常用数据库常用命令使用
SQL:Structured Query Language,结构化查询语言(数据以查询为主,99% 都是在进行查询操作)。
SQL 主要分为三种:
• DDL:Data Definition Language,数据定义语言,用来维护存储数据的结构(数据库、表),代表指令为create、drop和alter等。
• DML:Data Manipulation Language,数据操作语言,用来对数据进行操作(表中的内容)代表指令为insert、delete和update等,不过在 DML 内部又单独进行了一个分类,即 DQL(Data Query Language),数据查询语言,代表指令为select.
• DCL:Data Control Language,数据控制语言,主要是负责(用户)权限管理,代表指令为grant和revoke等。
SQL 是关系型数据库的操作指令,是一种约束,但不强制,类似于 W3C,因此这意味着:不同的数据库产品(如 Oracle 和 MySQL)内部可能会有一些细微的区别。
在 SQL 中,将数据类型分成了三大类,分别为:数值型、字符串型和日期时间型。
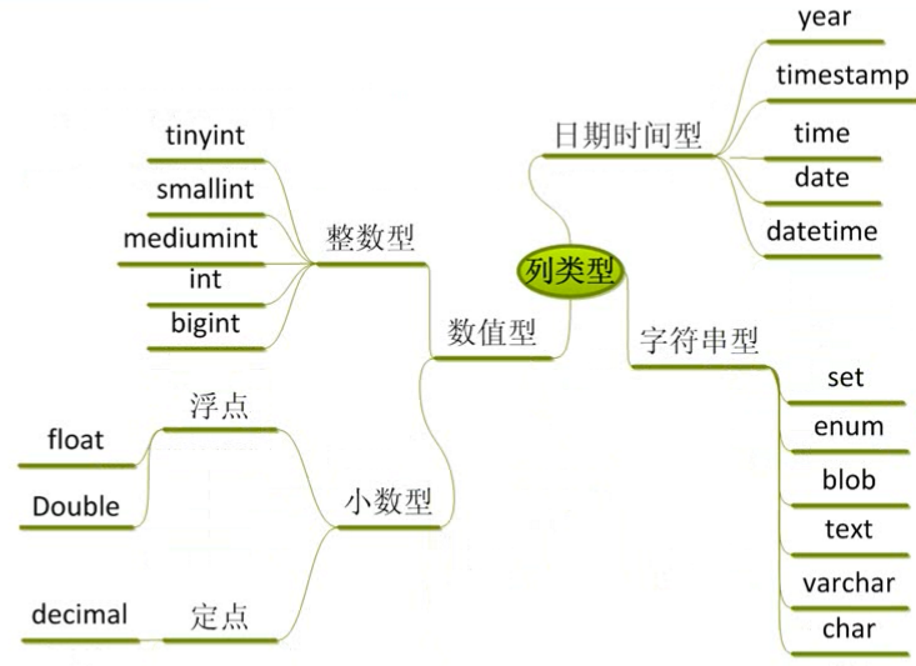
Oracle常用命令的使用:(以scott用户的默认创建的表做测试)
命令图示:
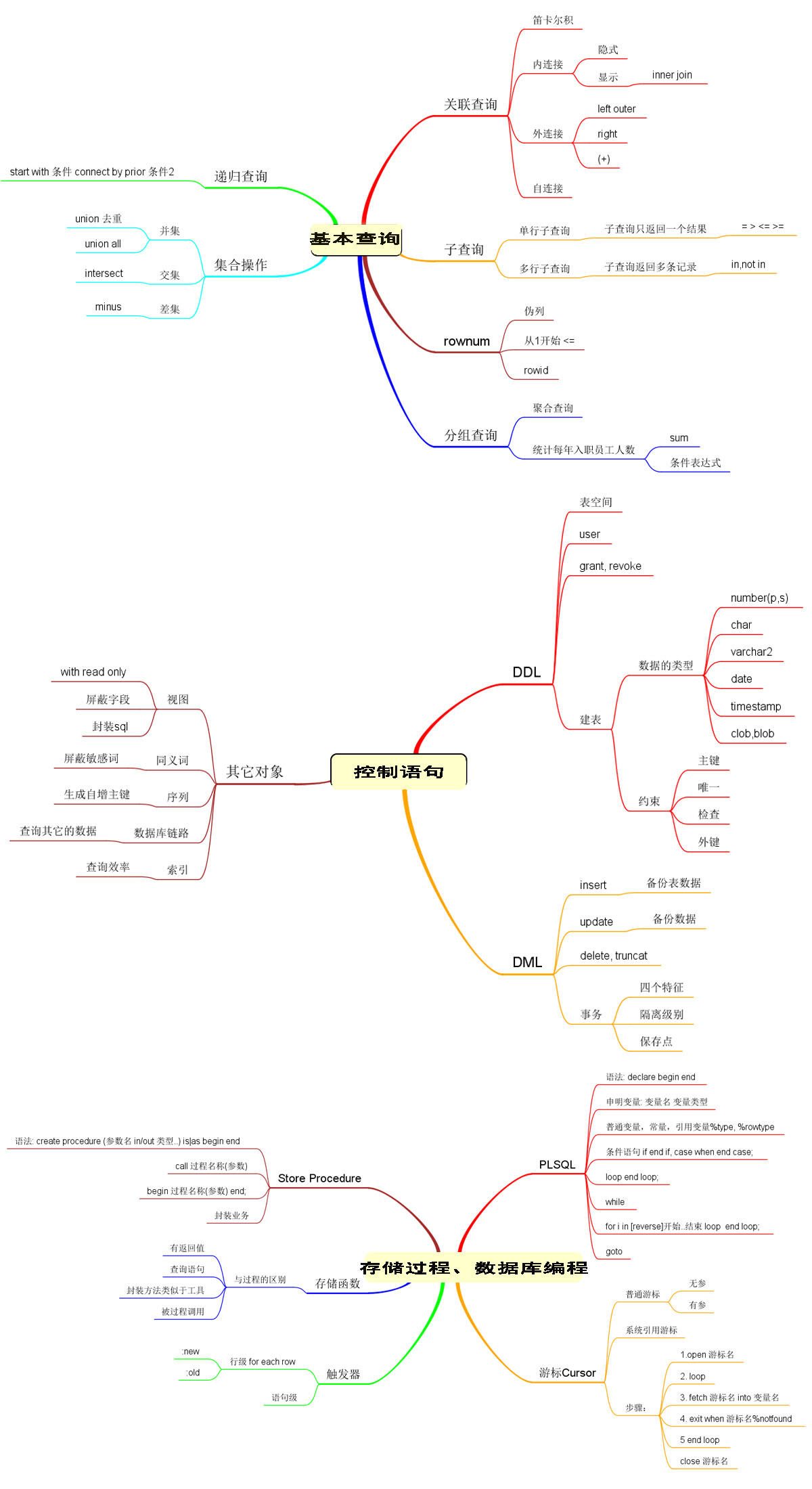
基本查询:
/\*\*EMP雇员--DEPT部门--SALGEADE销售分数\*\*/
select *from emp;
select * from dept;
select * from salgrade;
/**分组和聚合函数一起用**/
select distinct count(*) as empnum from emp group by deptno order by empnum desc;
/**别名查询(如果有特殊字符用双引号)和去重查询**/
select empno “ 雇员 编号 “, ename “ 雇员 名称 “ from emp;
select distinct deptno from emp;
/**对结果做运算**/
select empno,ename,sal+999 from emp;
select * from emp where not JOB = ‘CLERK’;
select * from emp where sal in (800,1000,1200,1400,1600,1800);
select * from emp where comm is not null;
select * from emp where comm is null;
select * from emp where sal between 1000 and 2900;
/**模糊查询**/
select * from emp where ename like ‘%T_‘;
/**带有特殊符号的查询使用转义字符,关键字指出转义符号**/
select * from emp where ename like ‘%\%R%’ escape ‘\‘;
/**空值处理、空值参与的运算都会导致结果为空**/
select (sal+nvl(comm,0))*12 年薪 from emp where empno = 7369;
select * from emp order by comm desc nulls first;/**空值排在前面**/
select * from emp order by comm desc nulls last;/**空值排在后面**/
/**常用函数—dual 虚表, 意义:补全语法**/
replace,substr,length,||,to\_char,to\_date,round,trunc,mod,decode,case when,nvl,Coalesce,count,max,min,avg,sum
/**字符串的操作**/
select substr(‘你好中国人’,0,2) from dual;
select replace(‘你好中国人’,’中国’,’外国’) from dual;
select length(‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz’) from dual;
select concat(‘你好’,’中国人’) from dual;/**或者||**/select ‘你好’ || ‘中国人’ from dual;
/**日期**/
select round(months_between(sysdate,hiredate)/12) from emp;/**round 返回当前值四舍五入后的值**/
