Tensorflow学习知识点记录
Tensorflow
- 快速理解tf.Session()
- Tensorflow 中使用 Variable
- Placeholder 传入值
- tensorflow reduction_indices理解
- An overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms 加速神经网络训练 (Speed Up Training)
快速理解tf.Session()
Session 是 Tensorflow 为了控制和输出文件的执行的语句. 运行 session.run() 可以获得你要得知的运算结果, 或者是你所要运算的部分。
import tensorflow as tf# create two matrixesmatrix1 = tf.constant([[3,3]])matrix2 = tf.constant([[2],[2]])product = tf.matmul(matrix1,matrix2)
因为 product 不是直接计算的步骤, 所以我们会要使用 Session 来激活 product 并得到计算结果. 有两种形式使用会话控制 Session 。
# method 1sess = tf.Session()result = sess.run(product)print(result)sess.close()# [[12]]# method 2with tf.Session() as sess:result2 = sess.run(product)print(result2)# [[12]]
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40458355/article/details/80351641
Tensorflow 中使用 Variable
在 Tensorflow 中,定义了某字符串是变量,它才是变量,这一点是与 Python 所不同的。
定义语法:state = tf.Variable()
import tensorflow as tfstate = tf.Variable(0, name='counter')# 定义常量 oneone = tf.constant(1)# 定义加法步骤 (注: 此步并没有直接计算)new_value = tf.add(state, one)# 将 State 更新成 new_valueupdate = tf.assign(state, new_value)
如果你在 Tensorflow 中设定了变量,那么初始化变量是最重要的!!所以定义了变量以后, 一定要定义 init = tf.initialize_all_variables() .
tf.global_variables_initializer()
到这里变量还是没有被激活,需要再在 sess 里, sess.run(init) , 激活 init 这一步.
# 如果定义 Variable, 就一定要 initialize# init = tf.initialize_all_variables() # tf 马上就要废弃这种写法init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # 替换成这样就好# 使用 Sessionwith tf.Session() as sess:sess.run(init)for _ in range(3):sess.run(update)print(sess.run(state))
注意:直接 print(state) 不起作用!!
一定要把 sess 的指针指向 state 再进行 print 才能得到想要的结果!
Placeholder 传入值
这一次我们会讲到 Tensorflow 中的 placeholder , placeholder 是 Tensorflow 中的占位符,暂时储存变量.
Tensorflow 如果想要从外部传入data, 那就需要用到tf.placeholder(), 然后以这种形式传输数据sess.run(***, feed_dict={input: **}).
import tensorflow as tf# 在 Tensorflow 中需要定义 placeholder 的 type ,一般为 float32 形式input1 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)input2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)# mul = multiply 是将input1和input2 做乘法运算,并输出为 outputouput = tf.multiply(input1, input2)
接下来, 传值的工作交给了sess.run() , 需要传入的值放在了feed_dict={}并一一对应每一个 input. placeholder 与 feed_dict={} 是绑定在一起出现的。
with tf.Session() as sess:print(sess.run(ouput, feed_dict={input1: [7.], input2: [2.]}))# [ 14.]
tensorflow reduction_indices理解
在tensorflow的使用中,经常会使用tf.reduce_mean,tf.reduce_sum等函数,在函数中,有一个reduction_indices参数,表示函数的处理维度,直接上图,一目了然:tf.reduce_mean求平均值 tf.reduce_sum 求和
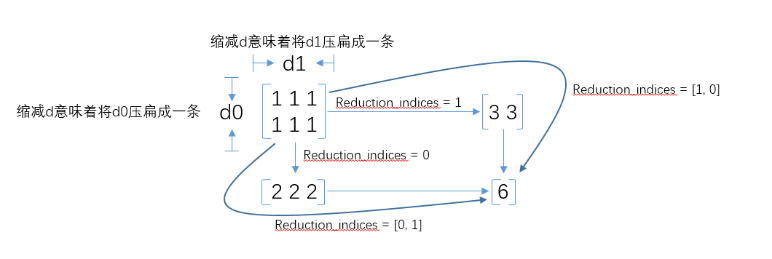
需要注意的一点,在很多的时候,我们看到别人的代码中并没有reduction_indices这个参数,此时该参数取默认值None,将把input_tensor降到0维,也就是一个数。
An overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms 加速神经网络训练 (Speed Up Training)
http://ruder.io/optimizing-gradient-descent/
这篇文章探讨了有多少最流行的基于梯度的优化算法实际工作。
Table of contents:
Gradient descent variantsBatch gradient descentStochastic gradient descentMini-batch gradient descentChallengesGradient descent optimization algorithmsMomentumNesterov accelerated gradientAdagradAdadeltaRMSpropAdamAdaMaxNadamAMSGradVisualization of algorithmsWhich optimizer to choose?Parallelizing and distributing SGDHogwild!Downpour SGDDelay-tolerant Algorithms for SGDTensorFlowElastic Averaging SGDAdditional strategies for optimizing SGDShuffling and Curriculum LearningBatch normalizationEarly StoppingGradient noiseConclusionReferences



































还没有评论,来说两句吧...