Linux设备模型--设备
linux中每个设备由一个 struct device描述:
- struct device {
- struct klist klist_children;
- struct klist_node knode_parent; /* node in sibling list */
- struct klist_node knode_driver;
- struct klist_node knode_bus;
- struct device *parent;
- struct kobject kobj;
- char bus_id[BUS_ID_SIZE]; /* 在总线上唯一标识该设备的字符串position on parent bus */
- unsigned uevent_suppress:1;
- const char *init_name; /* initial name of the device */
- struct device_type *type;
- struct semaphore sem; /* semaphore to synchronize calls to
- * its driver.
- */
- struct bus_type *bus; /*设备所在总线 type of bus device is on */
- struct device_driver *driver; /* 管理该设备的驱动which driver has allocated this
- device */
- void *driver_data; /* 该设备驱动使用的私有数据成员data private to the driver */
- void *platform_data; /* Platform specific data, device
- core doesn’t touch it */
- struct dev_pm_info power;
- #ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
- int numa_node; /* NUMA node this device is close to */
- #endif
- u64 *dma_mask; /* dma mask (if dma’able device) */
- u64 coherent_dma_mask;/* Like dma_mask, but for
- alloc_coherent mappings as
- not all hardware supports
- 64 bit addresses for consistent
- allocations such descriptors. */
- struct device_dma_parameters *dma_parms;
- struct list_head dma_pools; /* dma pools (if dma’ble) */
- struct dma_coherent_mem *dma_mem; /* internal for coherent mem
- override */
- /* arch specific additions */
- struct dev_archdata archdata;
- dev_t devt; /* dev_t, creates the sysfs “dev” */
- spinlock_t devres_lock;
- struct list_head devres_head;
- struct klist_node knode_class;
- struct class *class;
- struct attribute_group **groups; /* optional groups */
- void (*release)(struct device *dev);
- };
- struct device_private {
- struct klist klist_children;
- struct klist_node knode_parent;
- struct klist_node knode_driver;
- struct klist_node knode_bus;
- struct device *device;
- };
设备属性由device_attribute描述 - struct device_attribute {
- struct attribute attr;
- ssize_t (*show)(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
- char *buf);
- ssize_t (*store)(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
- const char *buf, size_t count);
- };
可以看出device结构体中也包含了一个kobject对象
注册一个设备
int device_register(struct device *dev)
删除一个设备
void device_unregister(struct device *dev)
注意:一条总线本身也是一个设备,也必须按设备注册,见上篇 Linux设备模型--总线
创建属性
int device_create_file(struct device *dev,struct device_attribute *attr)
删除属性
int device _remove_file(struct device *dev,struct device_attribute *attr)
添加设备例子,添加到前面创建的my_bus总线上:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
MODULE_AUTHOR(“David Xie”);
MODULE_LICENSE(“Dual BSD/GPL”);
extern struct device my_bus;
extern struct bus_type my_bus_type;
/* Why need this ?*/
static void my_dev_release(struct device *dev)
{
}
struct device my_dev = {
.bus = &my_bus_type,//设备所在总线
.parent = &my_bus,//设备父设备,这里就是 my_bus总线
.release = my_dev_release,
};
/*
* Export a simple attribute.
*/
static ssize_t mydev_show(struct device *dev, char *buf)
{
return sprintf(buf, “%s\n”, “This is my device!”);
}
static DEVICE_ATTR(dev, S_IRUGO, mydev_show, NULL);
static int __init my_device_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
/\* 初始化设备 \*/
strncpy(my_dev.bus_id, “my_dev”, BUS_ID_SIZE);
/\*注册设备\*/
device_register(&my_dev);
/*创建属性文件*/
device_create_file(&my_dev, &dev_attr_dev);
return ret;
}
static void my_device_exit(void)
{
device_unregister(&my_dev);
}
module_init(my_device_init);
module_exit(my_device_exit);
注册一个bus_id即名字为my_dev的设备,该设备的bus成员指向上一步创建的my_bus_type总线,parent成员指向上一步创建的my_bus总线设备。
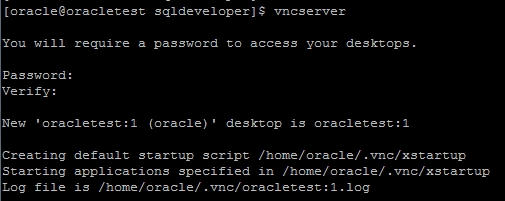
测试结果:
![Image 1][]
运行程序:
ls /sys/bus/my_bus/device
my_dev
[Image 1]:


























![sublime text3 提示[WinError 2] 系统找不到指定的文件 sublime text3 提示[WinError 2] 系统找不到指定的文件](https://image.dandelioncloud.cn/images/20221021/7c2d64239b9e47b8999ee78cb4480121.png)




还没有评论,来说两句吧...