MyBatis的 Mapper.xml 映射器语法
Java知识点总结:想看的可以从这里进入
目录
- 4、mapper映射器
- 4.1、sql
- 4.2、select
- 4.2.1、常用的元素
- 4.2.2、简单映射
- 4.2.3、多参数传递
- 1、使用map接口
- 2、注解
- 3、JavaBean
- 4.2.4、RowBounds
- 4.3、增删改
- 4.3.1、insert
- 1、简单语句
- 2、主键回填
- 3、自定义主键
- 4.3.2、update
- 4.3.3、delete
- 4.4、resultMap
- 4.4.1、简单结果集
- 4.4.2、association
- 4.4.3、collection
- 4.5、动态SQL
- 4.5.1、if
- 4.5.2、choose
- 4.5.3、辅助元素
- 4.5.4、foreach
- 4.6、缓存
- 4.6.1、一级缓存
- 4.6.2、二级缓存
- 4.6.3、EHCache
4、mapper映射器
映射器是MyBatis的核心组件,由一个接口和对应的XML文件组成。在映射器中可以配置参数、SQL语句、存储过程、缓存、级联等内容,可以通过映射规则映射到相应的实体对象上,相对于JDBC,节省了大量的底层代码。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace=""></mapper>
映射器内部常见的配置元素如下:
- select:查询语句,返回结果集
- insert:插入语句,返回受影响条数
- update:更新语句,返回受影响条数
- delete:删除语句,返回受影响条数
- sql:定义一部分的sql,然后在其他语句引用。比方说定义数据库的字段,在语句中使用 include 引用
- resultMap:描述如何从数据库结果集中加载对象
- cache:该命名空间的缓存配置。
- cache-ref: 引用其它命名空间的缓存配置。
在mapper映射器中有两种获取值的方法:
- ${}:本质是字符串拼接,使用字符串拼接的方式拼接sql,若为字符串类型或日期类型的字段进行赋值时,需要手动加单引号
#{}:本质是占位符赋值。使用占位符赋值的方式拼接sql,为字符串类型或日期类型的字段进行赋值时,可以自
动添加单引号
4.1、sql
sql元素时可以定义一条sql语句的一部分,方便后续的sql引用,最常用的就是设置一套数据库字段名的sql。
<!--设置数据字段,以后使用直接使用include引入即可 --><sql id="Base_Column_List">user_id, username, `password`, deleted</sql><select id="selectByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultMap="BaseResultMap">select <include refid="Base_Column_List" />from `user`where user_id = #{userId,jdbcType=INTEGER}</select>
4.2、select
4.2.1、常用的元素
查询语句是使用最多的语句,它内部常用配置如下:
| 元素 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| id | 和 mapper 的 namespace 组合使用,用来对应接口中的方法名 | 需要唯一,否则会出现异常 |
| parameterType | sql 语句接受的参数类型。 | 支持基本数据类型和 JavaBean、Map 等复杂数据类型 |
| resultType | sql 语句返回的结果类型(字段名和属性名完全一致时使用) | 如果是全表返回对应的实体类,如果是单独一条字段返回对应的数据类型 |
| resultMap | sql 语句返回的结果类型(当数据库的字段和类的属性不同时,使用其设置,将其进行转换) | 和resultType之间只能同时使用一个,是最复杂的元素,需要配置映射规则、级联等等 |
| flushCache | 将其设置为 true 后,在调用SQL后,清空本地缓存和二级缓存 | 默认值:false。 |
| useCache | 启动二级缓存,将本此结果缓存起来 | 默认值: true。 |
| timeout | 超时参数,超时抛出异常 | 单位 s,默认JDBC设置的秒数 |
| fetchSize | 获取记录的总条数设置 | |
| statementType | 告诉MyBatis使用那个JDBC的Statement工作 | STATEMENT:对应Statement PREPARED(默认) :对应PreparedStatement CALLABLE:对应CallableStatement |
| resultSetType | 对JDBC的resultSet而言, | FORWARD_ONLY(只允许向前访问) SCROLL_SENSITIVE(双向滚动,但不及时更新) SCROLLJNSENSITIVE(双向滚动,及时更新) |
| databaseId | 配合配置文件中databaseIdProvider使用,配置所使用的的数据库 |
4.2.2、简单映射