select months_between(to_date(‘1981/1/1’,’yyyy.mm.dd’),to_date(‘1978/1/1’,’yyyy.mm.dd’))from emp;
select*fromempwherehiredate>to_date(‘1981/1/1’,’yyyy.mm.dd’)and hiredate<to_date(‘1981/12/31’,’yyyy.mm.dd’)
/**数据处理**/
/**round四舍五入**/
select round(4.8) from dual;
select round(4.1) from dual;
/**trunc截断,舍弃小数部分**/
select trunc(3.141592654) from dual;
/**ceil向上取整**/
select ceil(3.15) from dual;
/**floor向下取整**/
select floor(3.9898) from dual;
/**绝对值**/
select abs(-56.5) from dual;
/**取余**/
select mod(25,4) from dual;
/**转换函数,orable不提供日期和字符串的自动转化**/
select to_char(sysdate) from dual;
select to_date(‘2018/3/20’,’yyyy,mm.dd’) from dual;
select to_number(‘12315’) from dual;
/**通用函数**/
select concat(‘123’,’456’) from dual;
/**nvl—第一个值不为空取之,若为空,则取第二个**/
select nvl(1,null) from dual;
/**nullif—相等则为null,否则取第一个**/
select nullif(4,1) from dual;
/**nvl2—如果第一个不为空则选择第二个,否则选择第三个**/
select nvl2(1,2,3) from dual;
/**coalesce—返回第一个不为空的值**/
select coalesce(null,null,null,9,null,8) from dual;
/**条件表达式**/
select * from emp;
select ename,(case job when ‘CLERK’ then ‘文员’
when ‘SALESMAN’ then ‘销售员’
when ‘MANAGER’ then ‘管理员’
else ‘其他’ end) from emp;
/**decode—特有关键字**/
select decode(job,’CLERK’,’文员’,’SALESMAN’,’销售员’,’MANAGER’,’管理员’) from emp;
/**多行函数**/
—分组函数
—(where与having区别
/**where 是在from后面, 在group by 前。where 过滤的是物理表(from)中的数据,先过滤再分组
having 是在group by 后面, 过滤分组后的数据**/
select * from emp;
select deptno,count(1) from emp group by deptno;
select deptno,count(1) from emp group by deptno having deptno = 10;
—聚合函数
—count,max,min,avg,sum
select count(1) from emp;
select max(sal) from emp;
select min(sal) from emp;
select avg(sal) from emp;
select sum(comm) from emp;
/**练习**/
select * from emp;
select ename
/**————————————————————-**/
—部门员工数量大于三
select count(1) from emp group by deptno having count(1)>3;
select * from emp
select e1.empno,e1.ename,e1.hiredate from emp e1,emp e2 where e1.empno = e2.mgr
/**内连接查询**/
—隐式内连接(雇佣表和部门表)
select * from emp e,dept d where e.deptno = d.deptno;
—显式内连接
select * from emp e join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;
/**外连接**/
