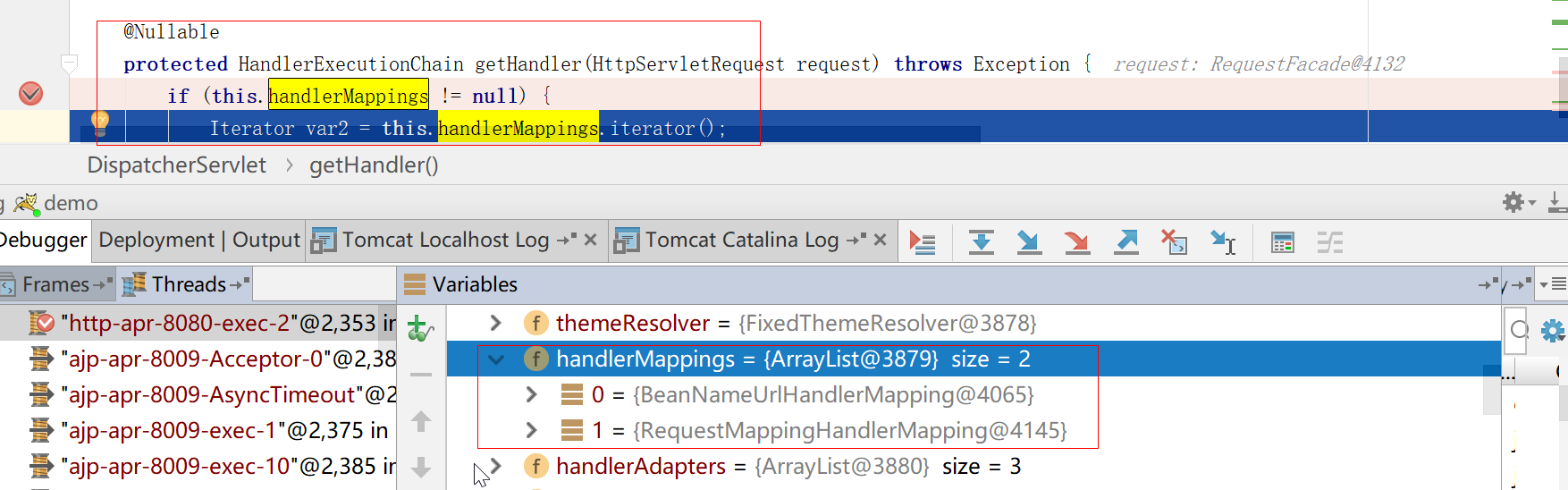
如图所示:是两个我们不认识的东西,我们继续往下看,
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);if (handler != null) {return handler;}
从mappings获取一个handler,然后返回了。

我们发现 handler就是我们的controll类的方法,我们以Bean的形式注册的Controller 可以从这个BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping里面 获取到对应的Handler ; 这里 我们是不是对于这个HandlerMapping有了懵懂的了解了
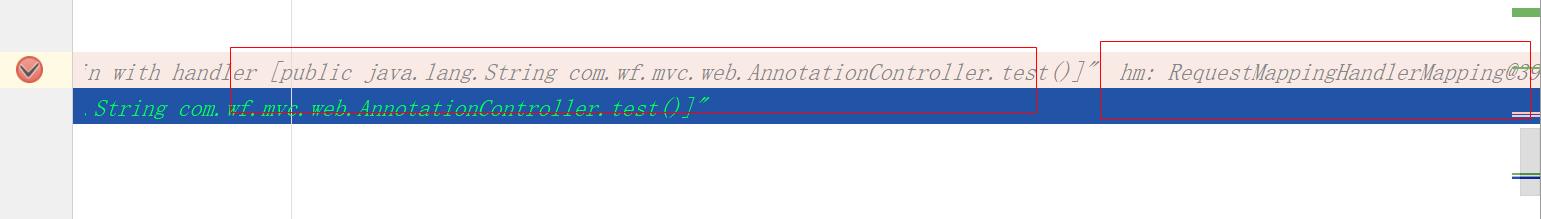
下面我们以Annotation方式注册的Controller,就会被第二个RequestMappingHandlerMapping获取对应的handler。如图所示:
问题3 什么是适配器
首先我们跟踪下代码
HandlerAdapter ha = this.getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {Iterator var2 = this.handlerAdapters.iterator();while(var2.hasNext()) {HandlerAdapter ha = (HandlerAdapter)var2.next();if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {this.logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]");}if (ha.supports(handler)) {return ha;}}}throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler + "]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");}
从代码上可以看出是迭代handlerAdapters,而这个从哪获取到的呢?也是从配置文件上获取的DispatcherServlet.properties
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
使用Annotation方式注册的Controller使用的是RequestMappingHandlerAdapter适配器

使用bean的形成注册controller使用的是SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter适配器
最后执行mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); 执行业务逻辑了。输出了test1
然后返回mv,mv就是试图了,然后渲染页面。
适配器就是对应不同的handler有不同的解决方案
总结
其实我们的SpringMVC关键的概念就在于Handler(处理器) 和Adapter(适配器)
通过一个关键的HandlerMappings 找到合适处理你的Controller的Handler 然后再通过HandlerAdapters找到一 个合适的HandlerAdapter 来执行Handler即Controller里面的逻辑。 最后再返回ModlAndView…





























还没有评论,来说两句吧...