//接口的方法User selectByPrimaryKey(int id);<select id="selectByPrimaryKey" resultType="user" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">select <include refid="Base_Column_List"/>from `user`where id=#{id}</select>
MyBatis的自动映射是默认开启的,只要实体类名和属性与数据库名和字段对应就会形成自动映射。这个设置在xml配置文件的settings中,autoMappingBehavior 是自动映射,mapUnderscoreToCamelCase 是驼峰式命名。
4.2.3、多参数传递
1、使用map接口
使用的不多,在sql语句中传递参数时,需要知道map 的键才能传递参数。
int selectByMap(Map<String,Object> district);<!-- 根据name和url模糊查询 --><select id="selectByMap" resultType="" parameterType="map">SELECT i<include refid="Base_Column_List"/>WHERE name LIKE CONCAT ('%',#{name},'%')AND url LIKE CONCAT ('%',#{url},'%')</select>Map<String,String> map = new HashMap();map.put("name","aaa");map.put("url","11111");districtMapper.insertDistrict(map);
2、注解
使用 @Param注解去定义映射器的参数名称,可以提高阅读性,当参数少时建议使用。
//接口设置方法List<User> selectByPrimaryKey(@Param("username")String username,@Param("note")String note);<select id="selectByPrimaryKey" resultType="user"> <!--user是通过typeAliases配置-->select<include refid="Base_Column_List"></include>from user where username=#{username} and note=#{note}</select>
3、JavaBean
通过传递实体类,映射器可以识别属性,当参数多时,建议使用
//接口设置方法List<User> selectByPrimaryKey(User user);<select id="selectByPrimaryKey" resultType="user" parameterType="user">select<include refid="Base_Column_List"/>from user where username=#{username} and sex=#{note} <!--#{属性}--></select>
4.2.4、RowBounds
RowBounds是用来处理分页的
mapper接口指定方法
List<User> selectByRowBounds(RowBounds rowBounds);
xml映射文件,RowBounds是MyBatis自动识别的,所以在映射文件中不需要配置这块的内容
<select id="selectByRowBounds" resultType="user">select <include refid="Base_Column_List"/> from `user`</select>
test测试:前五条数据
RowBounds rowBounds = new RowBounds(0,5); (起始,每页数量)List<User> list = userMapper.findByRowBounds(rowBounds);System.out.println(list);
4.3、增删改
insert(增)、update(改)、delete(删)三者很接近,主要有以下属性
| 元素 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| id | 和 mapper 的 namespace 组合使用,用来对应接口中的方法名 | 需要唯一,负责会出现异常 |
| parameterType | sql 语句接受的参数类型。 | |
| flushCache | 将其设置为 true 后,在调用SQL后,清空本地缓存和二级缓存 | 默认值:false。 |
| timeout | 超时参数,超时抛出异常 | 单位 s,默认JDBC设置的秒数 |
| statementType | 告诉MyBatis使用那个JDBC的Statement工作 | STATEMENT:对应Statement PREPARED(默认) :对应PreparedStatement CALLABLE:对应CallableStatement |
| useGeneratedKeys | 是否使用 JDBC 的 getGeneratedKeys 方法来取出由数据库内部生成的主键, | 默认false |
| keyProperty=“id字段名” | 在新增、修改的时候可以获得修改的那条数据的 主键 | (insert 和 update) |
| keyColumn | 设置生成键值在表中的列名,当主键列不是表中的第一列的时候,是必须设置的 | ( insert 和 update) |
4.3.1、insert
1、简单语句