—左外连接
select * from emp e left outer join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;
select * from dept;select * from emp;
—右外连接
select * from emp e right outer join dept d on d.deptno = e.deptno;
—Orable外连接(+号连接的是外表)
select * from emp e,dept d where e.deptno = d.deptno(+);
select * from emp e,dept d where e.deptno(+) = d.deptno;
/**自关联**/
select e.empno,e.ename,e.mgr,m.ename from emp e, emp m where e.mgr = m.empno;
/**子查询**/
select * from emp where sal = (select max(sal) from emp);
select * from emp where sal>(select sal from emp where empno = 7654) and job = (select job from emp where empno = 7788) and empno <> 7788;
select * from (select deptno,min(sal) from emp group by deptno) e,dept where e.deptno = dept.deptno
/**多行子查询**/
select * from emp where empno in (select distinct mgr from emp);
select * from emp where empno not in (select distinct mgr from emp where mgr is not null);
/**exists**/
select * from emp where exists(select * from emp where emp.deptno = 10);
select avg(sal) from emp e where e.deptno = (select min(deptno) from emp)
/**集合**/
—union
—union all
--row是一个伪列,rowid是数据存储的物理地址select rownum,rowid,ename from emp;--找出工资表中工资最高的前三名select rownum,ename,sal from emp order by sal desc;--要先按照降序排序后再使用伪列生成的序号进行显示select rownum,ename,sal from (select ename,sal from emp order by sal desc) where rownum<=3;select rownum,t.\* from (select ename,sal from emp order by sal desc) t where rownum<=3;/\*\*Oracle的分页补充:查询员工表中的第5条记录到第10条记录.<=5 and >=10\*/--rownum--每当按照条件查询出一条记录,则当前rownum+1生成对应的序号加到当前记录上,但是如果当前没有查询出满足条件的结果时,rownum当然不会自动增长了.rownum从1开始select \* from ( select rownum rn,e.\* from emp e where rownum<=10) t where t.rn>=5;/\*\*找出员工表中薪水大于本部门平均薪水的员工信息分析:部门的平均薪水\*/select \* from emp e where e.sal>(select avg(sal) from emp);/\*\*统计每年入职员工的个数分析:算出年 to\_char(hiredate,'yyyy')count, 按年分组\*/select to\_char(hiredate,'yyyy') 年份,count(to\_char(hiredate,'yyyy')) 数量 from emp group by to\_char(hiredate,'yyyy') order by 年份;--(EXTRACT:截取日期类型对应的部分)语法如下:--EXTRACT (-- \{ YEAR | MONTH | DAY | HOUR | MINUTE | SECOND \}-- | \{ TIMEZONE\_HOUR | TIMEZONE\_MINUTE \}-- | \{ TIMEZONE\_REGION | TIMEZONE\_ABBR \}select extract(year from hiredate ) 年份,count(extract (year from hiredate)) 数量 from emp group by extract(year from hiredate) order by 年份;select extract(year from hiredate ) 年份,count(1) 数量 from emp group by extract(year from hiredate) order by 年份;--行列互换--(重要)selectsum(decode(t.y,'1980',t.c,0)) "1980",sum(decode(t.y,'1981',t.c,0)) "1981",sum(decode(t.y,'1982',t.c,0)) "1982",sum(decode(t.y,'1987',t.c,0)) "1987",count(1) total from(select extract(year from hiredate ) y,count(1) c from emp group by extract(year from hiredate) order by y) t;--集合的运算(并、交、差)/\*\*select后面的列的类型,顺序必须一致运用场景:多张表的结果集合运算并集: union 去重复union all 所有交集: intersect差集: minus\*\*/select \* from emp union select \* from emp;select \* from emp union all select \* from emp;--工资大于1500,或者是20部门下的员工select \* from emp where sal>1500 or deptno = 20;select \* from emp where sal>1500unionselect \* from emp where deptno = 20;**控制语句:**
--创建表空间
create tablespace yang
datafile ‘c:\yang.dbf’
size 50M
autoextend on
next 10M ;
—给用户设置创建的表空间
alter user yanghao identified by yanghao default tablespace yang;
—查看用户的表空间
select username, default_tablespace from user_users;
—创建一张用户账号表
create table counts (id number(10) primary key,username varchar2(20),password varchar2(20),description clob);
—删除表
drop table counts;
—插入数据
insert into counts values(1,’1’,’hahaha1’,’good1 ideas’);
insert into counts values(2,’2’,’hahaha2’,’good2 ideas’);
insert into counts values(3,’3’,’hahaha3’,’good3 ideas’);
insert into counts values(4,’4’,’hahaha4’,’good4 ideas’);
insert into counts values(5,’5’,’hahaha5’,’good5 ideas’);
insert into counts values(6,’6’,’hahaha6’,’good6 ideas’);
—查看表数据
select * from counts;
—创建当前操作的一个保存点(方便回滚到固定的保存状态)
savepoint a_point;
rollback to a_point;
commit;
—创建一个counts表的试图,只显示当前1~3标号的用户
create or replace view count_view as
select * from counts where id<=3 with read only;
—查看当前的视图
select * from count_view;
—事务
—4个特性(ACID)
—A: 原子性, 不可再分割
—C: 一致性,要么成功,要么失败
—I: 隔离性 (脏读,不可重复读(update),虚/幻读(insert,delete))
—D: 持久化性, 事务一旦提交,就会保存到磁盘中
—MySql支持的事务级别有哪些?
