使用face_recognition进行人脸特征检测
效果图
调用face_recognition.face_landmarks()方法即可得到人脸特征点, 返回一个字典, 下图是返回的数据, 包括chin(下巴), left_eye(左眼)等.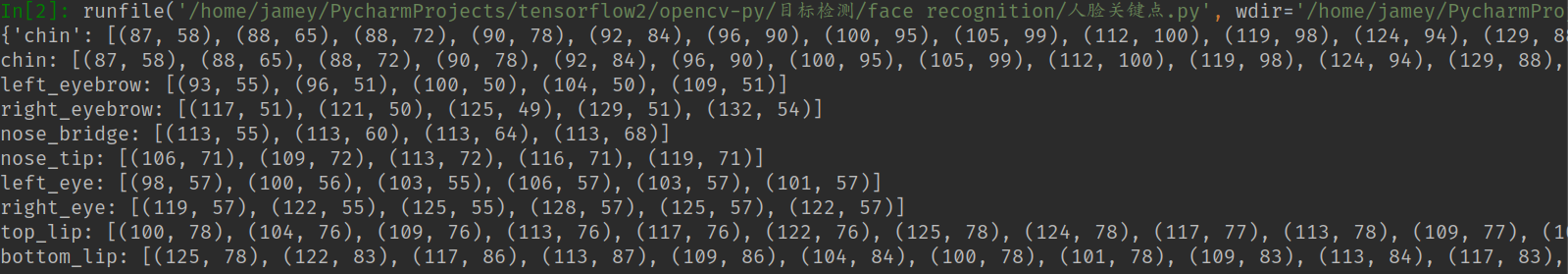
我画了两种图, 一种是遍历所有的点, 直接给点画图的图(点用实心圆绘制). 第二个是单独画下巴, 连成线, 用的是polylines方法.
我是4.10版本的opencv. 查阅官方py文档, 这是链接
完整代码:
import face_recognitionimport numpy as npimport cv2image = face_recognition.load_image_file("./data/奥巴马.png")image2 = image.copy()face_landmarks_list = face_recognition.face_landmarks(image)# print(face_landmarks_list)for each in face_landmarks_list:print(each)for i in each.keys():print(i, end=': ')print(each[i])for any in each[i]:image = cv2.circle(image, any, 3, (0,0,255), -1)cv2.imshow("奥巴马", image)# 单独画下巴for each in face_landmarks_list:pts = np.array(each['chin'])pts = pts.reshape((-1, 1, 2))cv2.polylines(image2, [pts], False, (0, 255, 255)) # false 参数使其不闭合cv2.imshow("奥巴马2", image2)cv2.waitKey(0)cv2.destroyAllWindows()
在线摄像机版本:
import face_recognitionimport numpy as npimport cv2camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0)while True:ret, image = camera.read()image = cv2.flip(image, 1)image2 = image.copy()face_landmarks_list = face_recognition.face_landmarks(image)# print(face_landmarks_list)for each in face_landmarks_list:print(each)for i in each.keys():print(i, end=': ')print(each[i])for any in each[i]:image = cv2.circle(image, any, 3, (0,0,255), -1)cv2.imshow("奥巴马", image)# 单独画下巴for each in face_landmarks_list:pts = np.array(each['chin'])pts = pts.reshape((-1, 1, 2))cv2.polylines(image2, [pts], False, (0, 255, 255)) # false 参数使其不闭合cv2.imshow("奥巴马2", image2)if cv2.waitKey(1000 // 12) & 0xff == ord("q"):breakcv2.destroyAllWindows()camera.release()
附一份在线的人脸搜索代码, 人脸数据保存在相对路径./data/mans 下
import cv2import face_recognitionimport numpy as npimport osimport re# 人脸数据, 文件, 编码, 名字files = os.listdir("./data/mans")face_images = [0]*len(files)face_encodings = [0]*len(files)face_names = [0]*len(files)# 获取编码和名称for i in range(len(files)):face_images[i] = face_recognition.load_image_file('./data/mans/' + files[i])face_encodings[i] = face_recognition.face_encodings(face_images[i])if len(face_encodings[i]) > 0:face_encodings[i] = face_encodings[i][0]else:face_encodings[i] = Noneface_names[i] = re.findall(r'(.*)\..*', files[i])[0]print(face_names)# 人脸比较# results = face_recognition.compare_faces(face_encodings[0], face_encodings[1])# print(results)# 人脸距离# face_distances = face_recognition.face_distance(face_encodings[0], face_encodings[1])# index = np.argmin(face_distances)# print(index)# camera = cv2.VideoCapture('./data/test.avi') # 从视频文件camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0) # 从摄像头while True:ret, img = camera.read()img = cv2.flip(img, 1)# img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 灰度处理locations = face_recognition.face_locations(img)for top, right, bottom, left in locations:cv2.rectangle(img, (left, top), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 2)sub_img = img[top:bottom, left:right]sub_img_code = face_recognition.face_encodings(sub_img)if len(sub_img_code) != 0:face_distances = face_recognition.face_distance(face_encodings, sub_img_code[0])print(face_distances)index = np.argmin(face_distances)name = face_names[index]cv2.putText(img, name, (left, top - 20), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, 255, 2)cv2.imshow('Face', img)if cv2.waitKey(1000 // 12) & 0xff == ord("q"):breakcv2.destroyAllWindows()camera.release()
































还没有评论,来说两句吧...