void insertUser(User user);<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="user">insert into user(username, password,sex) values (#{username},#{password},#{sex})</insert>
2、主键回填
我们在新增时并没有插入主键,因为主键采用了自增主键,所以mysql会自动生成主键,但是很多时候我们需要获取到这条主键以进行其他的操作,这个就是主键回填
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="user" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">insert into user(username, password,sex)values (#{username},#{password},#{sex})</insert>userMapper.insert(user);sqlSession.commit();System.out.println(user.toString());

3、自定义主键
在使用自增主键时不需要去管主键,但是如果主键的规则是我们自己设定的,比如初始为1,每次自增2。
这时可以使用selectKey标签
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="user"><selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="long" order="BEFORE">select if(max(id)=null,1,max(id)+2) from `user`</selectKey>insert into user(id,username, password,sex)values (#{id},#{username},#{password},#{sex})</insert>
4.3.2、update
update和delete的使用和insert类似
<update id="updataById">update user set user.usernam=#{username},user.password=#{password} where id=#{id}</update>
4.3.3、delete
<delete id="deleteById" parameterType="user">delete from user where id=#{id}</delete>
4.4、resultMap
它是用来定义映射规则、级联、类型转化等等,是最复杂的一块。比如:A表中有B表的id字段,在建实体类时属性会创建b的对象,而不是只是一个id属性,这就需要resultMap来定义映射的规则。
MyBatis在association、collection关联集合对象时支持延迟加载,即在需要使用数据时才进行加载,不用数据时就不进行加载。(一对多,多对多采用延迟加载。一对一、多对一采用立即加载)
不能和resultType共用。
<resultMap id="" type="" ><!-- 用来注入结果到构造方法 --><constructor><idArg/> <!-- 用于表示哪个列是主键 --><arg /></constructor><!-- 用于表示哪个列是主键 --><id /><!-- 注入到字段或JavaBean属性的普通结果 --><result/><!-- 用于一对一关联 --><association property=""/><!-- 使用结果值来决定使用哪个结果映射 --><discriminator javaType=""><!-- 某些值的结果映射 --><case value=""></case></discriminator><!-- 用于一对多、多对多关联 --><collection property=""/></resultMap>
4.4.1、简单结果集
使用 id、result 配置映射关系,数据库的字段和属性值的类型能对应上,可以只是名字上的不同,没有复杂的级联关系。
<resultMap id="userMap" type="user"><!-- 对应主键--><id column="字段" property="属性" javaType="java类型" jdbcType="数据库类型" typeHandler="类型转换器"/><!--其他字段--><result column="字段" property="属性" javaType="java类型" jdbcType="数据库类型" typeHandler="类型转换器"/></resultMap><!-- id是resultMap的标识,type是映射的实体类--><resultMap id="userMap" type="user"><!--id是主键,property是属性名,column是对应数据表的字段名 --><id column="字段名" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="属性名" /><!--实体类的username属性对用的是数据库的name字段--><result column="字段名" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="属性名" />.......</resultMap><!--resiltMap的值是设定好的resultMap的id--><select id="selectByPrimaryKey" resultMap="userMap"></select>