-可重复读(Repeatable Read,默认),提交读(Read Committed),序列化(Serializable), 未提交读(Read Uncommmited)
—Oracle支持的事务级别
-- Read Committed(默认), Serializable, read only--序列数据库提供一种数值类型,且按一定规则自动增长的序号 场景:需要自动增长主键,或需要自动增长的序号--创建自定义的序列create sequence incre\_keystart with 1minValue 1maxValue 10cycleincrement by 1cache 3--使用序列(在一次session累加)create table test(testId number(10),name varchar2(10));insert into test values(incre\_key.nextval,'haha');select incre\_key.currval from dual;drop table test;/\*\*索引是什么? 一组数据库已经算好了的数据结构作用: 提交查询效率,缺点:插入与删除的效率会降低使用 create index 名称 on table(列名,...), bitmap, btree如果有多个列,就叫复合索引(索引的列必须都用上时,索引才生效)一个表最多不要超过5个索引\*/--索引的使用--1. 数据量大的表--2. 经常执行表更新的操作(insert,update,delete), 不适合索引--3. 索引的列不要出现空值--4. 经常查询条件的列或排序的列可以建索引--索引的失效:-- not, in, is not, is nullselect \* from stu where sname='学生第1学生';--9.860--创建索引create index index\_stu\_sname on stu(sname);--再查询一次当前的数据时间减少select \* from stu where sname='学生第2学生';--0/\*\*触发器: 它是一段写好的plsql语句行级:影响了多少条记录,就触发多少次语句:不影响了多少记录,只触发一次create or replace triggerbefore|afteron insert|update|deletefor each row --代行级begin--代码end;作用: 记录日志,同步数据\*/create or replace trigger pre\_insertbeforeinsert on countsbeginraise\_application\_error(-20111,'周三不能插入员工信息');end;insert into counts values(88,'test','test','test');/\*\*移除触发器\*\*/drop trigger pre\_insert;/\*\*同义词:reate synonym 名字 for 表作用: 简化编写,屏蔽表名的含义, 数据库同步ETL\*/select \* from user\_tables;create synonym students for stu;select \* from students;select \* from counts;存储结构、数据库编程:/\*\*pl/sql编程\*\*/declarei number(10):=incre\_key.nextVal;name counts.username%type;psd counts.password%type;beginname:='test';psd:='test'insert into counts values(i,name,psd,'test');commit;dbms\_output.put\_line('name: '||test||'psd: 'psd);end;/\*\*游标的使用\*\*/--使用游标输出emp表中的员工编号和姓名declarecursor pc is select \* from scott.emp;--游标(返回整个emp表的数据)pemp scott.emp%rowtype;beginopen pc;--开启游标loopfetch pc --调用一次游标into pemp; --把游标当前行的结果存到变量pemp中dbms\_output.put\_line(pemp.empno||' '||pemp.ename);exit when pc%notfound;end loop;close pc;--关闭游标end;/\*\*例外/异常\*\*/declarepnum number;pnum2 varchar(10);beginpnum:=1/0;exceptionwhen zero\_divide thendbms\_output.put\_line('除零异常');when value\_error thendbms\_output.put\_line('数值转换异常');when others thendbms\_output.put\_line('其他异常');end;



































还没有评论,来说两句吧...