4.4.2、association
association 和 collection 主要是用来处理级联关系的映射,有 3 种级联关系:
- 一对一级联:一个学生只对应一个班级
- 一对多级联以:一个班级对应多个学生
- 多对多级联:一个角色可以对应多个用户,但是一个用户可以兼任多个角色
在数据中表A保存了表B的id,这是其对应的实体类的属性,必须是B的实体类,所以简单的映射无法满足,需要使用association进行配置,它配置的是一个对象,用来表示一对一的映射关系。
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| property | 指定映射到实体类的对象属性。 |
| column | 指定表中对应的字段 |
| javaType | 指定映射到实体对象属性的类型。 |
| select | 指定引入嵌套查询的子 SQL 语句,用于关联映射中的嵌套查询。 |
association 分步查询
Student的实体类
//学生表中有班级id。实体类中创建班级的实体属性private Integer sId;private String name;private Classes classes; //数据中保存的是班级id
Student实体类对应的xml映射器,它是分两部,先通过select语句查出Student的信息后,再通过association设置的select方法差相关的班级,再将班级的值添到对应的属性上
<!--resultMap设置映射规则--><resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.yu.mybatis.entity.Student"><id column="s_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="sId" /><result column="student_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name" /><!--property属性名,javaType对应的实体,select对应的查找classes的映射方法(会根据数据库中管理的班级id自动查找并返回班级) --><association property="classes" javaType="com.yu.mybatis.entity.Classes" column="classes_id"select="com.yu.mybatis.mapper.ClassesMapper.selectByPrimaryKey"/></resultMap><!--返回student的语句,设置resultMap --><select id="selectStudentAll" resultMap="BaseResultMap">select * from student</select>
classes实体对应的映射器
<!--这个是Student相关的xml映射器中 association标签的select属性对应的方法 --><select id="selectClassesById" resultMap="BaseResultMap">select * from classes where c_id = #{id}</select>
执行了两次 sql

也可以在 association 的内部定义:这种定义时通过一个SQL直接查询出来的数据,不需要第二次再去查询了
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap2" type="com.yu.mybatis.entity.Student"><id column="s_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="sId" /><result column="student_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="studentName" /><association property="classes" javaType="com.yu.mybatis.entity.Classes"><result column="c_id" property="CId"/> <!--内部嵌套--><result column="classes_name" property="classesName"/></association></resultMap><select id="selectByClassesId" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultMap="BaseResultMap2">SELECT * FROM student,classesWHERE student.classes_id = classes.c_id AND student.s_id = #{sId,jdbcType=INTEGER}</select>
只执行一次sql

4.4.3、collection
一对多的映射关系使用collection处理,collection 可以将关联查询的多条记录映射到一个 list 集合属性中。和association使用方式类似
| 属性 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
| property | 指定映射到实体类的对象属性。 |
| column | 指定表中对应的字段 |
| select | 指定引入嵌套查询的子 SQL 语句 |
| javaType | 指定映射到实体对象属性的类型 |
分步查询:这种查询是先根据select的方法查询出数据后,再次根据resultMap中设置的对应select方法查询
//班级内很多学生private Integer cId;private String name;private List<Student> studentList;<resultMap id="BaseResultMap2" type="classes"><id column="c_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="cId"/><result column="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name"/><collection property="studentList" ofType="student"> <!--ofType和javaType类似--><result column="s_id" property="SId"/><result column="s_name" property="name"/></collection></resultMap><select id="selectByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultMap="BaseResultMap2">select<include refid="Base_Column_List" />from classeswhere c_id = #{cId,jdbcType=INTEGER}</select>
这种查询是分了两步的,所以执行了两次SQL语句

内部定义
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap3" type="com.yu.mybatis.entity.Classes"><id column="c_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="cId" /><result column="classes_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="classesName" /><collection property="students" ofType="com.yu.mybatis.entity.Student"><result column="s_id" property="SId"/><result column="student_name" property="studentName"/></collection></resultMap><select id="selectClassesAndStudent" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultMap="BaseResultMap3">select <include refid="Base_Column_List" />,s_id,student_namefrom student,classeswhere student.classes_id = classes.c_id AND classes.c_id = #{CId,jdbcType=INTEGER}</select>
这种方式SQL语句只执行了一次

4.5、动态SQL
动态SQL是对sql语句进行动态的组装, 是 MyBatis 的强大特性之一。它可以通过判断自动选择要添加的sql语句,主要有以下元素:
- if:判断语句
- choose(when,otherwise):相当于switch,case语句
- trim(where,set):用于处理sql拼装问题,
- foreach:循环语句
4.5.1、if
类似于 Java 中的 if 语句,是 MyBatis 中最常用的判断语句。使用 if 标签可以节省许多拼接 SQL 的工作,把精力集中在 XML 的维护上。
if 语句使用方法简单,常常与 test 属性联合使用
<select id="" parameterType="string"><!--这里需要加1=1防止出错-->select id,username,password,sex from user where 1=1<!--如果传递的参数不为空,则内部的sql生效,否则不生效--><if test="id != null and id != ''">and id=#{id};</if><if test=" name != null and name !=''">and username=#{name};</if></select>
4.5.2、choose
choose、when、otherwise类似于java中的Switch、case、default的功能
<select id="" parameterType="string">select id,username,password,sex from user where 1=1<choose><!--username不为空则只用username查询--><when test="username != null and username != ''">and user.username = #{username}</when><!--password不为空根据password查询--><when test="password != null and password != ''">and user.password = #{password}</when><!--都为空查询性别为男的--><otherwise>and user.sex = '男'</otherwise></choose></select>
4.5.3、辅助元素
上面的几种情况可能会出现where后面没有条件的情况,所以在where后加了一句 1=1,来保证sql语句的正确性,但是我们期望的是where关键字根据条件而自己决定出现不出现,所以就有了,trim、where、set元素
where:至少有一个子元素成立,才会添加where元素,并且第一个条件的and、or元素会自动去除
<select id="" parameterType="string">select id,username,password,sex from user<where><if test="usernae != null and usernae != ''">user.username = #{username}</if><if test="password != null and password != ''">and user.password = #{password}</if></where></select>
set:用于动态设置update语句中的set条件,可以删除无关的 “,”
<update id="">update user<set><if test="usernae != null and usernae != ''">user.username = #{username},</if><if test="sex != null and sex != ''">user.sex = #{sex},</if></set>where id=#{id}</update>
trim:可以代替where和set
- prefix :前缀,插入代码快最前面
- prefixOverrides :前缀,去掉代码块第一个内容
- suffix,后缀,插入代码块最后面
suffixOverrides:后缀去掉代码块的最后一个内容
where是前缀的时候,会去掉and
set是前缀的时候,会去掉,
4.5.4、foreach
循环遍历,可以很好的支持数组、list、set集合。用于sql语句的 in 关键字。
- collection:传递的参数
- item:当前循环的元素
- index:当前元素在集合位置的下标
- open、close:以什么符号将元素包装起来
separator:元素的间隔符
4.6、缓存
对一些常用的且不经常改动的数据进行缓存,能有效的避免频繁的连接数据库,一定程度上解决高并发情况下的系统性能问题。
MyBatis允许使用缓存, 内部定义了两级缓存,和一个缓存接口:
- 一级缓存:默认开启,SqlSession级别缓存,为本地缓存
- 二级缓存:需要手动配置开启,是 namespace 级别的缓存。
- 缓存接口:Cache,通过实现接口可以自定义二级缓存。
4.6.1、一级缓存
一级缓存是默认开启的,作用域为SqlSession,当一个SqlSession对象执行同一条SQL语句时,第一次是在会去查询数据库,并将其写在缓存中,后续的就直接在缓存中加载。(每次查询时现在缓存中找,缓存中没有就去数据库中查询,并将数据卸载缓存中)
当两次SQL查询时,发生了增删改的操作时,缓存会清空。
SqlSession的缓存使用 HashMap,key为hashCode+statementId+sql语句,value为映射的结果集。
一级缓存从获取一个SqlSession到close方法关闭之间有效,默认开启,无法关闭。

缓存失效:
- 清理缓存:sqlSession.clearCache();
- 不同的查询语句
- 增删改的语句
- 不同的SqlSession
4.6.2、二级缓存
二级缓存是 SqlSession 级别的,对应一个Mapper映射文件,需要在映射文件中自行设置开启,所以二级缓存存在于所在的整个映射文件中。
第一次调用Mapper内的SQL查询时,数据会存放到对应的二级缓存区。第二次调用namespace下的mapper映射文件,向的sql会去对应的二级缓存区查找。
开启方法:
在mybatis-config.xml 文件中的settings中打开全局缓存<settings><setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/></settings>1、在所需要的mapper.xml文件中开启二级缓存<cache/> 默认的<cache eviction = "FIFO" flushInterval = "60000" size = "512" readOnly = "true" /> 自定义的eviction:缓存回收策略LRU – 最近最少使用:删除最长时间未使用的对象。FIFO – 先进先出:按照对象进入缓存的顺序删除对象。SOFT – 软引用:根据垃圾收集器状态和软引用规则删除对象。WEAK – 弱引用:根据垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则更积极地删除对象。flushInterval属性:刷新间隔,单位毫秒size属性:引用数目,正整数,代表缓存最多可以存储多少个对象readOnly属性:只读,true/falsetrue:只读缓存;会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例,效能最高。false:读写缓存;会返回缓存对象的拷贝(通过序列化)。效率稍慢但是安全,默认是false。2、在mapper接口上添加注解@CacheNamespace(blocking = true)
如果使用默认的配置,readOnly 默认为false,所以这个时候MyBatis会序列化和反序列化实体类,所以实体类需要实现Serializable接口。否则将会抛出异常

二级缓存必须在SqlSession关闭或提交之后有效
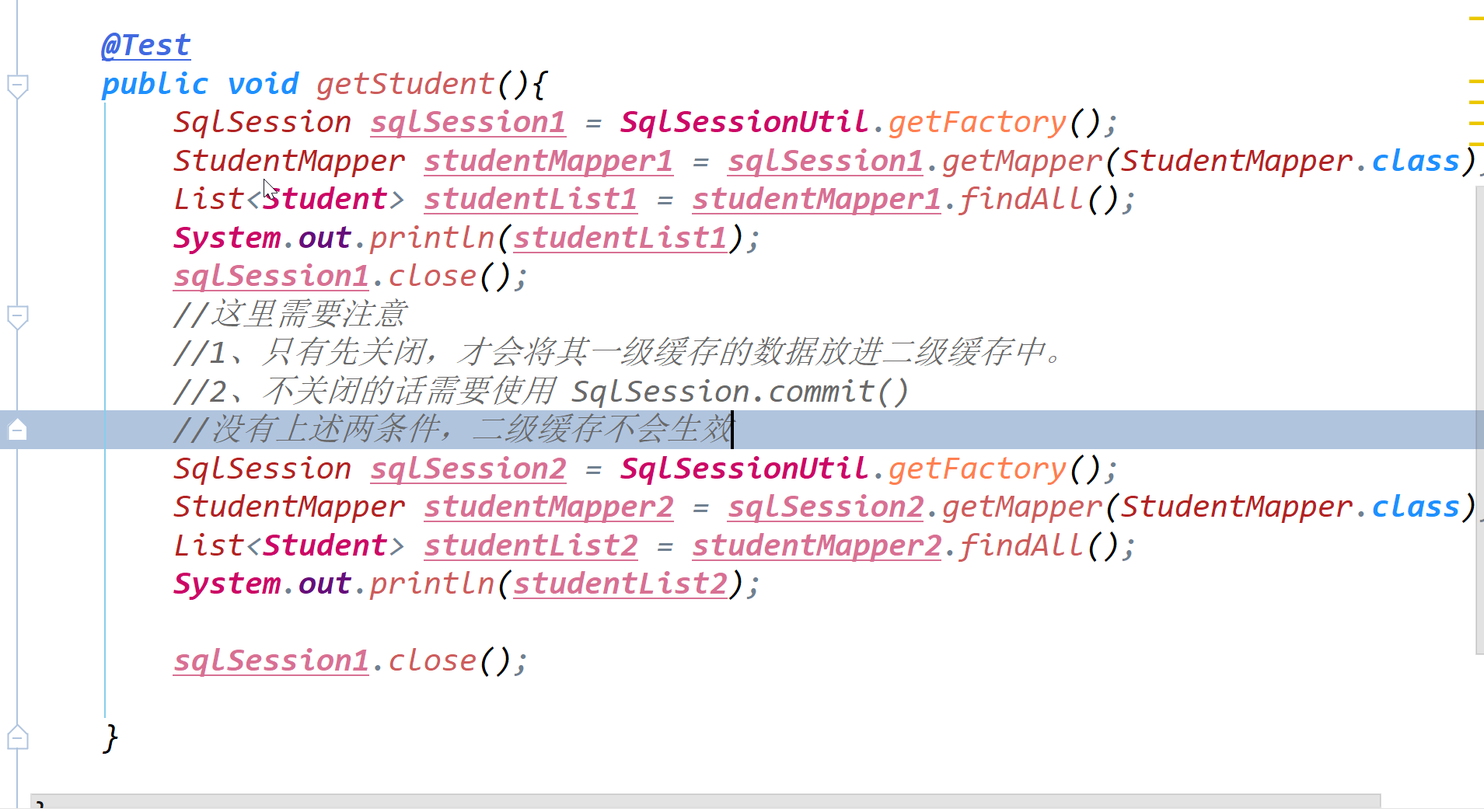

一级缓存和二级缓存的顺序:先查询二级缓存,因为二级缓存中可能会有其他程序已经查出来的数据,可以拿来直接使用。如果二级缓存没有命中,再查询一级缓存,如果一级缓存也没有命中,则查询数据库,SqlSession关闭之后,一级缓存中的数据会写入二级缓存。
4.6.3、EHCache
Mybitis 除了内置了缓存外,还可以引入第三方的缓存,而EHCache 就是实现 mybatis 二级缓存的产品之一。它是一种广泛使用的开源Java分布式缓存,具有快速、简单、多种缓存策略,缓存数据有内存和硬盘的特点。
使用ehcache需要注意的是,ehcache的依赖 slf4j 这个日志的jar包,会和log4j的jar冲突,导致日志不能显示,所以需要整合他们,导入联合jar包
<!-- 第三方缓存EHCache--><!-- Mybatis EHCache整合包 --><dependency><groupId>org.mybatis.caches</groupId><artifactId>mybatis-ehcache</artifactId><version>1.2.1</version></dependency><!-- slf4j和log4j整合包 --><dependency><groupId>org.slf4j</groupId><artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId><version>1.7.26</version></dependency>
然后在sql映射文件中的mapper标签下配置开启ehcace缓存
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
在mybatis-config.xml 文件中的settings中打开全局缓存
<settings><setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/></settings>
创建ehcache的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?><ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="../config/ehcache.xsd"><!-- 磁盘保存路径 --><diskStore path="D:\java\ehcache"/><!--maxElementsInMemory缓存最大数目--><!-- maxElementsOnDisk硬盘最大缓存个数 --><!--eternal设定elements是否永远不过期。true,始终有效,false,需要根据timeToIdleSeconds、timeToLiveSeconds判断--><!-- overflowToDisk当系统宕机时是否保存到磁盘--><!--timeToIdleSeconds当缓存在EhCache中的数据前后两次访问的时间超过timeToIdleSeconds时,数据便会删除--><!--timeToLiveSeconds缓存element的有效生命期--><!--diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds磁盘缓存的清理线程运行间隔,默认是120秒。每120s,相应的线程会进行一次EhCache中数据的清理工作--><!--memoryStoreEvictionPolicy当内存缓存达到最大,有新的element加入时,移除缓存中element的策略。默认是LRU(最近最少使用),可选的有LFU(最不常使用)和FIFO(先进先出)--><defaultCachemaxElementsInMemory="1000"eternal="false"timeToIdleSeconds="120"timeToLiveSeconds="120"overflowToDisk="true"maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"diskPersistent="false"diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/></ehcache>
可以直接运行测试:






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...